Evaluation of laryngoscopic view, intubation difficulty and sympathetic response during direct laryngoscopy in sniffing position versus simple head extension: a clinical comparative study
Abstract
Background: Proper position of the head and the neck is important for optimizing laryngoscopic view and for ease of endotracheal intubation.We compared two different positions, sniffing position and simple head extension during direct laryngoscopy on the basis of laryngoscopic view, intubation difficulty and sympathetic response.
Methodology: One hundred twenty patients of age group 20-50 years, scheduled for elective surgeries under general anaesthesia were divided into two equal groups in a randomized fashion. In group A (n = 60), sniffing position during laryngoscopy and intubation; and in group B(n =60),simple head extension position during laryngoscopy and intubation. Laryngoscopy view, ease of intubation and hemodynamic parameters were recorded.
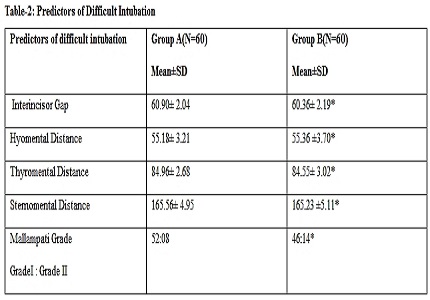
Results: Demographic data and the different parameters for assessment of difficult airway were similar in both groups. Glottic visualization grade was superior in group A and intubation difficulty score were higher in Group B (P < 0.05), Hemodynamic parameters at different time intervals were comparable.
Conclusion: Sniffing position during laryngoscopy was found to be superior to simple head extention position in respect of better glottis visualization and ease of intubation though no difference in sympathetic response to intubation was found.
Downloads
References
2. Bannister F, Macbeth R. Direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation. The Lancet. 1944 Nov 18;244(6325):651-4.
3. Wilson ME, Spiegelhalter D, Robertson JA, Lesser P. Predicting difficult intubation. British Journal of Anaesthesia. 1988 Aug 1;61(2):211-6. [PubMed]
4. Mallampati SR, Gugino LD, Desai SP, Waraksa B, Freiberger D, Liu PL: A clinical sign to predict difficult intubation: A prospective study. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1985 Jul;32(4):429-34. [PubMed]
5. Cormack RS, Lehane J. Difficult tracheal intubation in obstetrics. Anaesthesia. 1984 Nov 1;39(11):1105-11. [PubMed]
6. Adnet F, Borron SW, Racine SX, Clemessy JL, Fournier JL, Plaisance P, Lapandry C. The intubation difficulty scale (IDS) proposal and evaluation of a new score characterizing the complexity of endotracheal intubation. The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists. 1997 Dec 1;87(6):1290-7. [PubMed]
7. Caplan RA, Posner KL, Ward RJ, Cheney FW. Adverse respiratory events in anesthesia: a4` closed claims analysis. Anesthesiology. 1990 May;72(5):828-33.
8. American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Management of the Difficult Airway. Practice guidelines for management of the difficult airway. Anesthesiology. 1993;78:597-602. [PubMed]
9. Samsoon GL, Young JR. Difficult tracheal intubation: a retrospective study. Anaesthesia. 1987 May 1;42(5):487-90. [PubMed]
10. Jackson C :The technique of insertion of intratracheal insufflation tubes.Surg Gynecol Obstet 1913;17:507-9.
11. Adnet F, Borron SW, Dumas JL, Lapostolle F, Cupa M, Lapandry C. Study of the “sniffing position” by magnetic resonance imaging. The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists. 2001 Jan 1;94(1):83-6.
12. Chou HC, Wu TL. Rethinking the three axes alignment theory for direct laryngoscopy. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 2001 Feb 1;45(2):261-2. [PubMed]
13. Singhal SK, Malhotra N, Sharma S. Comparison of sniffing position and simple head extension for visualization of glottis during direct laryngoscopy. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia. 2008 Sep 1;52(5):546.
14. Adnet F, Baillard C, Borron SW, Denantes C, Lefebvre L, Galinski M, Martinez C, Cupa M, Lapostolle F. Randomized study comparing the “sniffing position” with simple head extension for laryngoscopic view in elective surgery patients. The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists. 2001 Oct 1;95(4):836-41.
15. Bhattarai B, Shrestha SK, Kandel S. Comparison of sniffing position and simple head extension for visualization of glottis during direct laryngoscopy. Kathmandu University Medical Journal. 2012 Jun 7;9(1):58-63.
16. Ambardekar M, Pandya S, Ahuja P. Comparison of the sniffing position with simple head extension for laryngoscopic view in elective surgical patients. Internet J Anesthesiol. 2008;17:15.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


