Skeletal Maturation in the pediatric population in a large tertiary care hospital in South India
Abstract
Background & Objectives: Determination of skeletal age is an important part of examination for many clinical problems with growth disorders. The Greulich and Pyle atlas method and the Tanner Whitehouse technique are used to assess bone age accurately. However time constraints force pediatricians to quickly assess bone age from age of appearance of epiphyseal centres. The aim of this study was to re-examine this method in today’s clinical practice to enable more practical and appropriate use.
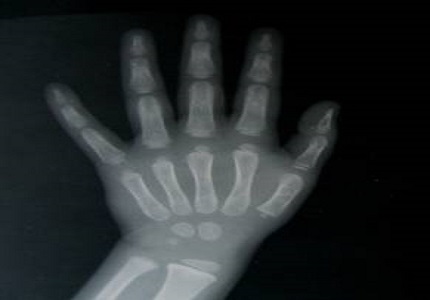
Methods: The study was undertaken in The Institute of Child Health and Hospital for Children, Egmore,(ICH & HC) Chennai. Normal children less than 12 years were included in the study. The children were grouped in different age groups, 100 girls and 100 boys in each age group totalling 3800 children. Depending on the chronological age of the child only the x ray films of the hand, wrist, elbow, or knees were taken. We used x-rays of hands for all age groups and elbow in those over 5 years. Only the appearance of ossification centers was noted. We also used x-ray of the patella for children in 3 to 5 year age groups.
Results: We found that the mean age of appearance of patellar ossification was similar in both boys and girls (mean age 4.8± 0.5). By 3-6 months capitate and hamate were present in all children (mean age 0.5± 0.1). There is high variability in the timing of ossification of carpal bones, which accounts for their elimination for age evaluation. However the pisiform follows a constant mean age at 10.6 for girls and 11.6 for boys.
Conclusion: Children can be adequately screened for age assessment from x rays of the hands in the early stages (upto 2 and half years) and later the elbows. We propose the use of knees lateral for patellar centre for children more than 3 and less than 6.
Downloads
References
Greulich WW, Pyle SI. Radiographic Atlas of skeletal development of hand and wrist.Stanford: Stanford University Press 1950 (reprint 1954).
Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH, Marshall WA, Goldstein H. Assessment of skeletal maturityand prediction of adult height. London: Academic Press, 1975.
Bull RK, Edwards PD, Kemp PM, Fry S, Hughes IA. Bone age assessment: a large scale comparison of the Greulich and Pyle, and Tanner and Whitehouse (TW2) methods. Arch Dis Child. 1999 Aug;81(2):172-3.doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.81.2.172.
Buckler JM. How to make the most of bone ages. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Oct;58(10):761-3.doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.58.10.761.
Goyal A, Gaillard F. Elbow ossification. Available at https://radiopaedia.org/articles/elbow-ossification.
Satoh M. Bone age: assessment methods and clinical applications. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2015 Oct;24(4):143-52. doi: https://doi.org/10.1297/cpe.24.143. Epub 2015 Oct 24.
Khadilkar V, Khadilkar A. Growth charts: A diagnostic tool. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Sep;15 Suppl 3:S166-71. doi: http://www.ijem.in/text.asp?2011/15/7/166/84854.
Flor-Cisneros A, Leschek EW, Merke DP, et al: In boys with abnormal developmental tempo, maturation of the skeleton and the hypothalamic- pituitary – gonadal axis remains synchronous. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89 (1): 236 – 41.doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2002-021954.
Maniar B. Skeletal maturity in Indian children. Indian J Pediatr. 1987 May-Jun;54(3):295-302.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02748910.
Bajaj ID, Bhardwaj OP, Bhardwaj S. Appearance and fusion of important ossification centres: a study in Delhi population. Indian J Med Res. 1967 Oct;55(10):1064-7.
Garn SM et al Med Radiogr Photogr in Caffey's Pediatric Radiology XIth edition 2008.
Acheson RM, Kemp JH, Parfit J. Height, weight, and skeletal maturity in the first five years of life. Lancet. 1955 Apr 2;268(6866):691-2.
VV Pillay, Chap 4 in Textbook of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology; 14th Edition Paras Publishers Hyderabad 2004.
Dr. KS Narayana Reddy, Chapter 4 in The Essentials of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology 24th Edition Published by Suguna Devi Hyderabad 2005.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


