Fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of Tuberculous lymphadenitis and utility of Ziehl Neelsen stain benefits and pitfalls
Abstract
Introduction: In a developing country like India, tuberculous lymphadenitis is one of the most common presentations at OPDs. However, anti-tubercular treatment cannot be administered only on clinical suspicion. Cytomorphology with acid fast staining proves to be a valuable tool in diagnosing these cases along with culture. The study was undertaken to study the utility, limitations of fine needle aspiration cytology and various cytomorphological presentations in reference to Ziehl-Neelsen staining in tuberculous lymphadenitis and correlate the culture findings.
Methods: The study was conducted for duration of two years with total of 170 cases at a tertiary care centre. The patients with clinically suspected lymphadenopathy were selected.
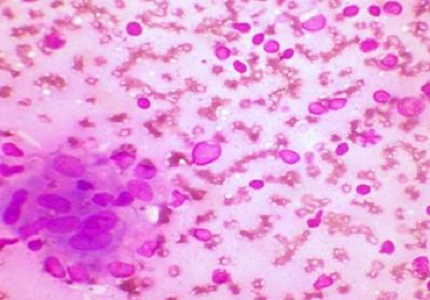
Results: The incidence of tuberculous lymphadenitis was 68.8%. Overall AFB positivity was 64.1 %. Epithelioid cell granulomas with lymphocytes were the most common cytological picture and cases showing necrosis had highest AFB positivity. Maximum patients presented in second to fourth decade of life. Cervical region was the most common site of involvement with solitary lymphadenopathy as the most common presentation in contrast to matted lymph nodes as reported by others.
Conclusion: Yet again Fine needle aspiration cytology is a safe, cheap and reliable procedure requiring minimal instrumentation and is highly sensitive to diagnose tuberculous lymphadenitis. The diagnostic index can be further increased by complementing cytomorphology with acid fast staining and culture techniques. However FNAC complimented with techniques like ELISA and PCR would give better dimensions to the current scenario of diagnosis and treatment modalities.
Downloads
References
2. Verma K, Kapila K. Aspiration cytology for diagnosis of tuberculosis--perspectives in India. Indian J Pediatr. 2002 Nov;69 Suppl 1:S39-43.
3. Jain A, Verma RK, Tiwari V, Goel MM. Dot-ELISA vs. PCR of fine needle aspirates of tuberculous lymphadenitis: a prospective study in India. Acta Cytol. 2005 Jan-Feb;49(1):17-21.
4. Chauhan LS. Challenges for the RNTCP in India. J Indian Med Assoc. 2003 Mar;101(3):152-3. [PubMed]
5. Kant L. Extra pulmonary tuberculosis: Coming out of the shadows. Indian J Tuberculosis 2004; 51: 189-90.
6. Sharma SK, Mohan A. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res. 2004 Oct;120(4):316-53.
7. Dandapat MC, Mishra BM, Dash SP, Kar PK. Peripheral lymph node tuberculosis: a review of 80 cases. Br J Surg. 1990 Aug;77(8):911-2.
8. Dua T, Ahmad P, Vasenwala S, Beg F, Malik A. A Correlation of cytomorphology with AFB positivity by smear and culture in tuberculous lymphadenitis. Indian Journal of tuberculosis 1996; 43:81-4.
9. Rajashekeran S, Gunasekeran M, Jayakumar DD, Jeyaganesh D, Bhanumati V. Tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis in HIV positive and negative patients. Indian journal of Tuberculosis 2001; 48:201-4.
10. Natraj G, Kurup S, Pandit A, Mehta P. Correlation of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology smears and culture in tuberculous lymphadenitis. Journal of Post Graduate Medicine 2002; 48:113-6.
11. Seth V, Donald PR. Essentials of tuberculosis in children. New Delhi, India: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd 1997:100-107.
12. Das DK, Pant JN, Chachra KL, Murthy NS, Satyanarayan L, Thankamma TC, Kakkar PK. Tuberculous lymphadenitis: correlation of cellular components and necrosis in lymph-node aspirate with A.F.B. positivity and bacillary count. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;33(1):1-10.
13. Gupta AK, Nayar M, Chandra M. Critical appraisal of fine needle aspiration cytology in tuberculous lymphadenitis. Acta Cytol. 1992 May-Jun;36(3):391-4.
