The study of psychometric test for detection and assessment in subclinical hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
Background: During past two decades, psychometric tests have been used extensively for detection of SHE. However, the results have been variables with different tests. In real practice we require the tests, which can be administered quickly by treating physician with simplicity and with simple instrument or only with a simple form.
Objective: (1) To apply a battery of psychometric tests in cases of cirrhosis of liver. (2) To correlate findings of psychometric tests with Child`s index of severity for cirrhosis of liver.
Methodology: 25 patients of cirrhosis of liver diagnosed by ultrasonography, biochemical and clinical evidence, admitted in the Medicine ward, will constitute the study group. These patients will undergo a battery of psychometric tests and EEG along with other routine hematological and radiological test. 25 control group with confounding factors as age, sex, education and socioeconomic status.
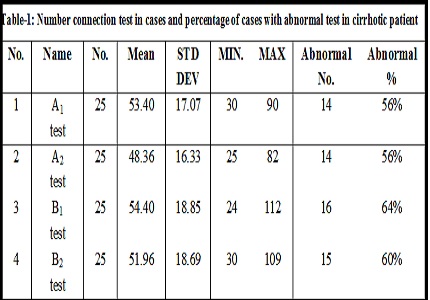
Results: We observed that on WAPIS test cirrhotic performed significantly worse than controls. Mean IQSD non-Alcoholic cirrhotic on WAPIS was [67.7811.29] and Mean IQSD of alcoholic cirrhotics was (66.459.71). On analysis of data the difference was not significant (p>0.005). Taken together the performance test was abnormal in 14 (56%) cases.
Conclusion: We concluded that for quick assessment of mental status and screening for detecting SHE in cases of cirrhosis of liver with portal hypertension, TMT test is useful and for complete assessment of cerebral function derangement WAPIS is most sensitive and complete test.
Downloads
References
Zeegen R, Drinkwater JE, Dawson AM. Method for measuring cerebral dysfunction in patients with liver disease. Br Med J. 1970 Jun 13;2(5710):633-6.
Conn HO. Trailmaking and number-connection tests in the assessment of mental state in portal systemic encephalopathy. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Jun;22(6):541-50.
Conn. H.O. The hepatic encephalopathy. In conn H.O.., Bircher J., eds, Hepatic Encephalopathy Syndromes and therapies Bloomington, lllionis Med Ed Press, 1994; 1-12.
Conn H.O. Lieberthal M.M.: Pathogenesis of portal systemic encephalopathy . In the hepatic Coma syndromes and Lactulose. Baltimore Williams & Wikins, 1978; 46-48.
R.M. Reiten, Validity of trail making test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept Mot Skills 8 1958; PP-271-276.
Bargara L., Sama C., Malavolti M. : The importance of recording in sub clinical hepatic encephalopathy, In: Therapy in liver Disease, J Rodes, V Arroyo eds. Barcelona: Ediciones Doyma, 1991;133-335.
Gitlin N, Lewis DC, Hinkley L. The diagnosis and prevalence of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in apparently healthy, ambulant, non-shunted patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1986;3(1):75-82.
Sood G.K, Sarin S.K Mahapta J et al. comparative efficacy of psychometric test in detection of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in nonalcoholic cirrhotics : search for a rational approach. Am J gastroenterol 1989; 84:156-159.
Rikkers L, Jenko P, Rudman D, Freides D: Subclinical Hepatic encephalopathy detection, Prevalence and Relationship to Nitrogen Metabolism. Gastroenterology 1978; 75:462-9.
Davidson E.A. Summerskill W.H.J. psychiatric aspects of liver disease. Postgrad Med J 1956;32:487-494. [PubMed]
Levy LJ, Leek J, Losowsky MS. Evidence for gamma Aminobutyric Acid as the inhibitor of gamma Aminobutyric Acid binding in plasma of Humans with liver diseases and Hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Sci (Lond). 1987 Nov;73(5):531-4.
Gilberstadt S.J. Gilberstadt H., Zieve L., et al:. Psychomotor performance defect in cirrhotic patients without overt encephalopathy. Arch Intern Med 1980; 140:519-521.
Groeneweg M, Moerland W, Quero JC, Hop WC, Krabbe PF, Schalm SW. Screening of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2000 May;32(5):748-53.
Gitlin N, Lewis D.C. Hinkely L. The diagnosis and prevalence of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in apparently health, ambulant, non-shunted patients with cirrhosis. J Heptol 1986;:3:75-82.
Sarin S.K. Nundy S. Sub normal encephalopathy after portosystemic shunts in patients with non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis. Liver. 1985 Jun;5(3):142-6.
Gilberstadt S.J. Gilberstadt H., Zieve L., et al. Psychomotor performance defect in cirrhotic patients without overt encephalopathy. Arch Intern Med. 1980 Apr;140(4):519-21.
Trate R.E. Hegedus A.M. Van Thiel D.H. et al.: Nonalcoholic cirrhosis associated with neurophsychological dysfunction in the absence of overt evidence of hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 1984;86:1421-1427.
Szerb JC, Butter worth RF. Effect of Ammonium ions on synaptic transmission in mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1992 Aug;39(2):135-53.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


