EGFR scoring in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its association with clinicopathological variables
Abstract
Background: Head and Neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the seventh most common cancer in the world with poor overall survival rate which is unchanged during the last two decades.
Aim: Aim of our study is to measure the level of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) expression in HNSCC by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and to correlate EGFR with clinicopathological variables.
Settings and Design: Cross sectional study from 1st October 2012 to 31st of March 2014 was performed.
Materials and Methods: After taking detailed history and a thorough examination, biopsy/ specimen of HNSCC region were evaluated to confirm the diagnosis of HNSCC. Paraffin blocks of such tumors were processed for EGFR staining. Staining intensity was evaluated by using scale from 1 to 4.
Statistical Analysis: Chi-square test was used as appropriate for data analysis.
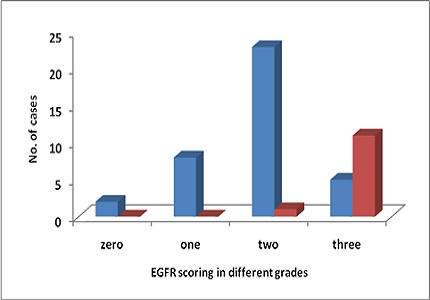
Results: In the present study 38/50 (78%) patients were diagnosed as well differentiated, 12/50(24%) were diagnosed as moderately differentiated. For EGFR staining, 24/50 (48%) scored as +2, 16/50(32%) as +3, 8/50(16%) as +1 and 2/50(4%) scored as 0. 23/38(60.5%) well differentiated SCC cases presented as +2, 5/38(13.2%) as +3, 8/38(21.1%) as +1 and 2/38(5.3%) as 0. 11/12(91.6%) moderately differentiated SCC cases were scored as +3, 1/12(8.3%) as +2. p value 0.001, which is highly significant. However, correlation of EGFR scoring with patients age, sex, addiction history, site of the tumor was insignificant.
Conclusion: EGFR was highly expressed in HNSCC. The result of our study showed that, high EGFR scoring was associated with high grade of the tumor. There was no significant relationship between EGFR scoring and clinicopathological variables.
Downloads
References
Boeckx C, Weyn C, Bempt IV, Deschoolmeester V, Wouters A, Specenier P,et al. Mutation analysis of genes in the EGFR pathway in Head and Neck cancer patients: implications for anti-EGFR treatment response. BMC Res Notes 2014; 7: 337. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-7-337.
Ahmad Kiadaliri A, Jarl J, Gavriilidis G, Gerdtham UG. Alcohol drinking cessation and the risk of laryngeal and pharyngeal cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58158. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058158. Epub 2013 Mar 1.
Joshi P, Dutta S, Chaturvedi P, Nair S. Head and neck cancers in developing countries. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2014 Apr 28;5(2):e0009. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.5041%2FRMMJ.10143. eCollection 2014 Apr.
Yavrouian EJ, Sinha UK. Recent advances in biomarkers and potential targeted therapies in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. ISRN Surg. 2012;2012:715743. doi: https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/715743. Epub 2012 Feb 15.
Chen IH, Chang JT, Liao CT, Wang HM, Hsieh LL, Cheng AJ. Prognostic significance of EGFR and Her-2 in oral cavity cancer in betel quid prevalent area. Br J Cancer 2003; 89: 681–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601171.
Takiar R, Nadayil D, Nandakumar A. Projections of number of cancer cases in India (2010-2020) by cancer groups. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2010;11(4):1045-9.
Stewart BW and Kleihues P, editors. World Cancer Report. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2003. 232-6.
Sarkis SA, Abdullah BH, Majeed BA, Talabani NG. Immunohistochemical expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in oral squamous cell carcinoma in relation to proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Head & Neck Oncol 2010; 2(13): 1-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-3284-2-13.
Ono M, Kuwano M. Molecular mechanisms of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) activation and response to gefitinib and other EGFR- targeting drugs. Clin cancer Res 2006; 12(24): 7242-51. doi: https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0646.
Sharafinski ME, Ferris RL, Ferrone S, Grandis JR. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck. 2010 Oct;32(10):1412-21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.21365.
Egloff AM, Grandis JR. Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and SRC pathways in head and neck cancer. Semin Oncol. 2008 Jun;35(3):286-97. doi: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2008.03.008.
Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press 2000; 1-370.
Xia W, Lau YK, Zhang HZ, Xiao FY, Johnston DA, Liu AR et al. Combination of EGFR, HER-2/neu, and HER-3 is a stronger predictor for the outcome of oral squamous cell carcinoma than any individual family members. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 4164-74.
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Smokeless Tobacco and Some Tobacco-Specific Nitrosamines. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Human. Lyon, France: IARC Press 2007; 1-250.
Bernardes VF, Gleber-Netto FO, Sousa SF, Silva TA, Aguiar MC. Clinical significance of EGFR, Her-2 and EGF in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a case control study. Journal of experimental and Clinical Cancer Research 2010; 29(40): 1-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-29-40.
Nandakumar A, Thimmasetty KT, Sreeramareddy NM, Venugopal TC, Rajanna, Vinutha AT, Srinivas, Bhargava MK. A population-based case-control investigation on cancers of the oral cavity in Bangalore, India. Br J Cancer. 1990 Nov;62(5):847-51.
Zanor A, Brennan P, Gajalakshmi V, Mathew A, Shanta V, Varghese C Et al. Independent and combined effects of tobacco and alcohol drinking of the risk of oral, pharyngeal and esophageal cancers in Indian men. Int J Cancer 2003; 105: 681-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.11114.
Fong Y, Chou SJ, Hung KF, Wu HT, Kao SY. An investigation of the differential expression of Her2/neu gene expression in normal mucosa, epithelial dysplasia, and oral squamous cell carcinoma in Taiwan. J chin Med Assoc 2008; 71(3): 123-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1726-4901(08)70003-0.
Thomas GR, Nadiminti H, Regalado J. Molecular predictors of clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Exp Pathol. 2005 Dec;86(6):347-63.
Schuler PJ, Boeckers P, Engers R, Boelke E, Bas M, Greve J, Dumitru CA, Lehnerdt GF, Ferris RL, Andrade Filho PA, Brandau S, Lang S, Whiteside TL, Hoffmann TK. EGFR-specific T cell frequencies correlate with EGFR expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2011 Oct 4;9:168. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-9-168.
Pectasides E, Rampias T, Kountourakis P Et al. Comparative Prognostic Value of Epidermal Growth Factor Quantitative Protein Expression Compared with FISH for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 2947-54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2040.
Sheikh Ali MA, Gunduz M, Nagatsuka H, Gunduz E, Cengiz B, Fukushima K, Beder LB, Demircan K, Fujii M, Yamanaka N, Shimizu K, Grenman R, Nagai N. Expression and mutation analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2008 Aug;99(8):1589-94. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00861.x.
Teman S, Kawaguchi H, El-Naggar AK, Jelinek J, Tang H, Liu DD et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor copy number alterations correlate with poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cancer. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 2164-70. doi: https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.06.6605.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


