A study on efficacy of limbal relaxing incisions in correcting corneal astigmatism along with clear corneal phacoemulsification in a tertiary eye care centre in South India
Abstract
Aim: The main aim of this study was to study the effectiveness of limbal relaxing incisions in correcting corneal astigmatism when combined with clear corneal phacoemulsification.
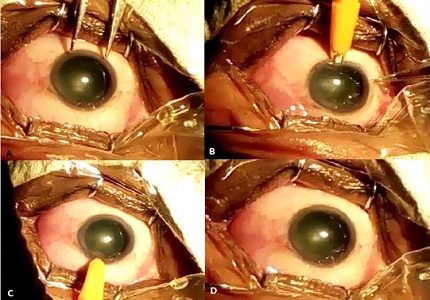
Materials and Methods: 50 eyes of 37 patients satisfying the inclusion and exclusion criteria were included in the study. After adequate pre operative workup, all patients underwent limbal relaxing incisions coupled with clear corneal phacoemulsification. The incisions were calculated based on Gills nomogram. Postoperative visual acuity and corneal topography were performed to assess the correction of corneal astigmatism.
Results: The mean age of our study population was 57.08± 10.07 years. 50 eyes of 21 males and 16 females were included in our study. The mean preoperative Uncorrected Visual Acuity was 1.0 with a standard deviation of 0.5 (in logMAR) and the best spectacle corrected visual acuity was 0.8 with a standard deviation of 0.4. The postoperative uncorrected visual acuity at 4 weeks 0.0±0.15 with a best corrected visual acuity was 0.09±0.1. At 12 weeks, uncorrected visual acuity was 0.0 with a standard deviation 0.07. There was 71.8% decrease in central corneal astigmatism after limbal relaxing incisions.
Conclusion: Therefore we conclude that limbal relaxing incisions can be used effectively in conjunction with cataract surgery to reduce the astigmatism <3 D at the corneal level and aids us in providing spectacle free optimal distance vision in patients.
Downloads
References
Carvalho M, Suzuki S, Freitas L, Branco B, Schor P, Lima A. Limbal Relaxing Incisions to Correct Corneal Astigmatism During Phacoemulsification. J Refract Surg.2007; 23: 499-504. doi: https://doi.org/10.3928/1081-597X-20070501-14.
Müller-Jensen K, Fischer P, Siepe U. Limbal relaxing incisions to correct astigmatism in clear corneal cataract surgery. J Refract Surg. 1999 Sep-Oct;15(5):586-9.
Bayramlar H, Dağlioğlu MC, Borazan M. Limbal relaxing incisions for primary mixed astigmatism and mixed astigmatism after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003 Apr;29(4):723-8.
Chylack LT Jr, Leske MC, McCarthy D, Khu P, Kashiwagi T, Sperduto R. Lens opacities classification system II (LOCS II) Arch Ophthalmol. 1989 Jul;107(7):991-7.
Kaufmann C, Peter J, Ooi K, Phipps S, Cooper P, Goggin M; Queen Elizabeth Astigmatism Study Group. Limbal relaxing incisions versus on-axis incisions to reduce corneal astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005 Dec;31(12):2261-5.
Ferrer-Blasco T, Montés-Micó R, Peixoto-de-Matos SC, González-Méijome JM, Cerviño A. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009 Jan;35(1):70-5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrs.2008.09.027.
Eliwa TF, Abdellatif MK, Hamza II. Effect of Limbal Relaxing Incisions on Corneal Aberrations. J Refract Surg. 2016 Mar;32(3):156-62. doi: https://doi.org/10.3928/1081597X-20160121-02.
Gibbons A. Use of a Toric Intraocular Lens and a Limbal-Relaxing Incision for the Management of Astigmatism in Combined Glaucoma and Cataract Surgery. Case Reports in Ophthalmology. 2016 Feb 23;7(1):96-102. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000444213.
Hashemi H, Khabazkhoob M, Soroush S, Shariati R, Miraftab M, Yekta A. The location of incision in cataract surgery and its impact on induced astigmatism. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;27(1):58-64. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/ICU.0000000000000223.
Mohammad-Rabei H, Mohammad-Rabei E, Espandar G, Javadi MA, Jafarinasab MR, Hashemian SJ, Feizi S. Three methods for correction of astigmatism during phacoemulsification. Journal of Ophthalmic & Vision Research. 2016 Apr;11(2):162. doi: http://www.jovr.org/text.asp?2016/11/2/162/183924.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


