Clinical study of benign lesions of larynx
Abstract
Aim of Study: To analyze over a period of 2 years, the demographics such as age, sex, distribution, occupation, the site of involvement, symptomatology and prognosis of the most frequent benign lesions of larynx.
Materials and Methods: 50 patients presenting with hoarseness of voice and diagnosed with benign lesion of larynx in ENT OPD of Dr. B.R.Ambedkar Medical College and Hospital were included in the study after taking their consent and the study was carried out for a period of 2 years between October 2013 to September 2015.
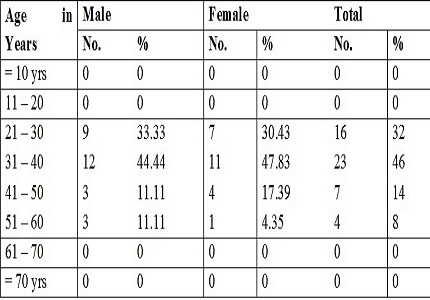
Results: In this study, it was noted that males were predominantly involved, maximum incidence between 31-40 years. Business men among males and housewives among females were commonly involved. Bilateral vocal cord nodule was the most common benign lesion of larynx, others included vocal cord polyp (both unilateral and bilateral) and Reinke’s edema. Most important predisposing factor was being vocal abuse in all the cases. Treatment given included speech therapy, medical management and MLS according to the diagnosis and patients were followed up for six months. 41.18% of patients with bilateral vocal cord nodule, 50% of patients with bilateral vocal cord polyp, 50% of patients with right vocal cord nodule, 75% of patients with left vocal cord polyp, 42.86% of patients with right vocal cord polyp and 100% of patient’s with Reinke’s edema were normal at follow up.
Conclusion: It was observed that vocal abuse was the most common predisposing factor for benign lesions of larynx and a multi modality treatment is necessary including medical, surgical and speech therapy to prevent recurrence.
Downloads
References
Singhal, P., Bhandari, A., Chouhan, M., Sharma, M. P., & Sharma, S. Benign tumors of the larynx: a clinical study of 50 cases. Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, 2009;61(1), 26-30.
Saudi, S. Benign lesions of the Vocal Cords in different ages: prospective Study of 60 Cases. Journal of Medical Science and Technology,2013; 2(3), 130-134.
Ahmed, S. U., Kabir, M., Alam, A. K., Hasan, D. M., Ahmed, K. U., & Khan, H. S. Benign vocal cord lesions-a study of 25 cases. Bangladesh Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006.
Bastian, R. W. Benign mucosal and saccular disorders: benign laryngeal tumors. Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 2nd ed. St Louis, Mo. Mosby-Year Book Inc, 1993; 1897-1924.
Johns MM. Update on the etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of vocal fold nodules, polyps, and cysts. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003 Dec;11(6):456-61.
Zeitels SM, Hillman RE, Bunting GW, Vaughn T. Reinke's edema: phonatory mechanisms and management strategies. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1997 Jul;106(7 Pt 1):533-43.
Bostijan Luzar, Nina Gale, Ulrika Klopcic Janez Fishinger. Laerngeal granuloma; Characteristic of covering epithelium. The journal of laryngology and otology 2000 April; Vol.114: 264-267.
Charles W. Cummings. John M. Febrickson, Lee A. Harker, Charles J. Krause. David E. Schuller. Otolaryngology. Head and Neck surgery. 2nd edition Mosby- Year Book.1993; 2020-2051.
Sharad Maheshwari. Management of hoarseness. Asian journal of ear, nose and throat, 2003- March.April.Vol.1:No.1: 1-9.
Jamina K. Casper, Thomas Murry. Voice therapy method in dysphonia. Otolarygologic clinics of North America-2000 Oct; Vol.33;No.5:983-1002.
Cohn JR, Spiegel JR, Sataloff RT. Vocal disorders and the professional voice user: the allergist's role. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1995 May;74(5):363-73; quiz 373-6.
John Jacob Ballenger, James B. Snow, Jr. Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. 15th edition. Williams and Wilkins. 1996; 438-465.
Phaniender Kumar. V, Srinivas Murthy MS, Ravikanth, Ratna Kumar. Phonomicro surgery for Benign vocal fold lesions: Our experience. Indian journal of otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery.2003. July-Sept.Vol.55; No.3: 184-186.
Hegde MC, Kamath MP, Bhojwani K, Peter R, Babu PR. Benign lesions of larynx-A clinical study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005 Jan;57(1):35-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907624.
Doloi, P. K., Khanna, S. A Study of Management of Benign Lesions of the Larynx. International Journal of Phonosurgery and Laryngology, 2011; 1(2), 61-64.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


