A study of clinico-hematological profile of pancytopenic patients in Central India
Abstract
Background: To segregate the causes of pancytopenia which are easily treatable, from those requiring sophisticated investigations & vigorous treatment, based on clinico-hematological profile of the patients and affordable diagnostic mathods.
Materials and Methods: 180 Pancytopenic patients were evaluated clinically along with hematological parameters, peripheral smears and bone marrow aspiration in the Department of Pathology, GMC, Bhopal for 3 years.
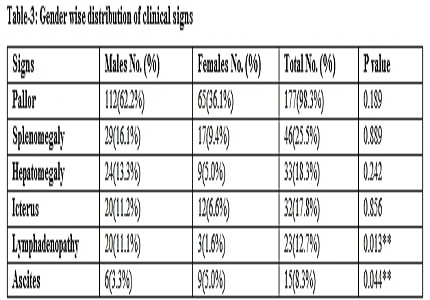
Result: Age range was 5 months-70 years (mean- 26.6 years), with Male preponderance (M: F: 1.76:1). Commonest symptoms were weakness (97.8%), breathlessness (75%) and signs were pallor (98.3%) and splenomegaly (25.5%). Patients who presented with per rectal bleeding, in 46.2% diagnosis was dimorphic anemia thus per rectal bleeding was cause of associated iron deficiency. Commonest peripheral smear finding was microcytic hypochromic picture (27.22 %) & bone marrow was hypercellular (70.00%). Bone marrow aspiration revealed commonest cause was megaloblastic anemia (25%) followed by dimorphic anemia (17.2%) and infections (17.2%). In our study MCV was <100 fl in 12/45 (26.66%) cases of megaloblastic anemia so even if a patient presents with MCV < 100 fl megaloblastic anemia should not be ruled out only on this basis. Sensitivity of peripheral smear for dimorphic anemia was very low 35.48% and specificity was 82.55%, so bone marrow examination should be investigation of choice for inconclusive peripheral smears.
Conclusion: Common causes of pancytopenia were easily treatable and reversible & can be detected by early and affordable diagnostic methods therefore should be considered at higher order in differential diagnosis of pancytopenia.
Downloads
References
Lilleyman J. De Gruchy’s Clinical Haematology in Medical Practice. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Apr;43(4):352.
Jella R, Jella V. Clinico-hematological analysis of pancytopenia. Int J Adv Med. 2016;176–9.
Tilak V, Jain R. Pancytopenia--a clinico-hematologic analysis of 77 cases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 1999 Oct 1;42(4):399.
Kumar R, Kalra SP, Kumar H, Anand AC, Madan H. Pancytopenia--a six year study. J Assoc Physicians India. 2001 Nov;49:1078–81.
Hamid GA, Shukry SAR. Patterns of pancytopenia in Yemen. J Turk Soc Haematol. 2008 Jun 5;25(2):71–4.
Santra G, Das BK. A cross-sectional study of the clinical profile and aetiological spectrum of pancytopenia in a tertiary care centre. Singapore Med J. 2010 Oct;51(10):806–12.
Gayathri BN, Rao KS. Pancytopenia: A Clinico Hematological Study. J Lab Physicians. 2011;3(1):15–20.
Raphael V, Khonglah Y, Dey B, Gogoi P, Bhuyan A. Pancytopenia: an etiological profile. Turk J Haematol Off J Turk Soc Haematol. 2012 Mar;29(1):80–1.
Jain A, Naniwadekar M. An etiological reappraisal of pancytopenia - largest series reported to date from a single tertiary care teaching hospital. BMC Blood Disord. 2013;13:10.
Jha A, Sayami G, Adhikari RC, Panta AD, Jha R. Bone marrow examination in cases of pancytopenia. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2008 Mar;47(169):12–7.
Bhatnagar SK, Chandra J, Narayan S, Sharma S, Singh V, Dutta AK. Pancytopenia in children: etiological profile. J Trop Pediatr. 2005 Aug;51(4):236–9.
Khodke K, Marwah S, Buxi G, Yadav RB, Chaturvedi NK. Bone marrow examination in cases of pancytopenia. J Indian Acad Clin Med 2001Jan-June. 2001;2:1–2.
Gupta V, Tripathi S, Tilak V, Bhatia BD. A study of clinico-haematological profiles of pancytopenia in children. Trop Doct. 2008 Oct 1;38(4):241–3.
Prabhala S, E J, B P, M S, T R. Bone marrow examination in pancytopenia: a study of six years. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2014 Nov 26;3(65):14189–95.
Pine M, Walter AW. Pancytopenia in Hospitalized Children: A Five-year Review. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010 Jul;32(5):e192–4.
Khunger JM, Arulselvi S, Sharma U, Ranga S, Talib VH. Pancytopenia--a clinico haematological study of 200 cases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2002 Jul;45(3):375–9.
N V, S D. A reappraisal of underlying pathology in adult patients presenting with pancytopenia. Trop Geogr Med. 1992 1992;44(4):322–7.
Azaad MAA, Li Y, Zhang Q, Wang H. Detection of Pancytopenia Associated with Clinical Manifestation and Their Final Diagnosis. Open J Blood Dis. 2015;5(3):17–30.
Imbert M, Scoazec JY, Mary JY, Jouzult H, Rochant H, Sultan C. Adult patients presenting with pancytopenia: a reappraisal of underlying pathology and diagnostic procedures in 213 cases. Hematol Pathol. 1989;3(4):159–67.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


