Serum testosterone levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes mellitus is a multifactorial disease which is characterised by hyperglycaemia, dyslipidaemia, involves various organ systems, and results in various long-term complications. Several studies have suggested that men with low testosterone levels are at a greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus, and that low testosterone levels may even predict the onset of diabetes. Recent studies have shown that a low serum testosterone level is strongly associated with an increased likelihood of the metabolic syndrome.
Aim: To compare the serum total testosterone levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with that of non-diabetic healthy controls.
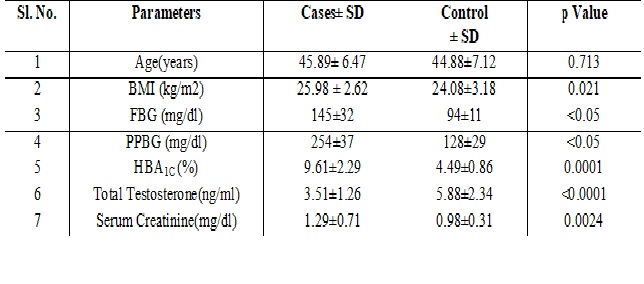
Material and Methods: The study was conducted in OPD of Medical College, Kolkata. In the present study 50 men aged 35-55 years who were diagnosed as type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and confirmed by the estimation of fasting plasma glucose (≥126mg/dl), post prandial blood glucose (≥200mg/dl) and HbA1C (≥6.5%) were selected, 50 healthy age and BMI matched individuals, were selected as controls. Patients with a known history of hypogonadism, panhypopituitarism, hyperthyroidism, patients taking exogenous testosterone and glucocorticoids, patients suffering from chronic debilitating disease, such as renal failure, cardiac failure, liver cirrhosis, or HIV, were excluded from the study. The laboratory investigations included evaluation of serum testosterone levels, fasting and postprandial blood glucose, with the levels of HbA1c and Creatinine. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 20.0. Results are represented as mean±SD and number (%). Pearson’s correlation test was performed to measure the linear dependence of the study parameters.
Results: Serum Total Testosterone level of diabetic group was 3.51±1.26ng/ml, which was found significantly lower than control group with serum total testosterone level 5.88±2.34ng/ml, (p-value < 0.0001).
Conclusion: This study has shown that there is a significant reduction in serum total testosterone levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Downloads
References
Haffner SM, Miettinen H, Karhapää P, et al. Leptin concentrations, sex hormones, and cortisol in nondiabetic men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997 Jun;82(6):1807-9.
Shores MM, Matsumoto AM, Sloan KL, et al. Low serum testosterone and mortality in male veterans. Arch Intern Med. 2006 Aug 14-28;166(15):1660-5.
Selvin E, Feinleib M, Zhang L, et al. Androgens and diabetes in men: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). Diabetes Care. 2007 Feb;30(2):234-8.
Kalyani RR, Dobs AS. Androgen deficiency, diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in men. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes; 2007; Vol. 14; 226-234.
Li C, Ford ES, Li B, et al. Association of testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in men. Diabetes Care. 2010 Jul;33(7):1618-24. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1788. Epub 2010 Apr 5.
Tong PC, Ho CS, Yeung VT, et al. Association of testosterone, insulin-like growth factor-I, and C-reactive protein with metabolic syndrome in Chinese middle-aged men with a family history of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Dec;90(12):6418-23. Epub 2005 Sep 27.
Yeap BB, Alfonso H, Chubb SA, et al. Reference ranges and determinants of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, and estradiol levels measured using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in a population-based cohort of older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Nov;97(11):4030-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-2265. Epub 2012 Sep 13.
Ding EL, Song Y, Malik VS, et al. Sex differences of endogenous sex hormones and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2006 Mar 15;295(11):1288-99.
Oh JY, Barrett-Connor E, Wedick NM, et al. Endogenous sex hormones and the development of type 2 diabetes in older men and women: the Rancho Bernardo study. Diabetes Care. 2002 Jan;25(1):55-60.
Corona G, Monami M, Rastrelli G, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and testosterone: a meta-analysis study. Int J Androl. 2011 Dec;34(6 Pt 1):528-40. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2010.01117.x. Epub 2010 Oct 24.
Kupelian V, Page ST, Araujo AB, et al. Low sex hormone-binding globulin, total testosterone, and symptomatic androgen deficiency are associated with development of the metabolic syndrome in nonobese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Mar;91(3):843-50. Epub 2006 Jan 4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-1326.
Yialamas MA, Dwyer AA, et al. Acute sex steroid withdrawal reduces insulin sensitivity in healthy men with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism; 2007; Rev. 92; 4254–4259.
Al Hayek A, Ajlouni K, Khader Y, Jafal S, Khawaja N, Robert A. Prevalence of low testosterone levels in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. J Family Community Med 2013; 20(3):179-186.
Pitteloud N, Mootha VK, Dwyer AA, et al. Relationship between testosterone levels, insulin sensitivity, and mitochondrial function in men. Diabetes Care. 2005 Jul;28(7):1636-42.
Basu AK, Singhania P, Bandyopadhyay R, et al. Late onset hypogonadism in type 2 diabetic and nondiabetic male: a comparative study. J Indian Med Assoc. 2012 Aug;110(8):573-5.
Saboor Aftab SA, Kumar S, Barber TM. The role of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the development of male obesity-associated secondary hypogonadism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2013 Mar;78(3):330-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.12092.
Dhindsa S, Prabhakar S, Sethi M, et al. Frequent occurrence of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Nov;89(11):5462-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-0804.
Hackett G, Cole N, Bhartia M, Testosterone replacement therapy improves metabolic parameters in hypogonadal men with type 2 diabetes but not in men with coexisting depression: the BLAST study. J Sex Med. 2014 Mar;11(3):840-56. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12404. Epub 2013 Dec 6.
Grossmann M, Thomas MC, Panagiotopoulos S, et al. Low testosterone levels are common and associated with insulin resistance in men with diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 May;93(5):1834-40. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-21777. Epub 2008 Mar 4.
Kapoor D, Aldred H, Clark S, et al. Clinical and biochemical assessment of hypogonadism in men with type 2 diabetes: correlations with bioavailable testosterone and visceral adiposity. Diabetes Care. 2007 Apr;30(4):911-7.
Cheung KK, Luk AO, So WY, et al. Testosterone level in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus and related metabolic effects: A review of current evidence. J Diabetes Investig. 2015 Mar;6(2):112-23. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12288. Epub 2014 Nov 3.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


