Drug Safety of Celecoxib
Abstract
Introduction: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs presently are the most widely used drugs in medicine and are the most frequent cause of adverse drug reactions, affecting multiple systems, mainly gastric, renal & cardiovascular, which is a major public health concern. Previous studies report, that selective COX-2 inhibitors are safer when compared to non-selective cyclooxygenase inhibitors. But, recent studies reveal, that the safety of these selective COX-2 inhibitors is not much better than that of conventional NSAIDs. In view of the wider usage of selective COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib in day to day practice by many clinicians, the study has been taken up to report, whether selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib has got any advantages over conventional NSAIDs or not.
Methodology: 15 patients were taken up for the study & all the patients were given celecoxib for 15 days. Both pre and post-treatment values of Hb%, blood urea, serum creatinine, serum bilirubin, bleeding time, clotting time, heart rate & blood pressure were recorded, tabulated & subjected to statistical analysis.
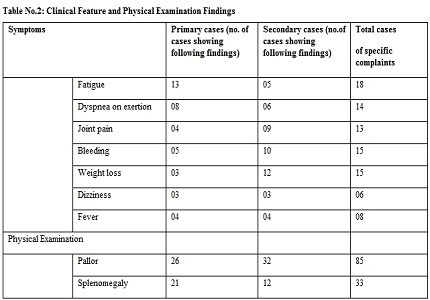
Results: Selective COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib has shown significant changes in bleeding time values & also good amount of gastric toxicity when assessed clinically. Hepatic, renal & other cardiovascular parameters were absolutely normal.
Conclusion: In our short-term study, selective COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib has shown good amount of gastric toxicity, showing no advantage over non-selective drugs. But, there is no hepatic, renal & cardiovascular toxicity.
Downloads
References
V. Dhikav, S. Singh, KS. Anand; Newer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - A review of their therapeutic potential and adverse drug reactions; Journal, Indian Academy of Clinical Medicine; October - December 2002; -Volume 3; No. 4; Page 332-338.http://medind.nic.in/jac/t02/i4/jact02i4p332.pdf.
Goodman and Gilman; Analgesic-Antipyretic and Anti-inflammatory agents; The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics; Eleventh Edition; Page 671-715.
HP Rang and MM Dale; Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant drugs; Rang and Dale’s Pharmacology; Seventh Edition: Page 318-335.
Jonathan J Deeks, Lesley A Smith, Matthew D Bradley; Efficacy, tolerability, and upper gastrointestinal safety of celecoxib for treatment of (Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis; systematic review of randomized controlled trials; British Medical Journal; 21 September, 2002; Volume 325; Page 619-623.doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.325.7365.619.
LLM waeky, JE Ruiz, J Duperly e1.al; Efficacy of celecoxib in treating symptoms of viral pharyngitis; a double-blind, randomized study of celecoxib versus diclofenac; The Journal of International Medical Research; 2002; Volume 30; Page 185-194.doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/147323000203000212.
Maarten Boers; NSAIDS and selective COX-2 inhibitors: competition between gastro protection and cardio protection; The Lancet; 21 April; Volume 357; Page 1222-1223. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(00)04451-2.
Paul Emery, Henning Zeidler, Tore K Kvien, Mario Guslandi, Raphael Naudin, Helen Stead, Kenneth M Verburg, Peter C Isakson, Richard C Hubbard, G Steven Geis; Celecoxib versus diclofenac in long-term management of rheumatoid arthritis; randomized double-blind comparison; The Lancet; 18/25 December, 1999; Volume 354; Page 2106-2111.doi: http://doi.cnki.net/doi/Resolution/Handler?doi=%2010.1016/S0140-6736(99)02332-6.
Peter Juni, Anne WS Rutjes, and Paul A Dieppe; Are selective COX-2 inhibitors superior to traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs? ; British Medical Journal; 1 June, 2002; Volume 324; Page 1287-1288.doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.324.7349.1287.
Christopher Cutts, Adam Lacaze and Susan Tett; A Clinical audit of the prescribing of celecoxib and rofecoxib in Australian rural general practice; British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology; 2002; Volume 54; Page 522-527.doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01666.x.
Goodman and Gilman; Analgesic - Antipyretic and Anti-inflammatory agents; The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics; Twelth Edition; Page 959-1004.
Jennifer Berg Hrachovee, Pharm D, MPH; Marc Mora, MD; Reporting of 6 -months VS 12-months data in a clinical trial of celecoxib; JAMA, 21 November , 2001; Volume 286; No.19; Page 2398.
Mark Feldman, MD, and Alexander T. Mc Mahon, MBA; Do cyclooxygenase inhibitors provide benefits similar to those of traditional non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs, with less gastro intestinal toxicity? ; Annals of Internal Medicine; 18 January 2000; Volume132; No.2; Page 134-143.
Harri Vainio, Gareth Morgan; Cyclo-oxygenase -2 and breast cancer prevention ; British Medical Journal; 26 September, 1998; Volume 317; Page 828.
Peter M. Brooks, M.D; And Richard 0.Day,M.D; Non-Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-Differences and similarities; the new England Journal of Medicine;13June, 1991;Volume 324; No. 24; Page1716-1724.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


