Clinicoradiological and demographic pattern in diffuse parenchymal lung diseases: An observational study
Abstract
Introduction: Diffuse parenchymal disease is a group of lung disease affecting alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, perivascular and perilymphatic tissue. It includes many diseases like IPF, Sarcoidosis, BOOP, COP, LAM etc. it is still under diagnosed entirety. Many patients die due to lack of awareness and investigating modalities.
Aims and objective: This study is to see Demographic pattern of DPLD, its clinical pattern and radiological findings in different type of ILDs.
Study Type: It is a Prospective Observational Study done over a period of 1 year.
Material & Method: Patients studied over20 years of age and having respiratory symptoms. We excluded patients of other diseases like COPD, Tuberculosis etc. Total 75 patients were diagnosed as a case of DPLD by clinical findings, and investigations like X ray chest, HRCT thorax, Bronchoscopy.
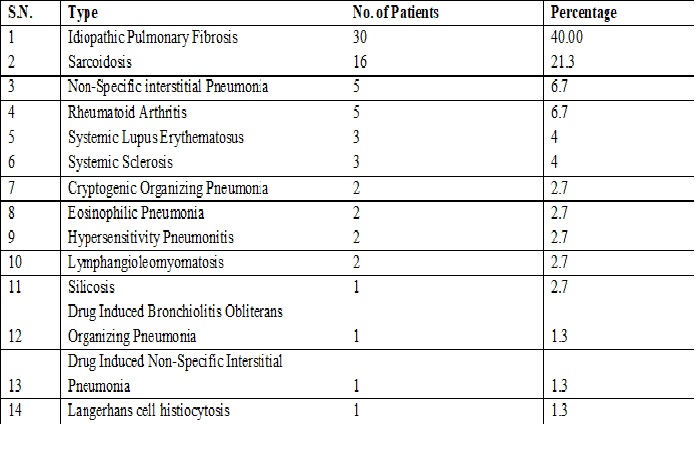
Results: Most common ILD (Interstitial lung Disease) is IPF 40.0% followed by Sarcoidosis etc. Most common clinical symptom was breathlessness (100.00%) in IPF, Fever & Chest Pain are common in Granulomatous type.
Conclusion: DPLD (Diffuse Paranchymal lung Disease) is a chronic lung disease characterized by progressive decline in lung function. IPF is most common in DPLD and leads to fast deterioration of lung function. HRCT (High Resolution computed tomography) is very important to assess type of disease. Spirometry, Broncoscopy are important for diagnosis of ILD and lung function.
Downloads
References
Raghu G. Interstitial lung disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, editors Cecil Medicine; 24th editon. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;2011:pp556-66.
Coultas DB, Zumwalt RE, Black WC, Sobonya RE. The epidemiology of interstitial lung diseases. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.150.4.7921471.
Morgenthau AS, Padilla ML. Spectrum of fibrosing diffuse parenchymal lung disease. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/msj.20087.
Jindal SK, Malik SK, Deodhar SD, Sharma BK. Fibrosing alveolitis: a report of 61 cases seen over the past five years. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 1979 Oct-Dec;21(4):174-9.
Raghu G, Mageto YN, Lockhart D, et al. The accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of new-onset idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other interstitial lung disease: A prospective study. Chest. 1999 Nov;116(5):1168-74.
American College of Radiology. Practice guideline for the breast conservation therapy in the management of invasive breast carcinoma. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.02.057.
Austin JH, Müller NL, Friedman PJ, et al. Glossary of terms for CT of the lungs: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee of the Fleischner Society. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.200.2.8685321.
Hunninghake GW, Zimmerman MB, Schwartz DA, et al. Utility of a lung biopsy for the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.164.2.2101090.
Honda O, Johkoh T, Ichikado K, et al. Comparison of high resolution CT findings of sarcoidosis, lymphoma, and lymphangitic carcinoma: is there any difference of involved interstitium? J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999 May-Jun;23(3):374-9.
Cushley MJ, Davison AG, du Bois RM, Egan J, Flower CD, Gibson GJ, Greening AP, Ibrahim NB, Johnston ID, Mitchell DM, et al. The diagnosis, assessment and treatment of diffuse parenchymal lung disease in adults. Thorax 1999;54:S1–S30.
Hubbard R, Venn A, Smith C, et al. Exposure to commonly prescribed drugs and the etiology of cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: a case-control study. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.157.3.9701093
Scott J, Johnston I, Britton J. What causes cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis? A case-control study of environmental exposure to dust. BMJ. 1990 Nov 3;301(6759):1015-7.
Kundu S, Mitra S, Ganguly J, et al. Spectrum of diffuse parenchymal lung diseases with special reference to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and connective tissue disease: An eastern India experience. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0970-2113.142115
Udwadia ZF, Sen T, Jindal SK. Interstitial lung diseases in a resource-limited setting: The case of India. Eur Respir Mon 2009;46:357-74.
Rajasekaran BA, Shovlin D, Lord P, et al. Interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001 Sep;40(9):1022-5.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


