Color Doppler study of uterine vasculature in pregnancy induced hypertension
Abstract
Objectives: 1. To study the blood flow pattern of uterine vessels in pregnancy induced hypertension by Color Doppler. 2. To assess the predictive value of Color Doppler Studies of uterine blood flow patterns for perinatal outcome.
Materials and Methods: The period of our study was for 2 years at a tertiary care hospital in rural area in RMC Loni.50 cases diagnosed as pregnancy induced hypertension beyond 28 weeks of gestation, i.e, period of viability of fetus were screened by Color Doppler for uterine artery during the above-mentioned period. Outcome of these pregnancies was then collected.It included the gestational age of delivery, mode of delivery, birthweight, APGAR score, still births andlivebirths.
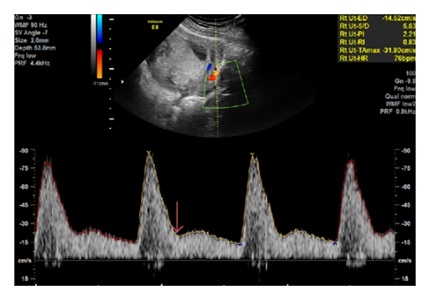
Results: In this study birth weight in grams in>36 weeks gestation at delivery showed highly significant difference between the present (1767+209.83) and absent (2289.98+358.96) diastolic notch group indicating that birth weight of the neonate was affected by the presence of diastolic notch. Similarly neonatal mortality was more(45.45%) in case of patients with presence of uterine artery diastolic notch as compared to absence of diastolic notch(0) which was statistically significant. Morbidity was 36.36% in diastolic notch group as compared to diastolic notch absent group (14.28%).
Conclusion: Doppler is an excellent armamentarium in the hands of obstetrician for non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring of PIH patients to identify the fetuses at risks and predicting perinatal morbidity and mortality. Doppler velocimetry gives us the idea about correct time of intervention so as to get good perinatal outcome thus preventing high fetal mortality and morbidity in hypertensive patients.
Downloads
References
Carroll BA. Duplex Doppler Systems in obstetric ultrasound. Radiol Clin N Am.1990;25(1):189-202.
Hoffman C, Galan HL. Assessing the at risk, fetus: Doppler ultrasound.Curr Opin Obstet Gynaecol.2009;21:161-166.
Chen F. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Gynakol Geburtsmed Gynakol Endokrinol 2008;4(1):24-34.
Kevin A, Mairi H, James P, Martin J, Pregnancy screening by Doppler uteroplacental and umbilical artery waveforms. Br J Obstetric Gynecology 1989, Oct;96:1163-67.
C J Bhatt, J Arora. Role of color Doppler in pregnancy induced hypertension (100 cases) IJRI 2003, Vol 13, 4, 417-420.
Geographic variation in the incidence of hypertension in pregnancy. World Health Organization International Collaborative Study of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jan;158(1):80-3. [PubMed]
Aharwal S, Agrawal R, Sharma S, A study of role of Doppler ultrasound in Pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH) and perinatal outcome: Int J Med Res Rev 2016;4(4):673-680.doi: 10.17511/ijmrr.2016.i04.34.
Gaikwad PR et al. International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology.2017 Jun;6(6):2354-2360.
Fleischer A, Schulman H, Farmakides G, Bracero L, Grunfeld L, Rochelson B, Koenigsberg M. Uterine arteryDoppler velocimetry in pregnant women with hypertension. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Apr;154(4):806-13. [PubMed]
Aquilina J, Harrington K. Pregnancy hypertension and uterine artery Doppler ultrasound. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Dec;8(6):435-40.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


