Histopathological study of breast lesions
Abstract
Objectives: To study the histopathological features of neoplastic and non neoplastic lesions of breast. To correlate the pathological findings with clinical parameters.
Design and methods: We have studied total 161 cases of breast lesions over a period of two years in our institute. The specimens were received in histopathology section of our department. Detailed gross examination of specimens was done followed by fixation, thorough sampling, and tissue processing. The different lesions were studied by histopathological examination and analysed. Neoplastic lesions were classified according to the WHO classification (2012).
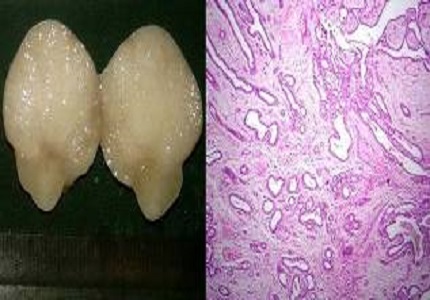
Results: Out of the 161 cases, 128 cases had neoplastic lesions and 32 cases had non-neoplastic lesions, and one case had coexistent neoplastic and nonneoplastic lesions. Two cases had dual neoplastic lesions. Out of the total 129 cases with neoplastic lesions, 76 cases had benign breast tumors, 53 cases had malignant breast tumors, and 2 cases had precursor lesions. Fibroadenoma was the most common benign tumour with 60 cases. Invasive carcinoma no special type was the most common malignant tumour with 43 cases. Special subtypes of invasive carcinoma found in our study were metaplastic carcinoma (3 cases) and mucinous carcinoma (1 case). The most common nonneoplastic lesion was mastitis with 12 cases, followed by duct ectasia and fibrocystic change. There were 4 cases of gynaecomastia. All the tumors involved upper outer quadrant most frequently. The benign tumors were most frequent in second, third and fourth decades, malignant tumours were seen beyond 4th decade. The nonneoplastic lesions were common in 4th decade.
Conclusion: Histopathological study is important in the management of breast lumps
Downloads
References
Lakhani S, Ellis I O, Schnitt S J, Tan P H, Van der vijver M J World Health Organization Classification of tumours of breast, Lyon, IARC press, 2012.
Dhillon PK, Breast Cancer Factsheet. South asia network for chronic disease. Public Health Foundation of India 2011.
Siddiqui M S, Kayani N, Gill M S, Pervez S , Aziz S A, Muzaffar S,Setna Z, Israr M, Hassan S H Breast diseases: a histopathological analysis of 3279 cases at tertiary care centre in Pakistan . JPMA 2003 53:94.
Olu-Eddo AN, Ugiagbe EE. Benign breast lesions in an African population:A 25 year histopathological review of 1864 cases. Niger Med J. 2011 Oct;52(4):211-6. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0300-1652.93790.
Mudholkar VG, Kawade SB, Mashal SN. Histopathological study of neoplastic lesions of breast. Ind Med Gazette 2012 Sept :353-64.
Oluwole ,Soji F, Harold P, Analysis of benign breast disease in blacks . Am J Surg. 1979 Jun;137(6):786-9.
Raju GC, Jankey N, Narayansingh V. Breast disease in young west Indian women: an analysis of 1051 cases. Postgrad Med J. 1985 Nov;61(721):977-8.
Haque R, Tyagi SP, Khan MH, Gahlaut YVS, Breast lesions, A clinicopathological study of 200 cases of breast lumps. Ind J Surg 1980;42:419-425.
Azzopardi JG, Chepick OF, Hartmann WH, Jafarey NA. The world health organization. Histological typing of breast tumors. Am J Clin Pathol 1982;78:806-816.
Shabtai M, Saavedra-Malinger P, Shabtai EL, Rosin D, Kuriansky J, Ravid-Magido M et al. Fibroadenoma of the breast :Analysis of associated pathological entities-A different risk marker in different age groups for concurrent breast cancer IMAJ 2001:3 813-817.
Sklair-Levy M, Sella T, Alweiss T, Cracium I, Libson E, Mally B. Incidence and management of complex fibroadenoma AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008 Jan;190(1):214-8.
Varghas MP, Merino MJ Infarcted myxoid fibroadenoma following fine needle aspiration Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1996 Nov;120(11):1069-71.
Skenderi F, Krakonja F, Vranic S. Infarcted fibroadenoma of the breast :report of two new cases with review of literature Diagn Pathol. 2013 Feb 27;8:38. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-8-38.
Osteen RT,Karnell LH. The national cancer data base report on breast cancer. Cancer. 1994 Apr 1;73(7):1994-2000.
Dauda AM, Misauno MA, Ojo EO. Histopathological types of breast cancer in Gombe north eastern Nigeria: A seven year review .African journal of reproductive health 2011 Mar 15(1):107-110.
Njeze G E .Breast lumps: A 21 year single centre clinical and histological analysis, Nigerian journal of surgery. 2014 Jan –June . 20(1) 38-41.
Lee AHS, Gillett CE, Ryder K, Fentiman IS, Miles DW. Millis RR, Different patterns of inflammation and prognosis in invasive carcinoma of breast. Histopathology. 2006 May;48(6):692-701.
Truong PT, Berthelet E, Lee J, Kader H, Olivotto I A. The prognostic significance of the percentage of positive /dissected axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer recurrence and survival in patients with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes. Cancer. 2005 May 15;103(10):2006-14.
Van der Vegt B, Dee Roos M A J , Peterse J L, Patriarca C, Hilkens J, De Bock G H & Wessling J. The expression pattern of MUC1 (EMA) is related to tumour characteristics and clinical outcome of invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Histopathology . 2007. 51: 322-335.
Yoshihara E, Smeets A, Laenen A, Reynders A, Soens J, Van Ongeval C et al Predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in early breast cancer and their applicability in clinical practice. Breast. 2013 Jun;22(3):357-61. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2012.09.003. Epub 2012 Sep 28.
Yip CH, Taib NA, Tan GH, Ng KL, Yoong BK, Choo WY Predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: is there role for minimal axillary surgery? World J Surg. 2009 Jan;33(1):54-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-008-9782-7.
Munjal K, Jain VK, Agrawal A, Bandi PK .Co existing tubercular axillary lymphadenitis with carcinoma breast can falsely overstage the disease-case series. Ind J Tuberc 2010;57:104-107.
Dave R, Dhruva G, Agravat A. Breast cancer and breast tuberculosis: a rare coexistence. Ind J Res Med, 2014;3(1): 108-110.
Johnson RE, Murad MH. Gynecomastia: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009 Nov;84(11):1010-5. doi: https://doi.org/10.4065/84.11.1010.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


