A correlation study of lipid profile with body mass index and waist hip ratio in Rohilkhand region
Abstract
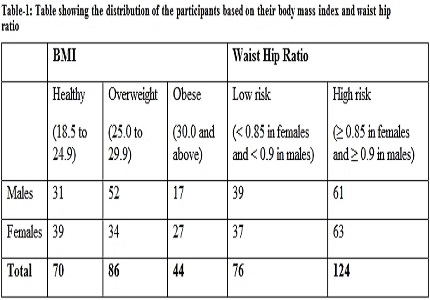
Background: Central or abdominal obesity is associated with metabolic disorders such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus and cardio vascular disease (CVD). Anthropometric tools especially BMI is commonly used to categorize obesity. BMI, calculated from the weight and height of an individual, represents generalized fat distribution. Waist hip ratio (WHR) is more reliable anthropometric tool for measuring abdominal obesity as it takes waist circumference into consideration. Therefore, this study was undertaken to study the correlation of dyslipidemia with BMI and WHR and conclude if WHR could be used as a reliable tool for identifying high risk patients.
Materials and Methods: Two hundred participants aged between35 to 45 years were randomly chosen. Lipid profile of all the participants was determined. These participants were divided into three groups based on their BMI. Same participants were also divided based on their WHR into two groups – Low risk and high risk. Mean of lipid profile was analyzed for significance by ANOVA and independent t test using SPSS 23.0. Correlation of dyslipidemia and BMI and WHR was analyzed using Pearson Coefficient. P<0.05 was considered significant.
Result: Participants with WHR in the high-risk category had TC/HDL ratio of 3.8±0.5 which was similar to those with BMI>30 Kg/m2. Pearson correlation coefficient of Total cholesterol, LDL-C and TC/HDL with WHR was 0.505, 0.484 and 0.528 respectively which was stronger than that with BMI.
Conclusion: WHR is a reliable tool to identify patients who are at high risk to develop CVD and other metabolic diseases.
Downloads
References
2. Santi-Canoo MJ. Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Obes Control Ther. 2014;1(1):1-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.15226/2374-8354/1/1/00105.
3. Rana G, Kafle D, Adhikari P, Sharma A, Sharma D.The global problem: Obesity and dyslipidemia. Int. Res J Pharm. App Sci. 2013;3(5):69-73.
4. Chehrei A, Sadrnia S, Keshteli AH, Daneshmand MA, Rezaei J. Correlation of dyslipidemia with waist to height ratio, waist circumference, and body mass index in Iranian adults. AsiaPac J Clin Nutr.2007;16(2):248-53.
5. Berry DC, Stenesen D, Zeve D, Graff JM. The developmentalorigins of adiposetissue. Development. 2013 Oct;140(19):3939-49. doi: 10.1242/dev.080549.
6. Flock MR, Green MH, Kris-Etherton PM. Effects of adiposity on plasmalipidresponse to reductionsindietarysaturated fatty acids and cholesterol. Adv Nutr. 2011 May;2(3):261-74. doi: 10.3945/an.111.000422. Epub 2011 Apr 30. [PubMed]
7. Klop B, Elte JW, Cabezas MC. Dyslipidemia in obesity: mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients. 2013 Apr 12;5(4):1218-40. doi: 10.3390/nu5041218. [PubMed]
8. Lemos-Santos MG, Valente JG, Gonçalves-Silva RM, Sichieri R. Waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio as predictors of serumconcentration of lipids in Brazilianmen. Nutrition. 2004 Oct;20(10):857-62.
9. Al-Ajlan AR. LipidProfile in Relation to AnthropometricMeasurements among CollegeMaleStudents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Biomed Sci. 2011 Jun;7(2):112-9. [PubMed]
10. Ferrier DR. Lippincott’s illustrated reviews. Biochemistry, 6th ed. New Delhi: Wolters Kluwer / Lippincott William & Wilkins Publishers Pvt Ltd;2014.
