Clinical profile of mortality predictors in Leptospirosis:a prospective study in a tertiary care center
Abstract
Aims and Objectives: To look for mortality predictors of Leptospirosis, with specific importance given to oli-guric renal failure and hypotension as possible predictors.
Materials and Methods: A Prospective Cohort study conducted over two years which enrolled patients with clinically and serologically confirmed Leptospirosis. Of these, 30 patients were included who had hypotension and 30 patients who had oliguric renal failure, as per statistical requirements. Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory data was collected at admission and the patients were followed up to look for outcome (discharge/death).
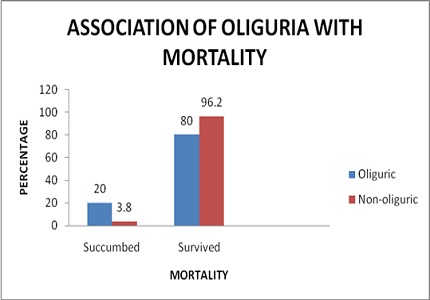
Results: A total of 83 patients were included in this study. Of these 8 patients died (Mortality of 9.6%). Data analysis with Chi Square Test showed that oliguric renal failure was significantly associated with mortality in Leptospirosis (p<0.05). Other factors were also found which were associated with mortality including elevated bilirubin and AST levels, anemia, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Alcohol Dependence Syndrome, and Chronic Liver Disease. However, hypotension was found to not be significantly associated with mortality.
Conclusion: In patients with Leptospirosis, significant mortality pre-dictors included oliguric renal failure, elevated bilirubin and AST levels, anemia, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Alcohol Dependence Syndrome, and Chronic Liver Disease.
Downloads
References
Haake DA, Levett PN. Leptospirosis in humans. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;387:65-97. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45059-8_5.
Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, et al Editors. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th edition. “In-fectious Diseases”, “Leptospirosis” p.1392.
Didier Musso and Bernard La Scola. Laboratory diagnosis of Leptospirosis. A challenge. Journal of Microbi-ology, Immunology and Infection, 2013-08-01, Volume 46, Issue 4, Pages 245-252. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2013.03.001.
Senior K. Leptospirosis and Weil’s syndrome: Cause for concern? Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2010 Dec; 10(12):823-4.
Walker BR, Colledge NR, Raiston SH, et al, Editors, Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine, 22nd Edition, “Infectious disease – Leptospirosis” p.336-338.
Rajapakse S, Rodrigo C, Haniffa R. Developing a clinically relevant classification to predict mortality in se-vere leptospirosis. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2010 Jul;3(3):213-9. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0974-2700.66519.
Goswami RP, Goswami RP, Basu A, Tripathi SK, Chakrabarti S, Chattopadhyay I. Predictors of mortality in leptospirosis: an observational study from two hospitals in Kolkata, eastern India. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2014 Dec;108(12):791-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/tru144. Epub 2014 Oct 30.
Pappachan MJ, Mathew S, Aravindan KP, Khader A, Bharghavan PV, Kareem MM, Tuteja U, Shukla J, Ba-tra HV. Risk factors for mortality in patients with leptospirosis during an epidemic in northern Kerala. Natl Med J India. 2004 Sep-Oct;17(5):240-2.
Panaphut T, Domrongkitchaiporn S, Thinkamrop B. Prognostic factors of death in leptospirosis: a prospective cohort study in KhonKaen, Thailand. Int J Infect Dis. 2002 Mar;6(1):52-9.
Prabhu M, Valsalan R, Ramachandran B., Prognostic markers and outcomes in severe leptospirosis in a tertiary hospital from south India. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2010-03-01, Volume 14, Pages e389-e389. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2010.02.485.
Spichler AS, Vilaça PJ, Athanazio DA, Albuquerque JO, Buzzar M, Castro B, Seguro A, Vinetz JM. Predic-tors of lethality in severeleptospirosis in urban Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008 Dec;79(6):911-4.
Taylor AJ, Paris DH, Newton PN, A Systematic Review of the Mortality from Untreated Leptospirosis PLoSNegl Trop Dis - June1, 2015; 9(6); Published: August14, 2015.doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003971.
Ko AI, Galvão Reis M, Ribeiro Dourado CM, Johnson WD Jr, Riley LW. Urban epidemic of severe leptos-pirosis in Brazil. Salvador Leptospirosis Study Group. Lancet. 1999 Sep 4;354(9181):820-5.
Dupont H, Dupont-Perdrizet D, Perie JL, Zehner-Hansen S, Jarrige B, DaijardinJB.Leptospirosis: prognostic factorsassociated with mortality. Clin Infect Dis.1997 Sep;25(3):720-4.
Unnikrishnan, Dilip;Pisharody, Ramdas; Vijayalakshmy, N, Prognostic ‘Factors in Leptospiroses: A study-from Kerala, India, InfectiousDiseases in ClinicalPractice:May 2005-Volume-13-Issue 3- pp 104-107.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


