Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in patients in a tertiary hospital in south India
Abstract
Aims: To estimate the prevalence of Retinopathy in patients attending a diabetic clinic and to evaluate the risk factors underlying its development.
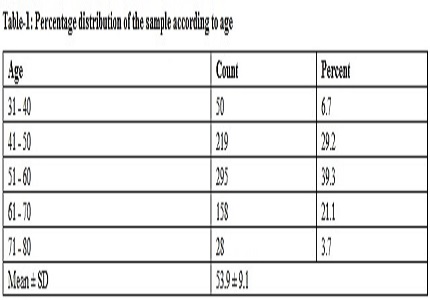
Methods: 750 diabetic patients who reported for executive check up in a preventive clinic were evaluated for absence or presence of retinopathy. Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) present was graded as non proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Risk factors were then evaluated in order to delineate those related to retinopathy. Investigations included complete blood count, blood sugar, serum lipids, ECG, Renal function tests and complete clinical examination.
Results: DR was detected in 111 patients (14.8 %) with NPDR in 106 patients (14.1%) and PDR in 5 patients (0.7%). Factors related to the incidence of retinopathy were duration of diabetes, presence of hypertension, high blood sugar level and hyperlipidemia. It was found that duration of diabetes, level of glycemic control and high levels of cholesterol were statistically significant for the occurrence of retinopathy.
Conclusion: In addition to glycemic control, lowering of serum lipids may be effective in lowering the incidence of retinopathy in diabetic patients .Hypertension was not related to the occurrence of retinopathy.
Downloads
References
Das A. Diabetic retinopathy: Battling the global epidemic. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;64(1):2-3. doi: http://www.ijo.in/text.asp?2016/64/1/2/178155.
Gadkari SS, Maskati QB, Nayak BK. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in India: The All India Ophthalmological Society Diabetic Retinopathy Eye Screening Study 2014. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;64(1):38-44. doi: http://www.ijo.in/text.asp?2016/64/1/38/178144.
Murthy GV, Das T. Diabetic care initiatives to prevent blindness from diabetic retinopathy in India. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;64(1):50-4. doi: http://www.ijo.in/text.asp?2016/64/1/50/178152.
Das T Aurora,Chhablani J . Giridhar A,Kumar A, Raman R et al.Evidence based review of diabetic macular oedema management.Consensus statement on Indian treatment guidelines.Indian J Ophthalmol 2016; 64:14-25.doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0301-4738.178142.
M Chakrabarti et al-An effective model for counselling in diabetic patients. Kerala J Ophthalmol 2008; 3:248-251.
Dr Jay J Meyer et al-Diabetic Retinopathy in Asia :Illumination.Journal of Aravind Eye Care System.Vol V11 No.1 Jan-Mar.2007:15-17.
Namperumalsamy P et al. Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in the population of over 30 years of age in Theni district of South India. Br J Ophthalmol.1999 Aug; 83(8):937-40.doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2008.147934.
Valverde C, Garcia M, Hornero R, Lopez-Galvez MI. Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal images. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;64(1):26-32. doi: http://www.ijo.in/text.asp?2016/64/1/26/178140.
Raman R, Gella L, Srinivasan S, Sharma T. Diabetic retinopathy: An epidemic at home and around the world. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;64(1):69-75. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0301-4738.178150.
Singh R, Ramasamy K, Abraham C, Gupta V, Gupta A. Diabetic retinopathy: an update. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2008 May-Jun;56(3):178-88.doi: http://www.ijo.in/text.asp?2008/56/3/179/40355.
el Haddad OA, Saad MK. Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy among Omani diabetics. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998 Aug;82(8):901-6.doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.82.8.901.
Cetin EN, Bulgu Y, Ozdemir S, Topsakal S, Akın F, Aybek H, Yıldırım C. Association of serum lipid levels with diabetic retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol. 2013 Jun 18;6(3):346-9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.03.17. Print 2013.
Lill.Inger Larsson, Albert Alm,Folke Lithner, Gosta Dahlen and Reinhold Bergstrom:The association of hyperlipidemia with retinopathy in diabetic patients aged 15-50 years in the county of Umea:Acta ophthalmol.scand. 1999;77:585-591.
Mishra B, Swaroop A, Kandpal RP. Genetic components in diabetic retinopathy. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Jan;64(1):55-61. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.178153.
Radha V, Rema M, Mohan V. Genes and diabetic retinopathy. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2002 Mar;50(1):5-11.doi: http://www.ijo.in/text.asp?2002/50/1/5/14823.
Kaur P,BBS ,Kaur I,Singh G,Singh B.Correlation of severity of Diabetic Retinopathy with various risk factors.Int J Res Health Sci(internet).2014 Apr 30;2(2):473-9.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


