The diagnostic accuracy of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for discrimination of malignant from benign cervical lymphadenopathy in head and neck tumours using histopathology as the reference standard
Abstract
Head and neck cancers accounts for maximum number of cancer cases in Indian hospital settings. Involvement of neck nodes is a very important prognostic factor of its outcome. Differentiation between benign and metastatic lymphadenopathy often presents a diagnostic challenge with conventional imaging techniques. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has emerged as a powerful non-invasive imaging technique that is capable of characterisation of these lesions as benign or malignant with the help of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps.
Aim: The aim of this cross-sectional study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of DWI to differentiate benign from malignant cervical lymph nodes in head and neck tumours, subsequently confirming the results using histopathology as the reference standard.
Materials and Methods: The cross-sectional study was conducted on 60 patients of either age or sex with enlarged neck lymph nodes over a period of 2 years, subsequently these patients underwent DW MRI imaging followed by histopathology of either neck dissection specimen or core biopsy or US guided FNAC as a part of the study.
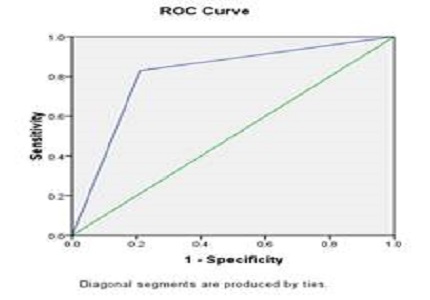
Results: Out of 60 patients, 41(68.33 percent) cases came out as malignant and 19 (31.67 percent) cases came out as benign. The results obtained were 36 true positives, 4 false positives, 15 true negatives and 5 false negatives. The overall sensitivity of DWI for differentiating malignant from benign cervical lymphadenopathy was 87.80% with specificity of 78.95%. The positive predictive value and negative predictive value were 90.00% and 75.00% respectively. The best ADC threshold value for distinguishing benign and malignant nodes was 1.005 × 10-3 mm2/sec.
Conclusion: DWI is an important tool to differentiate benign vs malignant lymphadenopathy and helps in guiding the clinician to treat these nodes accordingly.
Downloads
References
Vigneswaran N and Williams MD. Epidemiological Trends in Head and Neck Cancer and Aids in Diagnosis. Oral and maxillofacial surgery clinics of North America. 2014;26(2):123-141.
Kumaran PS, Thangaswamy SV, Navaneetham A. The need for early detection of neck nodal metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2012 ;4(2):S341-3.
Leusink FK, van Es RJ, de Bree R, Baatenburg de Jong RJ, van Hooff SR, Holstege FC, et al. . Novel diag-nostic modalities for assessment of the clinically node-negative neck in oral squamous-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol 2012 Dec;13(12):e554-61.
Castelijns JA, van den Brekel MW. Imaging of lymphadenopathy in the neck. Eur Radiol 2002;12:727–38.
Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, Vander Poorten V, Dirix P, Verbeken E, Nuyts S, et al. . Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for nodal staging. Radiology 2009;251:134–46.
Yamazaki Y, Saitoh M, Notani K, Tei K, Totsuka Y, Takinami S et al. Assessment of cervical lymph node metastasis using FDG-PET in patients with head and neck cancer. Am Nucl Med 2008;22(3):177–84.
Jeong HS, Baek CH, Son YI, Ki Chung M, Kyung Lee D, Young Choi J et al. Use of integrated (18)F-FDG PET/CT to improve the accuracy of initial cervical nodal evaluation in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2007;29(3):203-10.
Kotani J, Kawabe J, Higashiyama S, Kawamura E, Oe A, Hayashi T et al. Evaluation of diagnostic abilities of Ga-SPECT for head and neck lesions. Ann Nucl Med 2008;22(4):297–300.
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 1988;168(2):497–505.
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM, Chenevert TL, Thoeny HC, Takahara T, et al. . Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 2009 ; 11: 102–25.
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, King AD. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the head and neck. Radiology. 2012 Apr;263(1):19-32.
Johnson JT. A surgeon looks at cervical lymph nodes. Radiology. 1990 Jun;175(3):607-10.
Rekha R, Reddy MVV, Reddy PP. Epidemiological Studies of Head and Neck Cancer in South Indian Population. Research In Cancer and Tumor 2013;2(2):38-44.
De Bondt RB, Hoeberigs MC, Nelemans PJ, Deserno WM, Peutz-Kootstra C, Kremer B et al. Diagnostic accuracy and additional value of diffusion-weighted imaging for discrimination of malignant cervical lymph nodes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neuroradiology. 2009;51(3):183-92.
van den Brekel MW, Stel HV, Castelijns JA, Nauta JJ, van der Waal I et al. Cervical lymph node metastasis: assessment of radiologic criteria. Radiology. 1990;177(2):379-84.
Takes RP, Righi P, Meeuwis CA, Manni JJ, Knegt P, Marres HA et al.. The value of ultrasound with ultra-sound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy compared to computed tomography in the detection of regional metastases in the clinically negative neck. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1998;40(5):1027–32.
Sumi M, Van Cauteren M, Nakamura T. MR microimaging of benign and malignant nodes in the neck. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(3):749-57.
Ding ZX, Liang BL, Shen J, Xie BK, Huang SQ, Zhang B. Magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis from lingual squamous cell carcinoma. 2005;24(2):199-203.
Sumi M, Sakihama N, Sumi T, Morikawa M, Uetani M, Kabasawa H et al. Discrimination of metastatic cervical lymph nodes with diffusion-weighted MR imaging in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:1627–1634.
Zhong J, Lu Z, Xu L, Dong L, Qiao H, Hua R et al. The Diagnostic Value of Cervical Lymph Node Metas-tasis in Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma by Using Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography Perfusion. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:260859.
Singh P, Parihar H, Goel V. Differentiating Benign and Malignant Metastatic Cervical Lymph Nodes by Diffusion Weighted MRI Sequence, International Journal of Anatomy, Radiology and Surgery, 2015;4(4):47-50.
ElSaid NAE, Nada OMMN, Semesim ARS, Habib YSEH, Semeisem AR et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of dif-fusion weighted MRI in diagnosing cervical lymphadenopathy correlated with pathology results. The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine 2014;45(4):1115-25.
Perrone A, Guerrisi P, Izzo L, D’Angeli I, Sassi S, Mele LL, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in cervical lymph nodes: differentiation between benign and malignant lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2011;77(2):281-6.
Wang J, Takashima S, Takayama F, Kawakami S, Saito A, Matsushita T. Head and neck lesions: characterization with diffusion weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology. 2001;220(3):621-30.
Abish YG, Roshdy HM, Enaite AM. Benign versus malignant cervical lns: differentiation by diffusion weighted MRI. AAMJ 2011;9(3):1-20.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


