Effectiveness of social media as a medical teaching tool
Abstract
Introduction: Social media has become a pervasive force in the lives of 21st century learners. Mobile learning has been increasingly used in the educational context. However, its adoption in medical education has been slow, and its effectiveness in medical education is a new area of inquiry. This study was conceived to assess the effectiveness of social media as a medical teaching tool.
Materials and Methods: The study was conducted as a cross sectional, observational study with 150 III year MBBS students as study participants who were already enrolled in social network groups for educational purpose. A questionnaire catering to the objectives of the study was distributed and the response was evaluated.
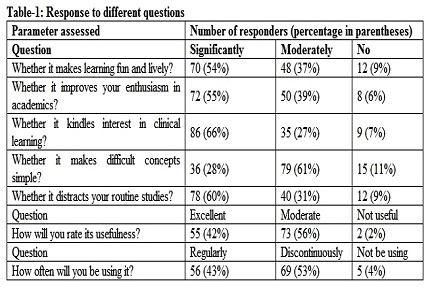
Results: 54% of the students answered that social media as a teaching tool, significantly made learning fun and lively. 55% of students responded that it significantly improved the academic enthusiasm. 66% of students observed that it was significantly effective in kindling interest in clinical learning. 61% felt that it simplified the difficult concepts moderately and 28% felt that it significantly simplified difficult concepts. 60% of students felt that it did not distract them from their routine studies. 42% and 54% of students rated the usefulness of the social media as an educational tool as excellent and as moderate respectively.
Conclusion: Social media is effective as a medical teaching tool improving enthusiasm in academics, kindling interest in clinical learning, making learning fun and lively, without much distraction to students and can be integrated in the medical educational context.
Downloads
References
Gitanjali Kalia. A Research Paper on Social media: An Innovative Educational Tool. Issues and Ideas in Education 2013 March; Vol.1 pp 43-50.
Yunus M, Salehi H, Nordin N. ESL pre-service teachers’ perceptions on the use of paragraph punch in teaching writing. ELT 2012 Aug 22;5(10):1453-1467. doi: https://doi.org/10.5539/elt.v5n10p138.
Mazman S, Usluel Y. Modeling educational usage of Facebook. Computers & Education 2010 Sep;55(2):444-453. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.02.008.
Quincy Conley, Kent E. Sabo. The social media instructional design model: a new tool for designing instruction using social media. Int. J. of Social Media and Interactive Learning Environments 2015; Vol.3, No.4 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1504/IJSMILE.2015.074008.
Harun Bin Sinen. A literature review on mobile learning. Int. J. of Social Media and Interactive Learning Environments 2015; Vol.3, No.3 doi: https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSMILE.2015.072266.
Couros A. Open, connected, social – implications for educational design. Campus-Wide Info Systems 2009 Jun 19;26(3):232-239.
Huang HM. Toward constructivism for adult learners in online learning environments. Br J Educ Technol. 2002 Jan; Vol.33, No.1.
Gila Kurtz. Facebook group as a space for interactive and collaborative learning. Int. J. of Social Media and Interactive Learning Environments 2013; Vol.1, No.4.
Ronald J.J. Voorn, Piet A.M. Kommers. Social media and higher education: introversion and collaborative learning from the student's perspective. Int. J. of Social Media and Interactive Learning Environments 2013; Vol.1, No.1 doi: https://doi.org/10.1504/ijsmile.2013.051650.
Kevin P. Brady, Lori B. Holcomb, Bethany V. Smith. The Use of Alternative Social Networking Sites in Higher Educational Settings: A Case Study of the E-Learning Benefits of Ning in Education. Journal of Interactive Online Learning. Summer 2010; Vol. 9, No.2.
Davis WM, Ho K, Last J. Advancing social media in medical education. CMAJ. 2015 May 19;187(8):549-50. doi: https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.141417. Epub 2015 Apr 7.
O'Sullivan E, Cutts E, Kavikondala S, Salcedo A, D'Souza K, Hernandez-Torre M, Anderson C, Tiwari A, Ho K, Last J. Social Media in Health Science Education: An International Survey. JMIR Med Education. 2017;3(1):e1 doi: https://doi.org/10.2196/mededu.6304. PMID: 28052842 PMCID: 5244031.
Cheston CC, Flickinger TE, Chisolm MS. Social media use in medical education: a systematic review. Acad Med. 2013 Jun;88(6):893-901. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0b013e31828ffc23.
El Bialy S, Jalali A. Go Where the Students Are: A Comparison of the Use of Social Networking Sites Between Medical Students and Medical Educators. JMIR Med Educ. 2015 Sep 8;1(2):e7.
Alsuraihi AK, Almaqati AS, Abughanim SA, Jastaniah NA. Use of social media in education among medical students in Saudi Arabia. Korean J Med Educ. 2016 Dec;28(4):343-354. Epub 2016 Dec 1.
Jalali A, Wood TJ. Teaching medical students social media: must or bust. Med Educ. 2014 Nov;48(11):1128-9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fmedu.12585.
George DR, Dellasega C. Social media in medical education: two innovative pilot studies. Med Educ. 2011 Nov;45(11):1158-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2011.04124.x. Epub 2011 Sep 21.
Avcı K, Çelikden S, Eren S, Aydenizöz D. Assessment of medical students' attitudes on social media use in medicine: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Educ. 2015 Feb 15;15:18. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-015-0300-y.
Paul S, Pusic M, Gillespie C. Medical student lecture attendance versus iTunes U. Med Educ. 2015;49:530–531.
Kind T, Genrich G, Sodhi A, Chretien KC. Social media policies at US medical schools. Med Educ Online. 2010 Sep 15;15. doi: https://doi.org/10.3402/meo.v15i0.5324.
Ozkan, B. & McKenzie, B. (2008). Social Networking Tools for Teacher Education. In K. McFerrin, R. Weber, R. Carlsen & D. Willis (Eds.), Proceedings of Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference 2008.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


