Cross-Sectional study of differences in phenomenology of acute psychosis with or without cannabis
Abstract
Background: Therehas been plethora of research regarding cannabis use disorder but very few studiesreporteddemographicand phenomenological differences of acute psychosis with cannabis use to those of acute psychosis without cannabis use. This study attempted to evaluate the demographic and phenomenology differences between two groups of patients presenting with acute psychosis with cannabis use and acute psychosis without cannabis use.
Material & Method: Two group of patients recruited for study were ‘Cases with Cannabis’ and ‘control without Cannabis’ presenting with acute psychosis with preceding cannabis use and second one presenting with acute psychosis without preceding cannabis use in out-patient department of psychiatry, M. Yhospital, Indore Assessment done using rating scales.
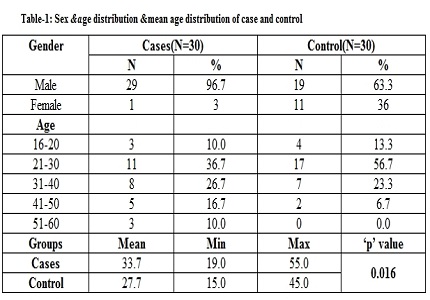
Results: Acute psychosis with cannabis wascharacterizedby primarily polymorphic clinical picture with predominance of positive and mood symptoms both in clear and disturbed sensorium.Acute psychosis without cannabis was characterized by mixed positive and negative symptoms in clear sensorium. In ‘Cases with cannabis’ group 96.7% were males and 3.3% were females, mean age was higher (33.7%) than control (27.7%) group.
Conclusion: Acute psychosis with cannabis is characterized by primarily polymorphic clinical picture with predominance of positive and mood symptoms both in clear and disturbed sensorium. Acute psychosis without cannabis is characterized by mixed positive and negative symptoms. General symptoms of psychosis were also more in acute psychosis without cannabis.
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. Cannabis: a health perspective and research agenda. (1997).
Marconi A, Di Forti M, Lewis CM, Murray RM, VassosE.Meta-analysis of the Association Between the Level of Cannabis Use and Risk ofPsychosis. Schizophr Bull. 2016 Sep;42(5):1262-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbw003. Epub 2016 Feb 15.
Mackie K.Distribution of cannabinoid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous system. HandbExp Pharmacol. 2005;(168):299-325.
De Petrocellis L, Cascio MG, Di Marzo V. The endocannabinoidsystem: a generalview and latestadditions.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Mar;141(5):765-74. Epub 2004 Jan 26.
Johns A. Psychiatric effects of cannabis. Br J Psychiatry. 2001 Feb;178:116-22.
Haobam M, Mohanty R, Senjam G, Heramani N. Cannabis and its associated psychopathology. Journal of Medical Society. 2017 Sep 1;31(3):143.
Cooper JE, World Health Organization. Pocket Guide to the ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: With Glossary and Diagnostic Criteria for Research: ICD-10/DCR-10. American Psychiatric Pub; 1994.
Varma LP. Cannabis psychosis. Indian Journal of Psychiatry. 1972 Jul 1;14(3):241.
Patel R, Dominguez MD, Fisher HL, Johnson S, Hodes M. EPA-1645–The impact of cannabis use on clinical presentation in first-episode psychosis: adolescent-versus adult-onset psychosis. European Psychiatry. 2014 Dec 31;29:1.
Caton CL, Drake RE, Hasin DS, Dominguez B, Shrout PE, Samet S, SchanzerB.Differences between early-phaseprimarypsychotic disorders with concurrentsubstance use and substance-induced psychoses. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005 Feb;62(2):137-45.
Basu D, Malhotra A, Bhagat A, Varma VK.Cannabispsychosis and acuteschizophrenia. a case-control study from India. Eur Addict Res. 1999 Jun;5(2):71-3.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


