Detection and quantification of liver fat with MRIT1 dixon sequence in patients with hepatic steatosis and it’s comparison with USG
Abstract
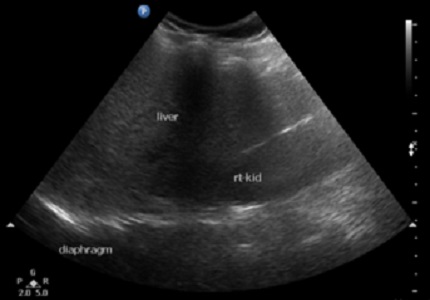
Introduction: Hepatic steatosis also known as fatty liver is due to abnormal and excessive accumulation of lipids with in hepatocytes. It is the most common chronic disease of liver. Magnetic resonance techniques can detect fatty liver more accurately than ultrasonography and become primary modalityto assess hepatic steatosis both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Aims: The aims of this study were detection and quantification of liver fat by MR technique in patients of hepatic steatosis. Comparison of USG and MRI in detection and quantification of liver fat.
Material and Methods: This cross-sectional study was carried out on 50 patients in Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Rajindra Hospital, Patiala in whom risk factors for hepatic steatosis were present. Considering T1 Dixon MRI of liver as reference its comparison with USG was done in these patients for detection of hepatic steatosis and quantification of liver fat.
Results: USG had sensitivity 73.68%, specificity 66.67%, positive predictive value 87.50% and negative predictive value 44.44% as compared to MRI T1 Dixon sequence for detection of fatty liver. When grading of fatty liver on USG was compared with percentage quantification of liver fat on MRI T1 Dixon sequence of liver, there was considerable overlapping of fat percentage in each grade.
Conclusion: Advantages of MRI as compared to USG is its more sensitivity and specificity for detection of hepatic steatosis, early detection of hepatc steatosis, quantify liver fat, objective and not observer dependent.
Downloads
References
Fromenty B, Pessayre D. Inhibition of mitochondrial beta-oxidation as a mechanism of hepatotoxicity. PharmacolTher. 1995;67(1):101-54.
Lebovics E and Rubin J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): why you should care, when you should worry, what you should do. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011;27(5):419-24.
Parekh S, Anania FA. Abnormallipid and glucosemetabolism in obesity: implications for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2007 May;132(6):2191-207.
Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A. Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. 2007 May;132(6):2169-80.
Yajima Y, Ohta K, Narui T, Abe R, Suzuki H, Ohtsuki M. Ultrasonographicaldiagnosis of fatty liver: significance of the liver-kidneycontrast. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1983 Jan;139(1):43-50.
Saadeh S, Younossi ZM, Remer EM, Gramlich T, Ong JP, Hurley M, Mullen KD, Cooper JN, Sheridan MJ. The utility of radiologicalimaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002 Sep;123(3):745-50.
Rofsky NM, Fleishaker H. CT and MRI of diffuseliver disease. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1995 Feb;16(1):16-33.
Reeder SB, Cruite I, Hamilton G, Sirlin CB. QuantitativeAssessment of LiverFat with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy. J MagnResonImaging. 2011 Oct;34(4):spcone.
Pacifico L, Martino MD, Catalano C, Panebianco V, Bezzi M, Anania C, Chiesa C. T1-weighteddual-echoMRI for fatquantification in pediatricnonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul 7;17(25):3012-9. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748%2Fwjg.v17.i25.3012.
Hussain HK, Chenevert TL, Londy FJ, Gulani V, Swanson SD, McKenna BJ, Appelman HD, Adusumilli S, Greenson JK, Conjeevaram HS. Hepaticfatfraction: MRimaging for quantitativemeasurement and display--early experience.Radiology. 2005 Dec;237(3):1048-55. Epub 2005 Oct 19.
Kreft BP, Tanimoto A, Baba Y, Zhao L, Chen J, Middleton MS, Compton CC, Finn JP, Stark DD. Diagnosis of fatty liver with MR imaging. J MagnReson Imaging. 1992 Jul-Aug;2(4):463-71
Cheng HY, Wang HY, Chang WH, Lin SC, Chu CH, Wang TE et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: prevalence, influence on age and sex, and relationship with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. International Journal of Gerontology. 2013 Dec 31;7(4):194-8.
Bellentani S, Saccoccio G, Masutti F, Crocè LS, Brandi G, Sasso F et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatic steatosis in Northern Italy. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132(2):112-7.
Palmentieri B, de Sio I, La Mura V, Masarone M, Vecchione R, Bruno S, Torella R, Persico M. The role of bright liver echo pattern on ultrasound B-mode examination in the diagnosis of liver steatosis. Dig Liver Dis. 2006 Jul;38(7):485-9. Epub 2006 May 22.
Perez NE, Siddiqui FA, Mutchnick MG, Dhar R, Tobi M, Ullah N et al. Ultrasound diagnosis of fatty liver in patients with chronic liver disease: a retrospective observational study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;41(6):624-9.
Hernaez R, Lazo M, Bonekamp S, Kamel I, Brancati FL, Guallar E, Clark JM. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of ultrasonography for the detection of fatty liver: A meta‐analysis. Hepatology. 2011;54(3): 1082-90.
Pacifico L, Celestre M, Anania C, Paolantonio P, Chiesa C, Laghi A. MRI and ultrasound for hepaticfatquantification:relationships to clinical and metaboliccharacteristics of pediatricnonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Paediatr. 2007 Apr;96(4):542-7. Epub 2007 Feb 14.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


