Prenatal sonographic evaluation of Arnold Chiari II Malformation
Abstract
Arnold Chiari malformations are a broad group of malformations with distinctive imaging findings. They are named after an Austrian pathologist Hans Chiari who first identified types I-III in 1891. It is a spectrum of congenital abnormalities of CNS, characterized by downward displacement of the parts of the cerebellum, fourth ventricle, pons and medulla oblongata into the spinal canal. Type II is the most common subtype and is invariably associated with open neural tube defects like myelomeningocele. They constitute an important cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality and hence the need for prenatal evaluation with ultrasound to detect the anomalies. In this article we describe the features of Arnold chiari malformation, illustrate type II cases with sonological parameters for assessment, discuss the findings for diagnosis and conclude with prognosis and management.
Downloads
References
Woodward P, Kennedy A, Sohaey R, Byrne JLB, Oh KY, Puchalski MD. Diagnostic imaging. 1sted. Canada, Amirsys Elsevier Saunders. 2005; chapter 2: 21.
Tubbs RS, Cohen-Gadol AA. Hans Chiari (1851-1916). J Neurol. 2010 Jul;257(7):1218-20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5529-0. Epub 2010 Mar 26.
Sarmah, Prakritish Bora. Arnold Chiarri Malformation Type II. Ped Rad. (serial online)Vol 9, no 10 http://www.kinderradiologie-online.de/radiology/20091018134917. shtml#.VGWfUzSUcR1.
Aboulezz AO, Sartor K, Geyer CA, Gado MH. Position of cerebellar tonsils in the normal population and in patients with Chiari malformation: a quantitative approach with MR imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985 Nov-Dec;9(6):1033-6.
Nyberg DA, Souter VL. Sonographic markers of fetal trisomies: second trimester. J Ultrasound Med. 2001 Jun;20(6):655-74.
Iruretagoyena JI, Trampe B, Shah D. Prenatal diagnosis of Chiari malformation with syringomyelia in the second trimester. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Feb;23(2):184-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/14767050903061769.
Rosenberg HK, Sherman NH, Gubernick JA. Pediatric head, In: McGahan JP, Goldberg BB, ed. Diagnostic ultrasound: A logical approach. 1st ed. Philadelphia, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1998; 1135-1176.
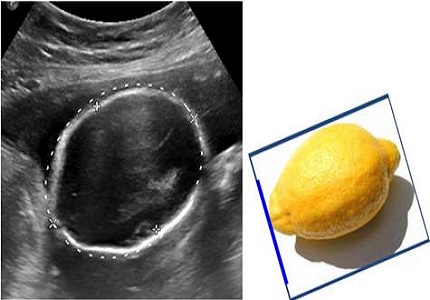
Ball RH, Filly RA, Goldstein RB, Callen PW. The lemon sign: not a specific indicator of meningomyelocele. J Ultrasound Med. 1993;12(3):131-134.
Goldstein RB, Podrasky AE, Filly RA, Callen PW. Effacement of the fetal cisterna magna in association with myelomeningocele. Radiology. 1989 Aug;172(2):409-13.
McLone DG, Dias MS. The Chiari II malformation: cause and impact. Childs Nerv Syst. 2003 Aug;19(7-8):540-50. Epub 2003 Aug 12.
Barkovich JA. Congenital malformarmation of the brain and skull. In: Barkovich JA(ed). Pediatric Neuroimaging. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005: 378-384.
Callen AL, Stengel JW, Filly RA. Supratentorial abnormalities in the Chiari II malformation, II: tectal morphologic changes. J Ultrasound Med. 2009 Jan;28(1):29-35.
Nicolaides KH, Campbell S, Gabbe SG, Guidetti R. Ultrasound screening for spina bifida: cranial and cerebellar signs. Lancet. 1986 Jul 12;2(8498):72-4.
Van den Hof MC, Nicolaides KH, Campbell J, Campbell S. Evaluation of the lemon and banana signs in one hundred thirty fetuses with open spina bifida. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Feb;162(2):322-7.
Maryam Nik Nejadi et al, Arnold-Chiari Type II Malformation: A Case Report and Review of Prenatal Sonographic Findings, IJFS, Vol 1, No 4, Feb-Mar 2008.
Buoni S, Zannolli R, di Bartolo RM, Donati PA, Mussa F, Giordano F, Genitori L. Surgery removes EEG abnormalities in patients with Chiari type I malformation and poor CSF flow. Clin Neurophysiol. 2006 May;117(5):959-63. Epub 2006 Mar 20.
Tubbs RS, Lyerly MJ, Loukas M, Shoja MM, Oakes WJ. The pediatric Chiari I malformation: a review. Childs Nerv Syst. 2007 Nov;23(11):1239-50. Epub 2007 Jul 18.
Sharma A, K V Amrutha, Abraham J. Arnold chiari malformation: case series. Int J Anat Res 2016;4(1):2151-2156. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.16965/ijar.2016.167.
Jianxin Jiang, Yanfei Zhang, Liang Wei, Zhiyang Sun, Zhongmin Liu. Association between MTHDI G1958A Polymorphism and neural tube defects susceptibility: A Meta-Analysis. Plos One. 2014;9(6):e1011169.
Lora Kahn, Nnenna Mbabuika, Edisan P, Valle-Giler, Juanita Graces, R. Clifton Moore, et al. Hilaireand Cuong J Bui. Fetal Surgery: The Ochsner experience with in-utero spina bifida repair. The Ochsner Journal. 2014;14(1):112-18.
Ganesh D, Sagayaraj BM, Barua RK, Sharma N, Ranga U. Arnold Chiari malformation with spina bifida: a lost opportunity of folic Acid supplementation. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014 Dec;8(12):OD01-3. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.7860%2FJCDR%2F2014%2F11242.5335. Epub 2014 Dec 5.
Callen AL, Filly RA. Supratentorial abnormalities in the Chiari II malformation, I: the ventricular "point". J Ultrasound Med. 2008 Jan;27(1):33-8.
Sindou M, Chávez-Machuca J, Hashish H. Cranio-cervical decompression for Chiari type I-malformation, adding extreme lateral foramen magnum opening and expansile duroplasty with arachnoid preservation. Technique and long-term functional results in 44 consecutive adult cases -- comparison with literature data. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2002 Oct;144(10):1005-19.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


