Effect of fluence smoothening in intensity modulated radiotherapy planning and delivery
Abstract
Objective: In Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) planning, optimization is a computational problem, potentially susceptible to noise and artifacts (high frequency spatial fluctuations) producing sharp fluence peaks and valleys in millimetric spatial scale. A solution to this problem is to smooth the beam profiles.
Methods and Materials: In the Eclipse TPS, fluence smoothing is achieved within the objective function of the inverse treatment planning systems. Plans were developed for a 6 MV photon beam from a Varian Clinac-DHX equipped with a 120 leaves MLC. Total of 160 dose plans were compared and fed into the analysis process. The dose plan quality has been analysed in terms of Statistical computation by means of two-sided paired t-test between two smoothening levels (s25 and s75) in terms of Homogeneity-Index, Conformity-Index, Target dose coverage and OAR dose differences in terms of max, min and mean doses.
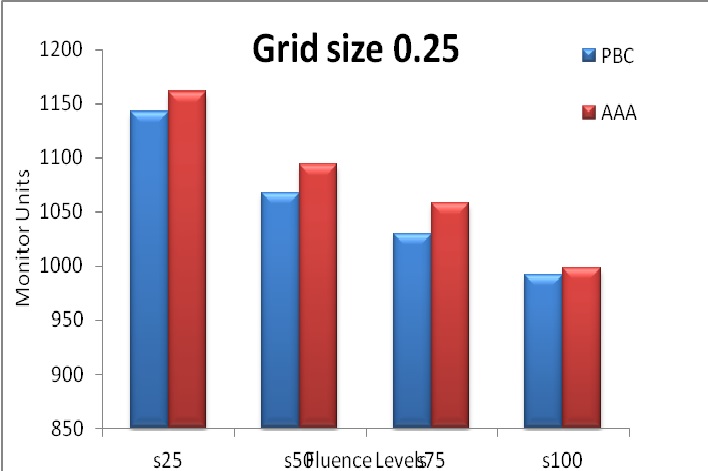
Results: From our present study on the influence of smoothening of fluence levels in IMRT plans results, there was a reduction in total MU’s with no significant statistical variation in terms of mean differences of HI Index, CI index, PTV coverages, OAR doses. Moreover, the reduction in MU’s will help the less head leakage dose hence the lower whole-body dose, which will help the patient to reduce the chances for secondary malignancies.
Conclusion: Hence, we conclude that, higher fluence smoothening levels with acceptable difference in target coverage and minimum variation of OAR should be selected for the execution.
Downloads
References
Hanušová T, Vondráček V, Badraoui K, Horáková I, Koniarová I. New Method For Estimation of Fluence Complexity in IMRT Fields; Lékař a technika: 2016, 46(1),29-32.
Bortfeld T, Jokivarsi K, Goitein M, et al. Effects of intra-fraction motion on IMRT dose delivery: statistical analysis and simulation. Phys Med Biol. 2002 Jul 7;47(13):2203-20.
Dogan N , King S, Emami B, et al. Assessment of different IMRT boost delivery methods on target coverage and normal-tissue sparing. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Dec 1;57(5):1480-91.
Fogliata A , Bolsi A, Cozzi L. Comparative analysis of intensity modulation inverse planning modules of three commercialtreatment planning systems applied to head and neck tumour model. Radiother Oncol. 2003 Jan;66(1):29-40.
Kam MK , Chau RM, Suen J, et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: dosimetric advantage overconventional plans and feasibility of dose escalation. Send toInt J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 May 1;56(1):145-57.
Nicolini, G., Fogliata, A., Vanetti, E., Clivio, A., Ammazzalorso, F., Cozzi, L. What is an acceptably smoothed fluence? Dosimetric and delivery considerations for dynamic sliding window IMRT. Radiat. Oncol., 2007, vol. 42, no. 2, p. 42–54.
Spirou SV , Fournier-Bidoz N, Yang J, et al. Smoothing intensity-modulated beam profiles to improve the efficiency of delivery. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1406522
Breedveld S , Storchi PR, Keijzer M, Heijmen BJ. Fast, multiple optimizations of quadratic dose objective functions in IMRT. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/51/14/019.
Crooks SM , McAven LF, Robinson DF, Xing L. Minimizing delivery time and monitor units in static IMRT by leaf-sequencing. Phys Med Biol. 2002 Sep 7;47(17):3105-16.
Langer M , Thai V, Papiez L. Improved leaf sequencing reduces segments or monitor units needed to deliver IMRT using multileaf collimators. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1420392.
Sun X , Xia P. A new smoothing procedure to reduce delivery segments for static MLC-based IMRT planning.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1713279.
Coselmon MM, Moran JM, Radawski JD, Fraass BA: Improving IMRT delivery efficiency using intensity limits during inverse planning. Med Phys 2005, 32:1234-1245.
Anker CJ , Wang B, Tobler M, et al. Evaluation of fluence-smoothing feature for three IMRT planning systems. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2010 Apr 16;11(2):3035.
Webb S The physical basis of IMRT and inverse planning. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/65676879.
Webb S Use of a quantitative index of beam modulation to characterize dose conformality: illustration by a comparison of full beamlet IMRT, few-segment IMRT (fsIMRT) and conformal unmodulatedradiotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 2003 Jul 21;48(14):2051-62.
Hall EJ , Wuu CS. Radiation-induced second cancers: the impact of 3D-CRT and IMRT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 May 1;56(1):83-8.
Rickhey M, Bogner L: Application of the inverse Monte Carlo treatment planning system IKO for an inhomogeneous dose prescription in the sense of dose painting. Z Med Phys 2006, 16:307-312.
Goitein M, Niemierko A. Intensity modulated therapy and inhomogeneous dose to the tumor: a note of caution. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996 Sep 1;36(2):519-22.
Mayo C, Urie M. Eclipse IMRT- A Practical Treatment Planning Guide. Las Vagas, NV: Varian Medical Systems; 2004; 24–27.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


