A study on incidence and severity of acute renal failure and its association with parasite density in hospitalised patients with falciparum malaria
Abstract
Aims of the study: To find out the incidence of acute renal failure in falciparum malaria and to correlate between the degree of parasitism at presentation with acute renal failure and its outcome in falciparum malaria.
Methodology: Each patient with a history of fever, suggestive of severe malaria was subjected to peripheral blood smear examinations, up to 3 samples were examined or till positive and/or Pf antigen positive cases. The selected patients were then grouped according to the clinical features, laboratory parameters and were followed up for the outcome.
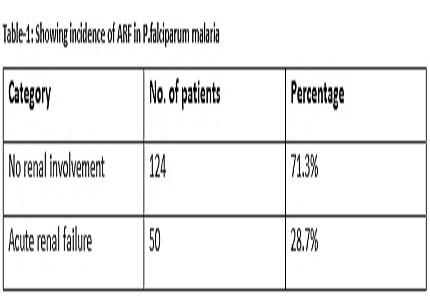
Results: Out of the 50 cases of acute renal failure due to falciparum malaria, 21 had Parasite density <5% (42%), 13 had 5-10%(26%) and 16 had >10%(32%). Out of 21 cases of mild ARF 12 patients had parasite density<5% and 9 had >5%. Out of 29 cases of severe ARF 9 patients had parasite density<5% and 20 had >5%. Dialysis was done in a total of 31 cases (62%). In the severe form of acute renal failure. hemodialysis was required in 29 cases (58%), in the milder form of renal failure; only 2 cases (4%) required hemodialysis. Rests of the cases were managed by conservative treatment.
Conclusion: Parasite Density has significant impact to predict the severity of renal failure, duration of hospital stays as well as the number of dialysis required. As the study was conducted with small number of cases, further study is necessary with large number of cases to arrive at a conclusion regarding the malady of acute renal failure in falciparum malaria.
Downloads
References
Hay SI, Shanks GD, Stern DI, Snow RW, Randolph SE, Rogers DJ. Climate variability and malaria epidemics in the highlands of East Africa.Trends Parasitol. 2005 Feb;21(2):52-3.
Hay SI, Guerra CA, Tatem AJ, Noor AM, Snow RW. The global distribution and population at risk of malaria: past, present, and future.Lancet Infect Dis. 2004 Jun;4(6):327-36.
Rosen S, Hano JE, Inman MM, Gilliland PF, Barry KG.The kidney in blackwater fever: light and electron microscopic observations.Am J Clin Pathology 1968. 49 (3): 358-70.
Sitprija V, Vongsthongsri M, Poshyachinda V, Arthachinta S. Renal failure in malaria: a pathophysiologic study.Nephron. 1977;18(5):277-87.
Ahsan T, Rab SM, Shekhani MS. Falciparum malaria or fulminant hepatic failure?J Pak Med Assoc. 1993 Oct;43(10):206-8.
Joshi YK, Tandon BN, Acharya SK, Babu S., Tandon M. Acute hepatic failure due to Plasmodium falciparum liver injury.Liver. 1986 Dec;6(6):357-60.
Zaki SA, Shenoy P, Shanbag P, Mauskar A, Patil A, Nagotkar L. Acute renal failure associated with malaria in children.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2013 Mar;24(2):303-8.
Thanachartwet V1, Desakorn V, Sahassananda D, Kyaw Win KK, SupapornT.Acute Renal Failure in Patients with Severe Falciparum Malaria: Using the WHO 2006 and RIFLE Criteria. Int J Nephrol. 2013;2013:841518. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/841518. Epub 2013 Jan 29.
Sitprija V, Kashemsant U, Sriratanaban A, et al.1970. Suki and Massry's therapy of renal diseases and related disorders.3:558.
Sitprija V, Vongsthongsri M, Poshyachinda V, Arthachinta S. Renal failure in malaria: a pathophysiologic study.Nephron. 1977;18(5):277-87.
Lumlertgul D, Keoplung M, Sitprija V, Moollaor P, Suwangool P. Furosemide and dopamine in malarial acute renal failure.Nephron. 1989;52(1):40-4.
Ston WJ, Hanchett JE, Knepshield JH. Acute renal insufficiency due to falciparum malaria. Review of 42 cases.Arch Intern Med. 1972 Apr;129(4):620-8.
Trang TT, Phu NH, Vinh H, Hien TT, Cuong BM, Chau TT, Mai NT, Waller DJ, White NJ. Acute renal failure in patients with severe falciparum malaria.Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Nov;15(5):874-80.
Ali H, Ahsan T, Mahmood T, Bakht SF, Farooq MU, Ahmed N. Parasite density and the spectrum of clinical illness in falciparum malaria.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2008 Jun;18(6):362-8. doi: https://doi.org/06.2008/JCPSP.362368.
Weber MW, Boker K, Horstmann RD, Ehrich JH. Renal failure is a common complication in non-immune Europeans with Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Trop Med Parasitol 1991; 42(2): 115-118.
Canfield CJ, Miller LH, Bartelloni PJ, Eichler P & Barry KG. Acute renal failure in Plasmodium falciparum malaria: treatment by peritoneal dialysis. Arch Intern Med. 1968;122(3):199-203.
Abdul Manan J, Ali H, Lal M. Acute renal failure associated with malaria.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2006 Oct-Dec;18(4):47-52.
Habte B. Acute renal failure due to falciparum malaria.Ren Fail. 1990;12(1):15-9.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


