Comparison of Universal Plan Indices for Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer treatment
Abstract
Objective: Manual evaluation of IMRT plans for head-and-neck cancers has been especially challenging necessitating efficient and objective assessment tools. Based on previous clinical experience, the radiation oncologists prescribe the dose to the tumour after critical evaluation of the dose to critical structures. We have evaluated the IMRT plan using Universal Plan Indices and Quality factor.
Methods and Materials: In the Eclipse Treatment Planning Systems, we have selected 15 head and neck cancer patients who underwent IMRT delivery in sliding window mode at Clinac DHX linear accelerator equipped with a 120 leaves MLC. All patients were treated using 6 MV photon beams. The UPI indices and Quality factor were calculated using HART software based on MATLAB background.
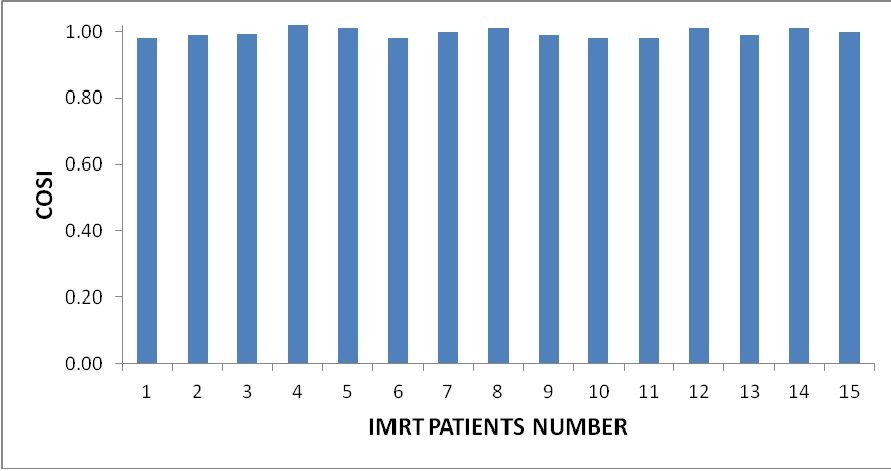
Results: The mean conformity numbers for all fifteen patients were found as 0.92±0.05 and the mean target volume ratio was 1.02±0.04. Similarly the other indices like DG, NCI and modified HI index were 0.95±0.03, 1.08±0.06 and 0.94±0.02 respectively. The mean overall quality factor was found to be 1.01±0.02. The typical value of this factor also to be unity and above unity referred to be overdosed and below the unity referred as under dosage of the structures contoured volume in the corresponding plan.
Conclusion: Hence, we have concluded that, evaluation of the IMRT plan of head and neck cancer patients using Universal plan Indices and Quality factor have been done successfully using HART software
Downloads
References
Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration, Fitzmaurice C1, Allen C2, Barber RM2, Barregard L, et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2706.
O'Sullivan B , Rumble RB, Warde P; et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the treatment of head and neck cancer. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2012.05.006.
Zelefsky MJ , Yamada Y, Fuks Z, et al. Long-term results of conformal radiotherapy for prostate cancer: impact of dose escalation on biochemical tumor control and distant metastases-free survival outcomes. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.11.066.
Austin-Seymour MM, Chen GT, Castro JR, et al. Dose volume histogram analysis of liver radiation tolerance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jan;12(1):31-5.
Lawrence TS , Tesser RJ, ten Haken RK. An application of dose volume histograms to the treatment of intrahepatic malignancies with radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1990 Oct;19(4):1041-7.
Shaw E , Kline R, Gillin M, et al. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group: radiosurgery quality assurance guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993 Dec 1;27(5):1231-9.
Wu Q , Mohan R, Morris M, et al. Simultaneous integrated boost intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locally advanced head-and-neck squamous cell carcinomas. I: dosimetric results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Jun 1;56(2):573-85.
Wang X , Zhang X, Dong L, et al. Effectiveness of noncoplanar IMRT planning using a parallelized multiresolution beam angle optimization method for paranasal sinus carcinoma. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.06.006
Pyakuryal A , Myint WK, Gopalakrishnan M, et al. A computational tool for the efficient analysis of dose-volume histograms from radiation therapy treatment plans. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2010 Jan 28;11(1):3013.
Menhel J , Levin D, Alezra D, et al. Assessing the quality of conformal treatment planning: a new tool for quantitative comparison. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/51/20/019
Knöös T , Kristensen I, Nilsson P. Volumetric and dosimetric evaluation of radiation treatment plans: radiation conformity index. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998 Dec 1;42(5):1169-76.
Leung LH , Chua DT, Wu PM. A new tool for dose conformity evaluation of radiosurgery treatment plans. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999 Aug 1;45(1):233-41.
Akpati H, Kim C, Kim B, et al. Unified dosimetry index (UDI): a figure of merit for ranking treatment plans. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2008 Jun 23;9(3):2803.
Yoon M , Park SY, Shin D, et al. A new homogeneity index based on statistical analysis of the dose-volume histogram. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2007 Mar 20;8(2):9-17.
Leung LH , Kan MW, Cheng AC, et al. A new dose-volume-based Plan Quality Index for IMRT plan comparison. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2007.10.018.
Paddick I. A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Technical note. DOI:https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.supplement.
Collins SP , Coppa ND, Zhang Y, et al. Cyber Knife radiosurgery in the treatment of complex skull base tumors: analysis of treatment planning parameters. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-1-46.
Prabhakar R , Rath GK. A simple plan evaluation index based on the dose to critical structures in radiotherapy. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0971-6203.89965.
Krishnan J , Shetty J , Rao S, et al. Comparison of Rapid Arc and Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy Plans Using Unified Dosimetry Index and the Impact of Conformity Index on Unified Dosimetry Index Evaluation. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2Fjmp.JMP_112_16
Semenenko VA , Reitz B, Day E, et al. Evaluation of a commercial biologically based IMRT treatment planning system. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3013556.
Wu QR , Wessels BW, Einstein DB, et al. Quality of coverage: conformity measures for stereotactic radiosurgery. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1120/jacmp.v4i4.2506


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


