A comparison of BMI and Lipid Profile in patients with metabolic syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease known by chronic hyperglycemia which results from defective insulin action and secretion. Metabolic syndrome consists of a constellation of metabolic abnormalities that confer increased risk of diabetes mellitus. The aim of the present study was to study BMI and lipid profile in patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Materials and methods: 50 controls, 50 individuals with metabolic syndrome and 50 individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus were selected by purposive sampling technique. BMI was calculated and serum levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, VLDL and HDL were estimated in controls and cases.
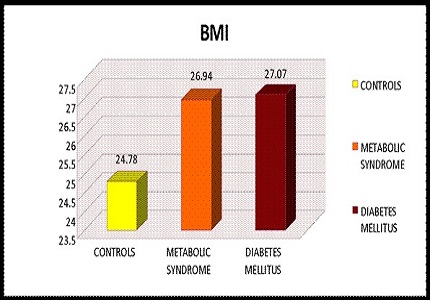
Results: BMI, serum triglycerides, VLDL, cholesterol/HDL ratio were significantly increased (p<0.05) and serum HDL levels were significantly decreased (p<0.05) in metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes compared to controls.
Conclusion: Our study concluded that there is significant dyslipidemia in patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Downloads
References
Augusthy A, Jeppu AK, Sahu S, Jawalekar S, Marakala V, Iqbal S. A study of liver functions in metabolic syndrome and Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Med Res Rev 2016;4(4):470-475. https://ijmrr.medresearch.in/index.php/ijmrr/article/view/504/978.
Kumar JA, Augusthy A. Oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome and Type 2 diabetes mellitus.Biomedicine.2011;31(2):166-170.
Kuo JF, Hsieh YT, Mao IC, Lin SD, Tu ST, Hsieh MC. The Association Between Body Mass Index and All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 5.5-Year Prospective Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Aug;94(34):e1398. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000001398.
Hadaegh F, Bozorgmanesh M, Safarkhani M, Khalili D, Azizi F. "Predictability of body mass index for diabetes: affected by the presence of metabolic syndrome?". BMC Public Health. 2011 May 25;11:383. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-11-383.
Gray N, Picone G, Sloan F, Yashkin A. Relation between BMI and diabetes mellitus and its complications among US older adults. South Med J. 2015 Jan;108(1):29-36. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.14423%2FSMJ.0000000000000214.
Singh O, Gupta M, Khajuria V. Lipid profile and its relationship with blood glucose levels in Metabolic Syndrome. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol 2015;5(2):134-137.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280758209_Lipid_profile_and_its_relationship_with_blood_glucose_levels_in_Metabolic_Syndrome.
Huang PL. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis Model Mech. 2009 May-Jun;2(5-6):231-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.001180.
Jeppu AK, Augusthy A, Kumar KA. Plasma Glucose and Serum Ceruloplasmin in Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2.Recent Adv Biol Med. 2016; 2:15-19.
Arnlov J, Sundström J, Ingelsson E, Lind L. Impact of BMI and the metabolic syndrome on the risk of diabetes in middle-aged men. Diabetes Care. 2011 Jan;34(1):61-5. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-0955. Epub 2010 Sep 17.
He Y, Jiang B, Wang J, Feng K,Chang Q, Zhu S, Fan L, Li X,Hu FB. BMI Versus the Metabolic Syndrome in Relation to Cardiovascular Risk in Elderly Chinese Individuals.Diabetes Care 2007 Aug; 30(8): 2128-2134.
Arnlov J, Ingelsson E, Sundström J, Lind L. Impact of body mass index and the metabolic syndrome on the risk of cardiovascular disease and death in middle-aged men. Circulation. 2010 Jan 19;121(2):230-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.887521. Epub 2009 Dec 28.
Meigs JB, Wilson PW, Fox CS, Vasan RS, Nathan DM, Sullivan LM, D'Agostino RB. Body mass index, metabolic syndrome, and risk of type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Aug;91(8):2906-12. Epub 2006 May 30.
Ganz ML, Wintfeld N, Li Q, Alas V, Langer J, Hammer M. The association of body mass index with the risk of type 2 diabetes: a case-control study nested in an electronic health records system in the United States. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014 Apr 3;6(1):50. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-5996-6-50.
Vittal BG,Praveen G, Deepak P. A study of body mass index in healthy individuals and its relationship with fasting blood sugar. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research [serial online] 2010 December [cited: 2017 Feb 16 ]; 4:3421-3424.
Songa RM ,Viswabarathi N ,KS. Comparative study of lipid profile in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus and obese non diabetes. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences Nov. 2015;14(11) :87-91.https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jdms/papers/Vol14-issue11/Version-1/S0141118791.pdf.
Krauss RM. Lipids and lipoproteins in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004 Jun;27(6):1496-504.
Brunzell JD, Ayyobi AF. Dyslipidemia in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 2003 Dec 8;115 Suppl 8A:24S-28S.
Alshehri AM. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk. J Family Community Med. 2010 May;17(2):73-8. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F1319-1683.71987.
Nsiah K, Shang VO, Boateng KA, Mensah FO. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2015 May-Aug;5(2):133-8. doi: http://www.ijabmr.org/text.asp?2015/5/2/133/157170.
Ugle SS, Bikkad MD. Altered triglycerides and HDL-c are better marker for coronary heart disease in NIDDM. Int J Res Med Sci 2016;4:461-4. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20160296.
Tangvarasittichai S, Poonsub P, Tangvarasittichai O. Association of serum lipoprotein ratios with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Med Res. 2010 May;131:641-8.
Garg N, Agrawal YB, Gupta S.A study of lipid profile levels in diabetics and nondiabetics taking TC/HDL ratio and LDL/HDL ratio into consideration. JIACM 2014; 15(3-4): 192-5.
WHO/IASO/IOTF.The Asia-Pacific perspective : redefining obesity and its treatment.Health Communications Australia:Melbourne, 2000.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