11. Binu J, Harnagle R. A Study on the prevalence of overweight and obesity and its influencing factors among rural geriatric population in Kerala. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci.2014;3(9):284-93.
12. Singh P, Umesh K, Dey AB. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among elderly patients attending a geriatric clinic in a tertiary care hospital in Delhi, India. Indian J Med Sci. 2004;58:162–63.
13. Mallick AK, Ahsan M. Evaluation and Interpretation of Lipid Profile Based on the National Cholesterol Education Programme Adult Treatment Panel III Guidelines. IJMHS 2016; 3(2): 12329.
14. Manjareeka M, Nanda S, Mishra J, Mishra S. Correlation between anthropometry and lipid profile in healthy subjects of Eastern India. J Mid-life Health 2015;6:164-8.doi 10.4103/0976-7800.172302.
15. Gierach M, Gierach J, Ewertowska M, Arndt A, Junik R. Correlation between Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. ISRN Endocrinol. 2014 Mar 4;2014:514589. doi: 10.1155/2014/514589. eCollection 2014.
16. Zilanawala A, Davis-Kean P, Nazroo J, Sacker A, Simonton S, Kelly Y. Race/ethnic disparities in early childhood BMI, obesity and overweight in the United Kingdom and United States. International journal of obesity. 2015;39(3):520-29.
17. Woudberg NJ, Goedecke JH, Blackhurst D, Frias M, James R, Opie LH, Lecour S. Association between ethnicity and obesity with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) function and subclass distribution. Lipids Health Dis. 2016 May 11;15:92. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0257-9.
18. Shamai L, Lurix E, Shen M, Novaro GM, Szomstein S, Rosenthal R, Hernandez AV, Asher CR. Association of body mass index and lipidprofiles: evaluation of a broadspectrum of body mass indexpatientsincluding the morbidlyobese. Obes Surg. 2011 Jan;21(1):42-7. doi: 10.1007/s11695-010-0170-7. [PubMed]
19. Huang YC, Chang PY, Hwang JS, Ning HC. Association of small dense lowdensity lipoprotein cholesterol in type 2 diabetics with coronary artery disease. Biomed J. 2014;37(6):375-79. doi: 10.4103/2319-4170.132883. [PubMed]
20. Wang J, Stančáková A, Soininen P, Kangas AJ, Paananen J, Kuusisto J, Ala-Korpela M, Laakso M. Lipoprotein subclass profiles in individuals with varying degrees of glucose tolerance: a population-based study of 9399 Finnish men. J Intern Med. 2012 Dec;272(6):562-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2012.02562.x.Epub 2012 Jul 27.
21. Jayarama1 N, Reddy PR, Reddy MM, Mahesh V. Relation between waist-hip ratio and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients Asian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2014 (5)3:51–53.
22. Aziz J, Siddiqui NA, Siddiqui IA, Omair A. Relation of body mass index with lipidprofile and blood pressure in younghealthystudents at ZiauddinMedicalUniversity. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2003 Oct-Dec;15(4):57-9. [PubMed]
23. Kanwar G, Shekhawat KS, Rathore S, Jain KB. Study of correlation of waist–hip ratio and lipid profile in type-2 diabetes mellitus subjects. J Pharm Biomed Sci 2016; 6(3):264–68. doi.org/10.20936/jpbms/160236.
24. Sandhu HV, Koley S and Sandhu KS.A Study of Correlation between Lipid Profile and Body Mass Index (BMI) in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. J. Hum. Ecol. 2008; 24(3):227-29. doi.org/10.1080/09709274.2008.11906119.
25. Himabindu Y, Sriharibabu M, Alekhya K, Saisumanth K, Lakshmanrao N, Komali K. Correlations between anthropometry and lipid profile in type 2 diabetics. Indian journal of endocrinology and metabolism. 2013;17(4):727. doi.10.4103/2230-8210.113769.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


