Spinal tuberculosis: imaging features on MRI
Abstract
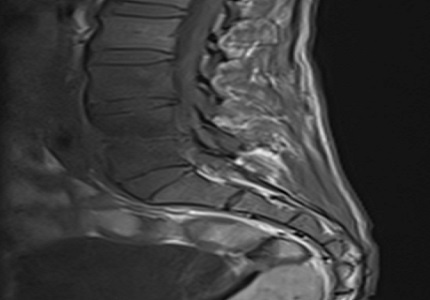
Introduction: Spine is the most common site of skeletal tuberculosis.Radiographic manifestations of tuberculous spondylitis include intraosseous and paraspinal abscess formation, subligamentous spread of infection, vertebral body destruction and collapse, and extension into the spinal epidural space. Significant instability and deformity of the spine can result, mandating prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent permanent neurologic damage.
Objective: This is a prospective and descriptive study to evaluate the role of MRI in spinal tuberculosis and various spectrum ofits manifestations.
Materials and Methods: This prospective study was on 25 patients of either age or sex with clinical suspicion of spinal TB over a period of 2 years and subsequently went MR Imaging and features were correlated with other investigations and histopathological diagnosis in few patients.
Results: Thoracic spine was the most common site of involvement.Vertebral body wedge collapse or compression fracture was seen in 64 % of patients. Posterior element involvement was found in 10 out of 25 cases. Prevertebral & paravertebral collections were seen in88% of cases. Epidural soft tissue component was seen in 56% of cases.
Conclusion: MRI is the best diagnostic modality for spinal TB and to demonstratethe various associated manifestations which help in assessing the extent and severity of the disease and thus inearly and correct management planning.
Downloads
References
Rasouli MR, Mirkoohi M, Vaccaro AR, Yarandi KK, Rahimi-Movaghar V. Spinal tuberculosis: diagnosis and management.Asian Spine J.2012Dec;6(4):294-308. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4184%2Fasj.2012.6.4.294. Epub2012Dec 14.
Moorthy S, Prabhu NK. Spectrum of MR imaging findings in spinal tuberculosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2002 Oct;179(4):979-83.
Ansari, S., Rauniyar, R.K., Dhungel, K., Sah, P.L.,. Chaudhary, P.,Ahmad, K., Amanullah, M.F., 2013. MR evaluation of spinal tuberculosis. Al Ameen J. Med. Sci.;6(3):219-25.
Garg RK, Somvanshi DS. Spinal tuberculosis: a review.J Spinal Cord Med. 2011;34(5):440-54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1179/2045772311Y.0000000023.
Ansari S, Amanullah MF, Ahmad K, Rauniyar RK. Pott's Spine: Diagnostic Imaging Modalities and Technology Advancements.N Am J Med Sci.2013 Jul;5(7):404-11. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F1947-2714.115775.
Toloba Y, Diallo S, Maiga Y, Sissoko B, Ouattara K, Soumaré D, Sidibé S. [Spinal tuberculosis (Pott's disease): epidemiological, clinical, radiological and evolutionary aspects at the University Hospital of Point G].Mali Med.2011;26(2):8-11.
Rauf F, Chaudhry UR, Atif M, urRahaman M. Spinal tuberculosis: Our experience and a review of imaging methods.Neuroradiol J. 2015 Oct;28(5):498-503. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177%2F1971400915609874. Epub 2015 Oct 8.
Rivas-Garcia A, Sarria-Estrada S, Torrents-Odin C, Casas-Gomila L, Franquet E. Imaging findings of Pott’s disease. European Spine Journal. 2013 Jun 1;22(4):567-78.
Smith AS, Weinstein MA, Mizushima A, Coughlin B, Hayden SP, Lakin MM, Lanzieri CF. MR imaging characteristics of tuberculous spondylitis vs vertebral osteomyelitis. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1989 Aug 1;153(2):399-405.
Shanley DJ. Tuberculosis of the spine: imaging features.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995 Mar;164(3):659-64.
Jacqueline P and Sharon S. Potts disease: Diagnosis with magnetic resonance imaging. Radiography, 2010; 16:84-88.
Zaidi H, Akram MH, Wala MS. Frequency and magnetic resonance imaging patterns of tuberculous spondylitis lesions in adults. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2010 May 1;20(5):303-6.
Andronikou S, Jadwat S, Douis H. Patterns of disease on MRI in 53 children with tuberculous spondylitis and the role of gadolinium.Pediatr Radiol.2002Nov;32(11):798-805. Epub2002 Aug 17.
Yus of MI, Hassan E, Rahmat N, Yunus R. Spinal Tuberculosis: The Association between Pedicle Involvement and Anterior Column Damage and Kyphotic Deformity. Spine, 2009; 34:713-717.
Ehara S, Shimamura T, Wada T. Single vertebral compression and involvement of the posterior elements in tuberculous spondylitis: observation on MR imaging.Radiat Med. 1997 May-Jun;15(3):143-7.
Jung NY, Jee WH, Ha KY, Park CK, Byun JY. Discrimination of tuberculous spondylitis from pyogenic spondylitis on MRI.AJR Am J Roentgenol.2004 Jun;182(6):1405-10.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


