A correlative study of autonomic neuropathy and gall bladder volume in patients with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetic autonomic neuropathy (DAN) is among the least recognized and understood complication of diabetes despite its significant negative impact on survival and quality of life in people with diabetes. Various studies showed that there is increased prevalence of gall bladder diseases like gall stones in patients with diabetes.
Methods: This study was done to evaluate gall bladder volume in diabetics, it’s comparison with a control group, and correlation of gallbladder volume in diabetics with various parameters like autonomic neuropathy, age, sex, body mass index, hyperlipidaemia and duration of diabetes. 100 proven diabetic patients and 100 healthy controls were recruited for the study. A detailed history and physical examination findings were recorded. Autonomic neuropathy was determined by using simple noninvasive bedside tests. Fasting gallbladder volume was calculated using ellipsoid formula by ultrasonography.
Results: The mean fasting gallbladder volume in diabetics was 23.1±7.3 ml as compared to controls i.e 13.0±3.4ml.
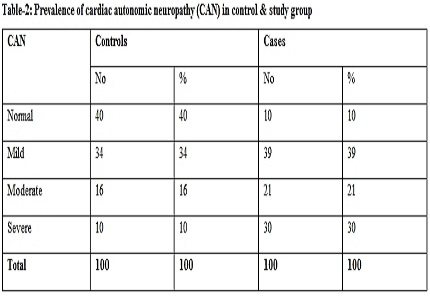
Conclusion: When type 2 diabetics were sub grouped according to the presence of autonomic neuropathy, higher gallbladder volumes were seen in patients with autonomic neuropathy.
Downloads
References
2. Jørgensen T. Prevalence of gallstones in a Danish population. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Nov;126(5):912-21. [PubMed]
3. Robbins SL. pathogenesis of diseases. 5th Edition, Philadelphia; WB Saunders; 1994.p. 884-888.
4. Paumgartner G, Sauerbruch T. Gallstones: pathogenesis. Lancet. 1991 Nov 2;338(8775):1117-21. [PubMed]
5. Hahm JS, Park JY, Park KG, Ahn YH, Lee MH, Park KN. Gallbladder motility in diabetes mellitus using real time ultrasonography. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Nov;91(11):2391-4. [PubMed]
6. Ewing D. J. Autonomic function testing (clinical)–Michael Poon’s Shrine of Neurology. 1985,1988 in www.Autonomic function testing. html. (Accessed on 4/1/03).
7. American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Care January 2010; 33:S62-S69.
8. A.B. Olokoba, B J Bojuwoye, L.B.Olokoba, K.W.Whab, K.T.Braimoh,A.K.Inikor et.al. The relationship between gall bladder disease and gallbladder wall thickness African scientist Dec 31, 2006;7(4):171-176.
9. S Singh, R Chander A Singh, S Mann Ultrasonographic Evaluation Of Gall Bladder Diseases In Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Ind J Radiol Imag 2006;16:4:505-508.
10. Sharma MP, Saraya A, Anand AC, Karmarkar MG. Gall bladder dysmotility in diabetes mellitus--an ultrasound study. Trop Gastroenterol. 1995 Jul-Sep;16(3):13-8. [PubMed]
11. Chapman BA, Chapman TM, Frampton CM, Chisholm RJ, Allan RB, Wilson IR, Burt MJ. Gallbladder volume: comparison of diabetics and controls. Dig Dis Sci. 1998 Feb;43(2):344-8. [PubMed]
12. Agarwal AK, Miglani S, Singla S, Garg U, Dudeja RK, Goel A. Ultrasonographic evaluation of gallbladder volume in diabetics. J Assoc Physicians India. 2004 Dec;52:962-5.
13. Güliter, Sefa, Ylmaz, Sevda, Karakan, Tarka. Evaluation of Gallbladder Volume and Motility in Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Patients Using Real-Time Ultrasonography Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. Oct 2003; 37(4):288-291. [PubMed]
14. Hendel HW, Højgaard L, Andersen T, Pedersen BH, Paloheimo LI, Rehfeld JF, Gotfredsen A, Rasmussen MH. Fasting gall bladder volume and lithogenicity in relation to glucose tolerance, total and intra-abdominal fat masses in obese non-diabetic subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998 Apr;22(4):294-302.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


