MRA evaluation of cerebrovascular stenosis and its association with acute stroke in Indian patients
Abstract
Introduction: The detection of intracranial atherosclerotic disease has been elusive, possibly because of the dearth of non-invasive methods for diagnosing the condition.
Material and Methods: In this study, we used time-of-flight MRA (TOF-MRA) to identify the presence, nature, and number of stenosis in the intra and extracranial arteries and anterior and posterior circulation systems in 60 Indian patients.
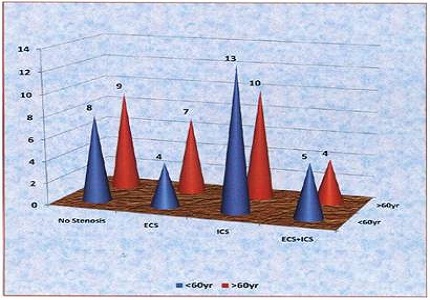
Results: It was found that there is a strong association between the presence of stenosis and hyperlipidemia and hypertension. Intracranial stenosis was more prevalent in the > 60 years age group, and it maximally affected the M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery. Comparatively, significant stenosis and total occlusion were predominant in the intracranial system; single stenosis was associated with the intracranial arteries, whereas multiple stenoses were observed in the extracranial system.
Conclusion: Hemiparesis was the most common symptom of the patients. Thus, TOF-MRA can be used successfully to evaluate the occurrence, prognosis, and treatment options for cerebrovascular stenotic diseases.
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. Cerebrovascular Disorders (Offset Publications). Geneva: World Health Organization; 1978.
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM. Stroke. Lancet. 2008 May 10;371(9624):1612-23. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60694-7.
Shuaib A, Hachinski VC. Mechanisms and management of stroke in the elderly. CMAJ. 1991 Sep 1;145(5):433-43.
Stam J. Thrombosis of the cerebral veins and sinuses. N Engl J Med. 2005 Apr 28;352(17):1791-8.
Chalela JA, Kidwell CS, Nentwich LM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in emergency assessment of patients with suspected acute stroke: a prospective comparison. Lancet. 2007;369(9558):293–298.
Liu HM, Tu YK, Yip PK, Su CT. Evaluation of intracranial and extracranial carotid steno-occlusive diseases in Taiwan Chinese patients with MR angiography: preliminary experience. Stroke. 1996 Apr;27(4):650-3.
Gillard JH, Oliverio PJ, Barker PB, Oppenheimer SM, Bryan RN. MR angiography in acute cerebral ischemia of the anterior circulation: a preliminary report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997 Feb;18(2):343-50.
Kumar G, Kalita J, Kumar B, Bansal V, Jain SK, Misra U. Magnetic resonance angiography findings in patients with ischemic stroke from North India. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010;19(2):146–152.
Shrivastava A, Srivastava T, Saxena R. CT angiographic evaluation of pattern and distribution of stenosis and its association with risk factors among Indian ischemic stroke patients. Pol J Radiol. 2016;81:357–362.
Suh DC, Lee SH, Kim KR, et al. Pattern of atherosclerotic carotid stenosis in Korean patients with stroke: different involvement of intracranial versus extracranial vessels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24(2):239–244.
Newman JD, Rockman CB, Kosiborod M, Guo Y, Zhong H, Weintraub HS, Schwartzbard A, Adelman MA, Berger JS. Diabetes mellitus is a coronary heart disease risk equivalent for peripheral vascular disease. Am Heart J. 2017 Feb;184:114-120. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 18.
Zarei H, Ebrahimi H, Shafiee K, Yazdani M, Aghili K. Intracranial stenosis in patients with acute cerebrovascular accidents. ARYA Atheroscler. 2008;3(4):206–210.
Heiserman JE, Masaryk TJ, Aygun N. MR Angiography: Techniques and Clinical Applications. In: Atlas SW, editors. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain and Spine – Volume Two. 4th Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a Wolters Kluwer Publication. 2009. p. 856.
Kim YD, Choi HY, Cho HJ, Cha MJ, Nam CM, Han SW, Nam HS, Heo JH. Increasing frequency and burden of cerebral artery atherosclerosis in Korean stroke patients. Yonsei Med J. 2010 May;51(3):318-25. doi: https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.318.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


