Hypoplasia of lung a rare entity mimicking as a case of tuberculosis
Abstract
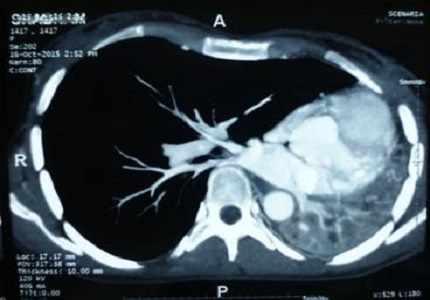
Pulmonary hypoplasia, a congenital malformation, is characterized by incomplete development of the lungs, leading to an abnormally less number or dimensions of bronchopulmonary segments / alveoli resulting in small fibrotic and non-functional lung. It is usually diagnosed in the neonatal period or in early childhood. Hypoplasia may be primary (idiopathic) or secondary. Primary pulmonary hypoplasia, not related to other congenital anomalies is extremely seldom diagnosed in adults. We report the case of a 32-year-old married female with two kids presented to us with chief complaints of cough and fever for past nine months. Chest radiograph showed opacification of the left hemi-thorax with decrease in its size and marked ipsilateral mediastinal displacement with an increase in volume of right lung. After investigations she was diagnosed as a case of left lung primary pulmonary hypoplasia. High level of excellent clinical judgement needed to spot and diagnose this congenital aberration, often wrongly diagnosed in adults. Hence, once confronted with an opaque hemi-thorax in a young person with ipsilateral shift of the mediastinum, differential diagnosis of “lung hypoplasia” ought to be kept in mind.
Downloads
References
Sundararajaperumal A, Vinodkumar V, Sundar V, Ranganathan D. Primary Pulmonary Hypoplasia in an adult. Pulmon 2008; 10(1):12–15.
Mardini MK, Nyhan WL. Agenesis of the lung. Report of four patients with unusual anomalies. Chest. 1985 Apr;87(4):522-7.
Devi YG, Rani NU, Rao GS, Narayana M, Kumar BD. A Rare Clinical Presentation of Primary Pulmonary Hypoplasia with Tuberculous Pleural Effusion. IJSS. 2014 Aug;1(3):16.
Currarino G, Williams B. Causes of congenital unilateral pulmonary hypoplasia: a study of 33 cases. Pediatr Radiol. 1985;15(1):15-24.
Schneider P, Schawatbe E. Die Morphologie der Missbildungen Des Menschen Under Thiere. 3 Part.2. Jena: Gustav Fischar.; 1912. pp. 817–22. [in German]
Cooney TP, Thurlbeck WM. Pulmonary hypoplasia in Down's syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine. 1982 Nov 4;307(19):1170-3.
Thurlbeck WM. Prematurity and the developing lung. Clinics in perinatology. 1992 Sep;19(3):497.
Lauria MR, Gonik B, Romero R. Pulmonary hypoplasia: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and antenatal prediction. Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1995 Sep 1;86(3):466-75.
Greenough A. Pulmonary Hypoplasia. In: Chervenak FA, Isaacson GC, Campbell S. Ultrasound in obstetrics and gynaecology. Boston: Little, Brown and company, corp, 1993: 903-8.
Cooney TP, Thurlbeck WM. and hydranencephaly.Cooney TP, Thurlbeck WM.Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):596-601.
Pathania M, Lali BS, Rathaur VK. Unilateral pulmonary hypoplasia: a rare clinical presentation. BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Mar 20;2013. pii: bcr2012008098. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2012-008098.
Morgan JR, Forker AD. Syndrome of hypoplasia of the right lung and dextroposition of the heart:" scimitar sign" with normal pulmonary venous drainage. Circulation. 1971 Jan 1;43(1):27-30.
Berrocal T, Madrid C, Novo S, Gutiérrez J, Arjonilla A, Gómez-León N. Congenital Anomalies of the Tracheobronchial Tree, Lung, and Mediastinum: Embryology, Radiology, and Pathology 1. Radiographics. 2004 Jan;24(1):e17.
Georgescu A, Nuta C, Bondari S. 3D Imaging in Unilateral Primary Pulmonary Hypoplasia in an Adult: A Case Report. Case Rep Radiol. 2011;2011:659586. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/659586. Epub 2011 Oct 19.
Singh U, Jhim D, Kumar S, Mittal V, Singh N, Gour H, Ramaraj M. Unilateral agenesis of the lung: a rare entity. Am J Case Rep. 2015 Feb 8;16:69.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


