Diagnostic evaluation of pancytopenia - a prospective institutional study in North-East India
Abstract
Introduction: Pancytopenia, the simultaneous reduction of all the three formed elements of blood, is diverse in its etiology. Full clinico-hematopathological work up is crucial in each case. This study was undertaken with the objectives of identifying the causes of pancytopenia and its phenotypic characteristics in relation to age, sex, ethnicity and socio- economic status.
Methods: Ninety two cases of pancytopenia studied here were diagnosed by complete hemogram study in automated hematology analyzer. Peripheral blood smear studies were carried out. All cases were subjected to bone marrow aspiration/ imprint smear cytology and trephine biopsy study. Hypoplastic anemia cases were investigated for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) with flow cytometric analysis of red blood cells treated with CD55 and CD59 antibodies.
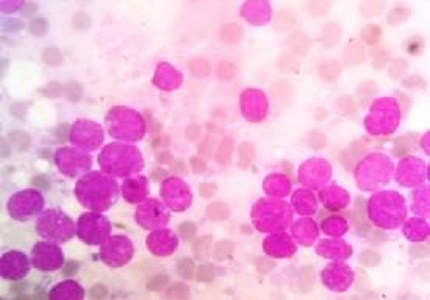
Results: Fifty eight percent of cases were males and mean age was 52 years. Children constituted 16% of patients. Thirty-seven percent of cases belonged to tribal community. Around 70% belonged to low socio-economic status. Causes of pancytopenia detected were primary hematological malignancies (Total 39.2 % with acute leukaemia 35.9%, lymphoma 2.2% and multiple myeloma 1.1%), hypoplastic anaemia (28.3%), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) (21.7%), megaloblastic Anemia (6.5%) and hypersplenism (4.3%). No PNH clone was detected amongst hypoplastic anemia cases.
Conclusion: It is concluded that pancytopenia often is the manifestation of serious disease-processes and the commonest cause, in our population of this North-Eastern state of Tripura, being acute leukemia. Bone marrow cytology and biopsy study must be performed in all cases of pancytopenia to find out the cause in order to institute an early treatment.
Downloads
References
2. Guinan EC, Shimamura A. Wintrobe's Clinical Hematology. In: Greer JP, Foerster J, Lukens JN, Rodgers GM, Paraskevas F, Glader B, editors. Acquired and inherited aplastic anemia syndromes. 11th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2004. pp. 1397–419.
3. Gayathri BN, Rao KS. Pancytopenia: a clinico hematological study. J Lab Physicians. 2011 Jan;3(1):15-20. doi: 10.4103/0974-2727.78555. [PubMed]
4. Desalphine M, Bagga PK, Gupta PK, Kataria AS. To evaluate the role of bone marrow aspiration and bone marrow biopsy in pancytopenia. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014 Nov;8(11):FC11-5. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/9042.5169. Epub 2014 Nov 20. [PubMed]
5. Tilak V, Jain R. Pancytopenia--a clinico-hematologic analysis of 77 cases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 1999 Oct;42(4):399-404. [PubMed]
6. Kumar R, Kalra SP, Kumar H, Anand AC, Madan H. Pancytopenia--a six year study. J Assoc Physicians India. 2001 Nov;49:1078-81. [PubMed]
7. Dasgupta S, Mandal PK, Chakrabarti S. Etiology of Pancytopenia: An Observation from a Referral Medical Institution of Eastern Region of India. J Lab Physicians. 2015 Jul-Dec;7(2):90-5. doi: 10.4103/0974-2727.163136.
8. Devi PM, Laishram RS, Sharma PS, Singh AM, Singh MK, Singh YM. Clinico-hematological profile of pancytopenia in Manipur, India. Kuwait Med J. 2008;40:221–4. [PubMed]
9. Raphael V, Khonglah Y, Dey B1, Gogoi P, Bhuyan A. Pancytopenia: an etiological profile. Turk J Haematol. 2012 Mar;29(1):80-1. doi: 10.5505/tjh.2012.98360. Epub 2012 Mar 5. [PubMed]
10. Lewis SM, Bain BJ, Bates I. Dacie and Lewis Practical Haematology. Basic haematological techniques; Preparation and staining methods for blood and bone marrow films; Erythrocyte and leucocyte cytochemistry - leukaemia classification. 9th ed. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh 2001: pp 19-64 & 269-95.
11. Suvarna KS, Layton C and Bancroft JD . Bancroft's Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. The hematoxylin and eosin (Ch.10). 7th ed. Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia 2013: pp. 172–86. [PubMed]
12. Hunt BJ, Andrews V, Pettingale KW. The significance of pancytopenia in miliary tuberculosis. Postgrad Med J. 1987 Sep;63(743):801-4. [PubMed]
13. Niazi M, Raziq F . The incidence of underlying pathology in pancytopenia. An experience of 89 cases. J Postgr Med Inst 2004; 18(1): 76-9.
14. Basak TB, Talukder SI. Etiological Spectrum of Pancytopenia. Dinajpur Med Col J 2014;7 (1):21-5.
15. Kumar DB, Raghupati AR, Clinicohematological analysis of pancytopenia Basic and Applied Pathology 2012 5:19-21. [PubMed]
16. Jha A, Sayami G, Adhikari RC, Panta AD, Jha R. Bone marrow examination in cases of pancytopenia. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2008 Jan-Mar;47(169):12-7. [PubMed]
17. Memon S, Shaikh S, Nizamani MA. Etiological spectrum of pancytopenia based on bone marrow examination in children. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2008 Mar;18(3):163-7. doi: 03.2008/JCPSP.163167. [PubMed]
18. Das Makheja K, Kumar Maheshwari B, Arain S, Kumar S, Kumari S, Vikash. The common causes leading to pancytopenia in patients presenting to tertiary care hospital. Pak J Med Sci. 2013 Sep;29(5):1108-11. [PubMed]
19. Khunger JM, Arulselvi S, Sharma U, Ranga S, Talib VH. Pancytopenia--a clinico haematological study of 200 cases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2002 Jul;45(3):375-9. [PubMed]
20. Jain A and Naniwadekar M. An etiological reappraisal of pancytopenia - largest series reported to date from a single tertiary care teaching hospital. BMC Hematol. 2013; 13: 10. Published online 2013 November 6. doi: 10.1186/2052-1839-13-10. [PubMed]
21. Young NS, Maciejewski JP, Sloand E, Chen G, Zeng W, Risitano A, Miyazato A. The relationship of aplastic anemia and PNH. Int J Hematol. 2002 Aug;76 Suppl 2:168-72. [PubMed]
22. Kinoshita T, Inoue N. Relationship between aplastic anemia and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Int J Hematol. 2002 Feb;75(2):117-22. [PubMed]
23. Parab RB. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: a study of 17 cases. J Postgrad Med. 1990 Jan;36(1):23-6. [PubMed]
24. Gupta PK, Charan VD, Kumar H. PNH revisited: Clinical profile, laboratory diagnosis and follow-up. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2009 Jan-Mar;52(1):38-41.
25. Luzzatto L, Notaro R. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. In : Handin RI, Lux SE, Stossel TP editors. Blood: Principles and Practice of Hematology. Philadelphia; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: 2003: pp. 318-32.
26. Naithani R, Mahapatra M, Dutta P, Kumar R, Pati HP, Choudhry VP. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in childhood and adolescence--a retrospective analysis of 18 cases. Indian J Pediatr. 2008 Jun;75(6):575-8. doi: 10.1007/s12098-008-0111-9. Epub 2008 Aug 31.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


