Study of clinical risk factors and predictors of post stroke vascular cognitive impairment
Abstract
Introduction: Cognitive impairment due to cerebro vascular disease is termed” vascular cognitive Impairment “(VCI) and forms a spectrum that includes vascular dementia and milder forms of cognitive impairment. Vascular cognitive impairment has some varied and diverse aetiology. This is particularly important as apart from age vascular risk factors, are the most important and presently the only treatable precursor to dementia. This prospective observational study was carried out in indept. Of medicine, GMC Bhopal.
Methods: A standard protocol was applied at admission and 3 months after stroke, this protocol included clinical, functional and cognitive assessments, various lab tests and MMSE.
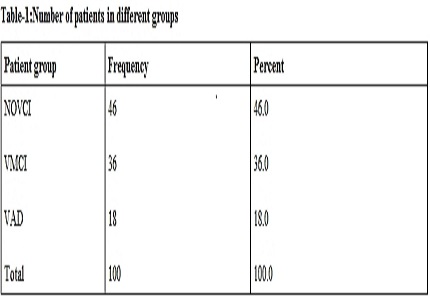
Results: Amongst the various risk factors hypertension, diabetes mellitus, prior stroke, dyslipidemia, ischemic heart disease, tobacco chewing, smoking, family history of dementia was more frequently seen in vascular cognitive impairment group. In this study, the frequency of patients having post stroke vascular cognitive impairment (VCI)is 54%. 18%of the patients had VaD (Vascular dementia), 36% of the patients had VMCI(vascular mild cognitive impairment), 46% of the patients had NO VCI (no vascular cognitive impairment. There was significant association of risk factors like Hypertension (p=0.022) diabetes mellitus (P=0.038), dyslipidaemia (p=0.034), prior stroke(p=0.046) with development of vascular cognitive impairment. Post stroke dementia has considerable morbidity.
Conclusion: The predictors of development of Vascular cognitive impairment following stroke in this study are lower educational status, Hypertension, Diabetes mellitus, Dyslipidemia, Prior stroke, urinary incontinence, High sys. BP, NIHSS score, LDL level, abnormal ECG, Strategic site lesion and greater severity of age related white matter changes.
Downloads
References
2. Ingles JL, Wentzel C, Fisk JD, Rockwood K. Neuropsychological predictors of incident dementia in patients with vascular cognitive impairment, without dementia. Stroke. 2002 Aug;33(8):1999-2002. [PubMed]
3. Román GC. Vascular dementia may be the most commonform of dementia in the elderly. J Neurol Sci. 2002 Nov 15;203-204:7-10.
4. Erkinjuntti T, Román G, Gauthier S, Feldman H, Rockwood K. Emerging therapies for vascular dementia and vascularcognitive impairment. Stroke. 2004 Apr;35(4):1010-7.
Epub 2004 Mar 4.
5. Censori B, Manara O, Agostinis C, Camerlingo M, Casto L, Galavotti B, Partziguian T, Servalli MC, Cesana B, Belloni G, Mamoli A. Dementia after first stroke. Stroke. 1996 Jul;27(7):1205-10. [PubMed]
6. Inzitari D,Di Carlo A,Pracuccig et el.Incidents and Determinants of Post Stroke Dementia as Defined by A Informant Interview Method In Hospital Based Stroke Registry..Stroke1998;29:2087-2093.
7. Loeb C, Gandolfo C, Croce R, Conti M. Dementia associated with lacunar infarction. Stroke. 1992 Sep;23(9):1225-9. [PubMed]
8. Pohjasvaara T, Erkinjuntti T, Vataja R, Kaste M. Dementia three months after stroke. Baseline frequency and effect of different definitions of dementia in the Helsinki Stroke Aging Memory Study (SAM) cohort. Stroke. 1997 Apr;28(4):785-92. [PubMed]
9. Pohjasvaara T, Erkinjuntti T, Ylikoski R, Hietanen M, Vataja R, Kaste M. Clinical determinants of poststroke dementia. Stroke. 1998 Jan;29(1):75-81.
10. Tatemichi tk, how acute brain failure becomes chronic: a view of the mechanisms of dementia related to stroke .neurology.1990;40:1652-1659.
11. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Mini-mental state". A practicalmethod for grading the cognitivestate of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189-98. [PubMed]
12. Tangalos EG, SmithGE,IvnikRJ,et al. The mini mental state examination in general medical practice: The utility and acceptance. Mayo clinproc 199671:829...
13. khedr Em, Hamed SA , El-Shereef HK, et al, cognitive impairment after cerebrovascular stroke: relationship to vascular risk factors. Neuropsychiatry Dis Treat 2009;5:103-16
14. Serrano S, Domingo J, Rodriguez-Garcia E,et al. Frequency of cognitive impairment without dementia in patients with stroke: a two-year follow-up study. Stroke 2007;38(1):105-10.
15. Del Ser T, Barba R, Morin MM, Domingo J, Cemillan C, Pondal M, Vivancos J. Evolution of cognitive impairment after stroke and risk factors for delayed progression. Stroke. 2005 Dec;36(12):2670-5. Epub 2005 Oct 27. [PubMed]
16. Rasquiun SM Lodder J, Ponds RW et al. Cognitive functioning after stroke: a one-year follow-up study. Dementia Geriatric Cognitive Disorder.2004;18(2):138-44.
17. Sachdev PS, Brodaty H, Valenzuela MJ, Lorentz L, Looi JC, Berman K, Ross A, Wen W, Zagami AS. Clinicaldeterminants of dementia and mild cognitive impairmentfollowing ischaemic stroke: the SydneyStrokeStudy. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2006;21(5-6):275-83. Epub 2006 Feb 10.
18. Pohjasvaara T, Erkinjuntti T, Ylikoski R, Hietanen M, Vataja R, Kaste M. Clinical determinants of poststroke dementia. Stroke. 1998 Jan;29(1):75-81.
19. Barba R, Martínez-Espinosa S, Rodríguez-García E, Pondal M, Vivancos J, Del Ser T. Poststroke dementia : clinical features and risk factors. Stroke. 2000 Jul;31(7):1494-501. [PubMed]
20. Madureira S, Guerreiro M, Ferro JM. Dementia and cognitive impairment three months after stroke. Eur J Neurol 2001;8:621-7. [PubMed]
21. Rasquin SM, Lodder J, Ponds RW, et al. Cognitive functioning after stroke: a one-year follow-up study. Dementia Geriatric Cognitive Disorder2004;18(2):138-44.
23. Sudo FK, Alves CE, Alves GS, Ericeira-Valente L, Tiel C, Moreira DM, Laks J, Engelhardt E. White matter hyperintensities, executive function and globalcognitiveperformance in vascularmild cognitive impairment. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2013 Jul;71(7):431-6. doi: 10.1590/0004-282X20130057.
23. Sudo FK, Alves CE, Alves GS, Ericeira-Valente L, Tiel C, Moreira DM, Laks J, Engelhardt E. White matter hyperintensities, executive function and globalcognitiveperformance in vascularmild cognitive impairment. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2013 Jul;71(7):431-6. doi: 10.1590/0004-282X20130057.
24. Gemmell E, bosomworth H, Allan L, et al. hippocampal neuronal atrophy and cognitive function in delayed post stroke and age related dementias . stroke 2012;43:808.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


