Early CRRT and antibiotic management in shock patient due to urosepsis with immunocompromised post renal transplantation
Abstract
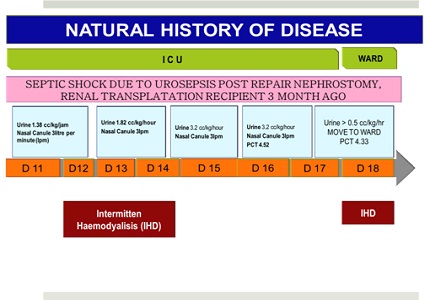
Septic shock is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the ICU. A 32-year-old patient was diagnosed with septic shock due to urosepsis, hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), and acute kidney injury (AKI) post renal transplantation. Continue Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) was performed to remove inflammation mediator. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, blood glucose control, adequate volume status, nutritional support, and temporary withdrawal of immunosuppressive drugs were ensured. Patient was stable on the 5th day, extubated by day 8th, and discharged from ICU 10 days later. It can be concluded that early CRRT could prevent organ failure and further complications caused by septic shock.
Downloads
References
Giessing M. Urinary Tract Infection in Renal Transplantation. Arab Journal of Urology 2012;10(2):162-8.
Bjerklund Johansen TE, Cek M, Naber K, Stratchounski L, Svendsen MV, Tenke P; PEP and PEAP studyinvestigators; EuropeanSociety of Infections in Urology.Prevalence of hospital-acquired urinary tract infections in urology departments. Eur Urol. 2007 Apr;51(4):1100-11; discussion 1112. Epub 2006 Aug 28.
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GSOpal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016 Feb 23;315(8):801-10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.0287.
Bouza E, San Juan R, Muñoz P, Voss A, Kluytmans J; Co-operative Group of the European Study Group on Nosocomial Infections. A European perspective on nosocomialurinary tract infections II. Report on incidence, clinical characteristics and outcome (ESGNI-004study). European Study Group on Nosocomial Infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001 Oct;7(10):532-42.
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, Osborn TM, Nunnally ME, Townsend SR, Reinhart K, Kleinpell RM, Angus DC, Deutschman CS, Machado FR, Rubenfeld GD, Webb SA, Beale RJ, Vincent JL, Moreno R; Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee including the Pediatric Subgroup. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb;41(2):580-637. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af.
Concia E, Azzini A M. Aetiology and Antibiotic Resistance Issues Regarding Urological Procedures. J Chemother. 2014;26 Suppl 1:S14-23.
Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, et al. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: A Worldwide Practice Survey, The Beginning and ending supportive therapy for the kidney (B.E.S.T. Kidney) Investigators. Intensive Care Med 2007;33:1563-70.
Naber KG, Bergman B, Bishop MC, Bjerklund-Johansen TE, Botto H, Lobel B, Jinenez Cruz F, Selvaggi FP; Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Working Group of the Health CareOffice (HCO) of the EuropeanAssociation of Urology (EAU). EA Uguidelines for the management of urinary and male genital tractinfections. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Working Group of the Health CareOffice (HCO) of the EuropeanAssociation of Urology (EAU). Eur Urol. 2001 Nov;40(5):576-88.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


