A study to assess the role of contrast-enhanced multiphasic, multidetector computed tomography in the evaluation of renal lesions
Abstract
Aim: To assess the role of Contrast-Enhanced Multiphasic Multidetector Computed Tomography in the evaluation of renal lesions and its potential role in differentiating benign from malignant lesions.
Material and Method: This prospective study was done in the Department of Radiodiagnosis Chirayu Medical College and Hospital Bhopal. A total of 100 patients to our department with strong clinical suspicion of renal lesions and those diagnosed by ultrasonography underwent Contrast-Enhanced Multiphasic Multidetector Computed Tomographic evaluation of abdomen using 64 Multislice Spiral CT scanner from August 2015 to July 2019.
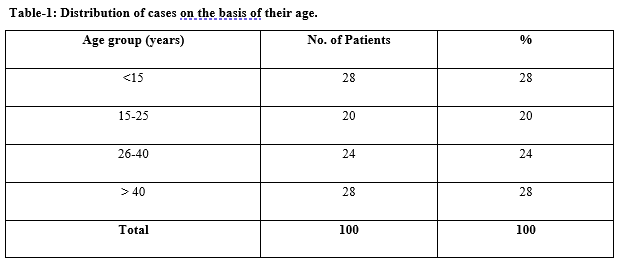
Results: The majority of patients presenting with renal lesions were each of the age groups <15 years and >40 years. Most of the patients were males 57%. The most common clinical complaint was renal colic 58(46%) and hematuria. The most common pathology was calculus 35(35%) second most common pathology was congenital anomalies 23(23%). The CT accuracy for detection of benign cystic lesion in this study was 94.7%, benign lesions were 92.6%and for malignant lesions was 86.6% in the present study.
Conclusion: The accuracy of Contrast-Enhanced Multiphasic Multidetector Computed Tomography in detecting and characterizing renal lesions is high and it should be considered in the imaging workup of any patient with a renal complaint
Downloads
References
Srougi V, Kato RB, Salvatore FA, Ayres PP, Dall'Oglio MF, Srougi M. Incidence of benign lesions according to tumor size in solid renal masses. Int Braz J Urol. 2009;35(4):427-431. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/s1677-55382009000400005.
Israel GM, Bosniak MA. How I do it: evaluating renal masses. Radiol. 2005;236(2):441–450. doi: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2362040218.
Ng CS, Wood CG, Silverman PM, Tannir NM, Tamboli P, Sandler CM. Renal cell carcinoma: diagnosis, staging, and surveillance. Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191(4):1220-1232. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.07.3568.
Coll DM, Smith RC. Update on radiological imaging of renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2007;99(5 Pt B):1217-1222. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410x.2007.06824.x.
Pahernik S, Ziegler S, Roos F, Melchior SW, Thüroff JW. Small renal tumors: correlation of clinical and pathological features with tumor size. J Urol. 2007;178(2):414-417. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.03.129.
Caoili EM, Cohan RH, Korobkin M, Platt JF, Francis IR, Faerber GJ, et al. Urinary tract abnormalities: initial experience with multi–detector row CT urography. Radiol. 2002;222(2):353-360. doi: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2222010667.
Lin WC, Wang JH, Wei CJ, Chang CY. Assessment of CT urography in the diagnosis of urinary tract abnormalities. J Chi Med Assoc. 2004;67(2):73-78.
Smith RC, Verga M, Dalrymple N, McCarthy S, Rosenfield AT. Acute ureteral obstruction: value of secondary signs of helical unenhanced CT. AJR. Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167(5):1109-1113. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.167.5.8911160.
Birnbaum BA, Jacobs JE, Ramchandani P. Multiphasic renal CT: comparison of renal mass enhancement during the corticomedullary and nephrographic phases. Radiol. 1996;200(3):753-758. doi: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.200.3.8756927.
Bosniak MA. Diagnosis and management of patients with complicated cystic lesions of the kidney. AJR. Am J Roentgenol. 1997;169(3):819-821. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.169.3.9275903.
Majd M, Nussbaum Blask AR, Markle BM, Shalaby-Rana E, Pohl HG, Park JS, et al. Acute pyelonephritis: comparison of diagnosis with 99mTc-DMSA SPECT, spiral CT, MR imaging, and power Doppler US in an experimental pig model. Radiol. 2001;218(1):101-108. doi: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.218.1.r01ja37101.
Catalano C, Fraioli F, Laghi A, Napoli A, Pediconi F, Danti M, et al. High-resolution multidetector CT in the preoperative evaluation of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180(5):1271-1277. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.180.5.1801271.
Millan-Rodriguez F, Palou J, De la Torre-Holguera P, Vayreda-Martija JM, Villavicencio-Mavrich H, Vicente-Rodriguez J. Conventional CT signs in staging transitional cell tumors of the upper urinary tract. Europe Urol. 1999;35(4):318-322. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000019869.
Fishman EK, Hartman DS, Goldman SM, Siegelman SS. The CT appearance of Wilms tumor. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1983;7(4):659-665. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00004728-198308000-00014.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


