Social anxiety disorder co-morbid with schizophrenia: a cross-sectional study from India
Abstract
Introduction: The co-morbidity of various psychiatric disorders with schizophrenia (SZ) is increasingly being recognized, with anxiety disorders (ADs) being no exception. Among the various ADs, the co morbidity of social anxiety disorder (SAD) and SZ is not well studied. We hypothesized that the prevalence of SAD in SZ is high.
Objective: We aimed to study the prevalence of SAD in patients with SZ, and to determine the associated socio-demographic and clinical correlates.
Materials and methods: This was an outpatient study on consecutively sampled 64 International Diagnostic Criteria (ICD-10) diagnosed treatment-naive SZ patients, who were rated on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS), the Social Interaction Anxiety Scale (SIAS), the WHO-5 Well-Being Index (WHO-5) and the Global Assessment of Functioning Scale (GAF).
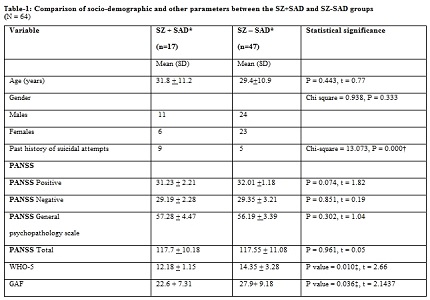
Results: The prevalence of SAD in or sample of SZ patients was 26.56%. Compared to the SZ without SAD group, the SZ with SAD group had a lower quality of life (QoL) and GAF scores, but, no significant difference in the PANSS ratings.
Conclusions: The SAD is highly co morbid with SZ, and appears to be independent of psychosis, and is associated with lower QoL and psychosocial functioning. Future follow-up studies should evaluate whether this SAD co-morbidity has any impact on the treatment outcome of SZ.
Downloads
References
Achim AM, Maziade M, Raymond E, et al. How prevalent are anxiety disorders in schizophrenia? a meta-analysis and critical review on a significant association. Schizophr Bull 2011; 37 (4): 811–821.
Pallanti S, Quercioli L, Hollander E. Social anxiety in outpatients with schizophrenia: a relevant cause of disability. Am J Psychiatry. 2004 Jan;161(1):53-8.
Voges M, Addington J. The association between social anxiety and social functioning in first episode psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2005 Jul 15;76(2-3):287-92.
Braga RJ, Mendlowicz MV, Marrocos RP, Figueira IL. Anxiety disorders in outpatients with schizophrenia: prevalence and impact on the subjective quality of life. J Psychiatr Res. 2005 Jul;39(4):409-14. Epub 2004 Nov 13.
Mazeh D, Bodner E, Weizman R, Delayahu Y, Cholostoy A, Martin T, Barak Y. Co-morbid social phobia in schizophrenia. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2009 May;55(3):198-202. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177%2F0020764008093447.
Cosoff SJ, Hafner RJ. The prevalence of comorbid anxiety in schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and bipolar disorder. Aust NZ J Psychiatry 1998; 32: 67-72.
Lowengrub KM, Stryjer R, Birger M, et al. social anxiety disorder comorbid with schizophrenia: the importance of screening for this under recognized and undertreated condition. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci 2015; 52 (1): 40-46.
World Health Organisation. (1992).International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10). Geneva: WHO.
Blanchard JJ, Mueser KT, Bellack AS. Anhedonia, positive and negative affect, and social functioning in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1998;24(3):413-24.
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1987;13(2):261-76.
Mattick R, Clarke C. Development and validation of measure of Social Phobia Scrutiny Fear and Social Interaction Anxiety. Behav Res Ther 1998; 36:455–70.
Bech P. Clinical Psychometrics. Oxford, UK: Wiley Blackwell; 2012.
American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
Tibbo P, Swainson J, Chue P, LeMelledo JM. Prevalence and relationship to delusions and hallucinations of anxiety disorders in schizophrenia. Depress Anxiety 2003; 17: 65-72.
Michail M, Birchwood M. Social anxiety disorder in first-episode psychosis: incidence, phenomenology and relationship with paranoia. Br J Psychiatry. 2009 Sep;195(3):234-41. doi: https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.108.053124.
Pallanti S, Quercioli L, Pazzagli A. Social anxiety and premorbid personality disorders in paranoid schizophrenic patients treated with clozapine. CNS Spectr 2000; 5: 29-43.
Pallanti S, Quercioli L, Rossi A, Pazzagli A. The emergence of social phobia during clozapine treatment and its response to fluoxetine augmentation. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999 Dec;60(12):819-23.
Churchland PS, Winkielman P. Modulating social behavior with oxytocin: how does it work? What does it mean? Horm Behav. 2012 Mar;61(3):392-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.12.003. Epub 2011 Dec 14.
Williams MT, Capozzoli MC, Buckner EV, et al. Cognitive-behavioural treatment of social anxiety disorder and comorbid paranoid schizophrenia. Clinical Case Studies 2015; 14 (5): 323-341.
Kingsep P, Nathan P, Castle D. Cognitive behavioural group treatment for social anxiety in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2003 Sep 1;63(1-2):121-9.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


