Three port versus four port laparoscopic cholecystectomy- a prospective study
Abstract
Introduction: Cholelithiasis is the most common and important cause of biliary tract disease. In today’s world, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the gold standard treatment for gallstones. Decrease in the size or number of ports provide better results in laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Objective: We aim the study to find out feasibility of three port lap cholecystectomy over four port lap cholecystectomy regarding post-op pain, duration of surgery, conversion rate, hospital stay and complications.
Materials & Methods: Patients who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were included. 76 patients enrolled for the study and divided into two groups as 3 port and 4 port. Surgical preformed assessment proforma used to collect the data.
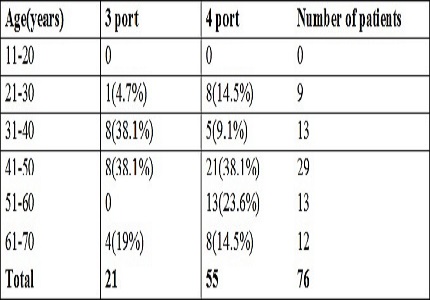
Results: The mean age of the studied patients was 46.38 years with female preponderance. The Mean operative time for three ports was 66.90 minutes and for four ports it was 75.45minutes. Mean duration of post-operative stay for three port was 4.66 and for the conventional group it was 5.30.
Conclusion: Patients who underwent the three port technique had a lesser hospital stay compared to patients who underwent the conventional 4 port technique. Patients had less postoperative pain, lesser requirement of analgesics in three port group. 2 patients from the 4 port group had fever 48 hours after surgery.
Downloads
References
Barbara L, Sama C, Labate AM, Taroni F, Rusticali AG, Festi D, Sapio C, Roda E, Banterle C, Puci A, Formentini F. A population study on the prevalence of gallstone disease: the Sirmione Study. Hepatology. 1987 Sep 1;7(5):913-7.Cuschieri A. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J R CollSurgEdinb 1999; 44:187-92.
Ji W, Li LT, Li JS. Role of laparoscopic subtotal cholecystectomy in the treatment of complicated cholecystitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2006 Nov 15;5(4):584-9.
Navez B, Mutter D, Russier Y, et al. Safety of laparoscopic approach for acute cholecystitis: retrospective study of 609 cases. World J Surg. 2001; 25:1352–6.
Schafer M, Krahenbuhl L, Buchler MW. Predictive factors for the type of surgery in acute cholecystitis. Am J Surg. 2001; 182: 291 –7.
Kauvar DS, Braswell A, Brown BD, Harnisch M. Influence of resident and attending surgeon seniority on operative performance in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Surg Res. 2006; 132:159-63.
Rai R, Sinha A, Rai S: Randomised clinical trial of open versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the treatment of acute cholecystitis. Br J Surg. 2005, 92:44-49. Br J Surg. 2005; 92:494-9.
Nuzzo G, Giuliante F, Persiani R: The risk of biliary ductal injury during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Chir (Paris). 2004,141:343-53.
Roberto Saintambrogio et al. Technical difficulties and complications during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Predictive use of ultrasonography. World J.Surg. 20:978- 982,1996.
Jagdish Nachnani, Avinash Supe. Preoperative prediction of difficult laparoscopic cholecystectomy using clinical and ultrasonographic parameters. Indian journal of gastroenterology, 2005: 24:16-18.
Clavien PA, Sanabria JR, Strasberg SM. Proposed classification of complications of surgery with examples of utility in cholecystectomy. Surgery. 1992 May;111(5):518-26.
Barbara L, Sama C, Morselli Labate AM, Taroni F, Rusticali AG, Festi D, Sapio C, Roda E, Banterle C, Puci A, et al. A population study on the prevalence of gallstone disease: the Sirmione Study. Hepatology. 1987 Sep-Oct;7(5):913-7.
Gracie WA,Ranshoff DF The natural History of silent gall stones N. England J. Med. ; 307 1982: 798-800.
Leon Morgenstern AD, Wong L, Berci G: Twelve hundred open cholecystectomies before the laparoscopic era. A standard for comparison. Arch Surg 1992; 127:400-403.
S L Malhotra Epidemiological study of cholelithiasis among railroad workers in India with special reference to causation. Gut. 1968 Jun; 9(3): 290–295.
Gaharwar A. Factors favouring cholelithiasis in north Indian population. IOSR Journal Of Pharmacy. 2013 Jun; 3(5):01-3.
Bansal A, Akhtar M, Bansal AK. A clinical study: prevalence and management of cholelithiasis. IntSurg J. 2014; 1(3): 134-139.
Hussain A1, Mahmood HK, Duluk K.Laparoscopic cholecystectomy can be safely performed in a resource-limited setting: the first 49 laparoscopic cholecystectomies in Yemen.JSLS. 2008 Jan-Mar;12(1):71-6.
C Palanivelu, Kalpesh Jani, and Gobi S. Mahesh Kumar. Single Center Experience of Laparoscopic CholecystectomyJournal of Laparoendoscopic& Advanced Surgical Techniques. October 2007, 17(5): 608-614.
Kimura K et al. Prospective study of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in two hundred and fifty patients.Endoscopy 1992;24(9)740-4.
Ganey JB, Johnson PA Jr, Prillaman PE, McSwain GR. Cholecystectomy: clinical experience with a large series. Am J Surg. 1986 Mar;151(3):352-7.
Jeffrey D browning, jaya prakash serenerasimhaiah. Gallstone disease. sleisenger and fordtran‘s gastro intestinal and liver disease: 8th edition: Saunders Elsevier publication: vol1 chapter 62: 1387-1417.
Sun S, Yang K, Gao M, He X, Tian J, Ma B. Three-port versus four-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. World J Surg 2009; 33:1904-8.
Slim K, Pezet D, Stencl J Jr, Lechner C, Le Roux S, Lointier P, et al. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: An original three-trocar technique. World J Surg 1995; 19:394-7.
Trichak S. Three-port vs standard four-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc. 2003 Sep;17(9):1434-6. Epub 2003 Jun 13.
Dion YM, Morin J. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a report of 60 cases. Canadian journal of surgery. Journal canadien de chirurgie. 1990 Dec; 33(6):483-6.
Kumar M, Agrawal CS, Gupta RK. Three-port versus standard four-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled clinical trial in a community-based teaching hospital in eastern Nepal. JSLS. 2007 Jul-Sep;11(3):358-62.
Harsha H S, Gunjiganvi M, Singh C, Moirangthem G S. A study of three-port versus four-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Med Soc 2013; 27:208-11.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


