Comparison of outcome in IUGR and Normal Pregnancies- A retrospective study
Abstract
Introduction: High perinatal and infant mortality is one of the major public health problems in developing countries like ours. The birth of an intra uterine growth restricted baby evokes considerable psychological stress on the mothers which is directly related to lack of knowledge in these mothers regarding IUGR.
Material and Methods: It was a retrospective record based study carried out in tertiary care hospital in Delhi where the authors work between May 2013 and December 2014. The study population consisted of 400 patients of whom 200 were IUGR cases (babies weighing less than 2 kgs) included in study group and 200 other normal weighted babies were taken as control group.
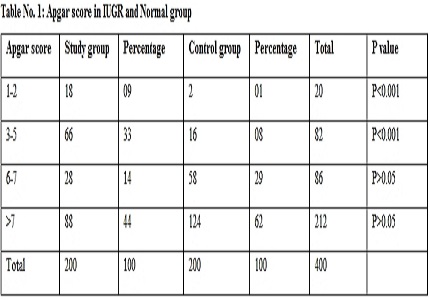
Results: In our study, 9% of infants had severely depressed, 33% had moderately depressed apgar score compared to 1% and 8% in the control group. Thus most IUGR babies had low Apgar scores. In our study, 36% of infants in the study group were asphyxiated, 10% had hypoglycaemia, 12% had hypoglycaemia, 6% had pulmonary complications, 10% were hypothermic, 5% had congenital malformations, 20.5% had infections and 5% patients were normal. In the control group 10%, 4%, 3.5%, 1%, 6%, 0.5%, and 18% of the patients had hypoglycaemia, hypocalcemia, pulmonary complications, hypothermia, congenital malformations and infection respectively. This increased incidence of complications was statistically significant (P<0.001).
Conclusion: The clinical significance of IUGR is based on the fact that birth weight is the most important indicator of perinatal morbidity and mortality. A scientific approach for prevention of IUGR requires an understanding of many variables, which govern and affect intrauterine growth and development.
Downloads
References
2. Selvaraj J P. A study on IUGR. Nightingale nursing times.2007.june; 3(3):P.9-11.
3. Shah PM, Selwyn BJ, Shah K, Kumar V. Evaluation of the home-based maternal record: a WHO collaborative study. Bull World Health Organ. 1993;71(5):535-48. [PubMed]
4. Dre Y De M, Artal F. Effectiveness of a parent ‘Buddy’. University of GUELPH ont, CMAJ.2003.April.
5. Arora. N. K, Paul. V.K, Singh Meharban- neonatal section. journal Of Paediatrics.2002 August; l 4(6):25.
6. Moore LG, Zamudio S, Zhuang J, Sun S, Droma T. Oxygen transport in tibetan women during pregnancy at 3,658 m. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2001 Jan;114(1):42-53. [PubMed]
7. Low JA, Pancham SR, Piercy WN, Worthington D, Karchmar J. Intrapartum fetal asphyxia: clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and significance in relation to pattern of development. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Dec 15;129(8):857-72.
8. Cetrulo CL. Bio- Electric evaluation in IUGR. ClinObsGyn 1977; 70: 1979.
9. Richard E, Robert M. nelson Textbook of Pediatrics: 16th Edition.
10. John P Cloherty, Stark AM ; Manual of Neonatal care, 4rth Edition.
11. Bisquera JA, Cooper TR, Berseth CL. Impact of necrotizing enterocolitis on length of stay and hospital charges in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2002 Mar;109(3):423-8.
12. Susan W Aucott, Pamela K Donohueand. Frances J Northington. Increased Morbidity in Severe Early Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Journal Perinatology (2004) (24); 435–440.
13. Warsof SL, Sayegh SK. Ultrasound diagnosis of intrauterine growth retardation. Fetal Ther. 1987;2(1):31-6. [PubMed]
14. Basso O. Risk of Pre-term delivery, LBW and Growth Retardation following Spontaneous Abortion. International Journal of Epidemiology August 1998; 27 (4): 642-646.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