14. Tripathy SN, Mishra N, Patel NM, Samantray DK, Das BK, Mania RN. Place of Aspiration Biopsy in the diagnosis of Lymphadenopathy. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 1985; 32:130-4.
15. Madhusudan MTV. Tuberculous lymphadenitis in children. Indian Pediatrics 1976; XIII:533-8.
16. Bedi RS, Thind GS, Arora VK. A clinico pathological study of Superficial lymphadenopathy in Northern India. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 1987; 34: 189-91.
17. Ahmed SS, Akhtar S, Akhtar K, Naseem S, Mansoor T, Khalil S. Incidence of Tuberculosis from Study of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Lymphadenoapathy and Acid fast Staining. Indian Journal of Community Medicine 2005; 30 (2).
18. David HL. Bactteriology of Mycobacteriosis. CDC Atlanta and US PHS,HEW, Supritendent of Documents US Govt. printing Office Washington DC 1976.
19. Katoch VM. National JALMA Institute for Leprosy and other Mycobacterial Diseases (ICMR). Indian Journal Medical Research 2006; 123:735-38.
20. Das DK, Lymph nodes. In Bibbo M eds Comprehensive Cytopathology, 2nd Edition Philadelphia: Saunders Company 1997:703-730.
21. Chakrabarti AK, Haider KK, Das S, Chakrabarti S. Morphological classification of tuberculous lesions: preliminary observations. Indian journal of Tuberculosis 1994; 41: 139-42.
22. Malakar D Jajoo ILN, Swarup K,Gupta OP,Jain AP, Poflee VW. Clinical Evaluation of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy. Indian Journal
tuberculosis 1991; 38:17-19.
23. Heerde PV, Miliakaus J. Lymph nodes. In Orell SR, Sterrett GF, Whitaker D eds. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology . 4th edition New Delhi : Churchill Livingstone,2005;83-124.
24. Singh UR, Bhatia A, Gadre DV, Talwar V. Cytologic diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis in children by fine needle aspiration. Indian J Pediatric. 1992 Jan-Feb;59(1):115-8.
25. Bayazit YA, Bayazit N, Namiduru M. Mycobacterial cervical lymphadenitis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2004;66(5):275-80.
26. Jindal N, Devi B, Aggarwal A. Mycobacterial cervical lymphadenitis in childhood. Indian J Med Sci. 2003 Jan;57(1):12-5. [PubMed]
27. Verenker MP, Kamath K, Pinto WMJ, Rodrigues S, Pinto WRG. Mycobacterial study of Fine Needle Aspiration in Cervical Lymphadenitis. Indian Journal Tuberculosis 1996; 43: 187-89.
28. Jayaram G, Chew MT. Fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes in HIV-infected individuals. Acta Cytol. 2000 Nov-Dec;44(6):960-6.
29. Nayak S, Puranik SC, Deshmukh SD, Mani R, Bhore AV, Bollinger RC. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Tuberculous lymphadenitis of patients with and without HIV infections. Diagnostic Cytopathol 2003; 31(4):205-206.
30. Prasoon D. Acid-fast bacilli in fine needle aspiration smears from tuberculous lymph nodes. Where to look for them. Acta Cytol. 2000 May-Jun;44(3):297-300. [PubMed]
31. Paliwal Nidhi, Thakur Sapna, Mullick Shalini and Gupta Kumud. FNAC in Tuberculous lymphadenitis: Experience from a Tertiary level reference centre. Indian Journal of tuberculosis Indian J Tuberc 2011; 58: 102-7.
32. Aljafari AS, Khalil EA, Elsiddig KE, El Hag IA, Ibrahim ME, Elsafi ME, Hussein AM, Elkhidir IM, Sulaiman GS, Elhassan AM. Diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis by FNAC, microbiological methods and PCR: a comparative study. Cytopathology. 2004 Feb;15(1):44-8.
33. Llatjos M, Romeu J, Clottet B et al. Distinctive Cytology pattern for diagnosing tuberculous lymph node in AIDS J Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome1993;6:1335-338.
34. Arora B, Arora DR. Fine needle aspiration cytology in diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. Indian J Med Res. 1990 May;91:189-92.
35. Radhika S, Gupta SK, Chakrabarti A, Rajwanshi A, Joshi K. Role of culture for mycobacteria in fine-needle aspiration diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. Diagn Cytopathol. 1989;5(3):260-2.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


