Study of carotid intimal thickness in ischemic stroke and coronary artery disease
Abstract
Introduction: Intima medial thickness of common carotid arteries can be used to measure generalized atherosclerosis and also surrogate marker of coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke. It is extensively used examine the carotid IMT and to evaluate the regression of atherosclerosis lesion in interventional studies.
Material and methods: It was a cross sectional study conducted in the department of Medicine of a tertiary care centre, Indore, India. Carotid ultrasonography examinations were performed with the use of shimad Zu (SDU 2200) & Toshiba just vision-400 sonography machine equipped with a 7.5 to 10 MHz linear-array transducer. With the subject in the supine position and the neck in slight hyperextension the common carotid artery, carotid bulb, and the extra-cranial part of internal carotid artery was identified of both side and IMT was measured as the distance between the luminal Intimal interface and the medial adventitial interface.
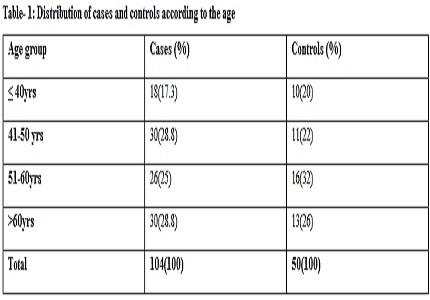
Results: P < .001 which is highly significant i.e. increased IMT is strong risk factor for Ischemic stroke and CAD in all the age groups. P < .001 which is highly significant i.e. increased IMT is strong risk factor for both ischemic stroke and Coronary artery disease. When carotid intimal thickness between patients of ischemic heart disease and coronary artery disease is compared, we observed a P value > .05, which is not significant, i.e. there is no much difference of IMT in ischemic Stroke and Coronary artery disease.
Conclusion: Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson plus syndrome is a group of sporadic, neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system. There are only a few reports about the frequency of neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with Parkinson disease from India and no such Indian report in patients with Parkinson plus syndrome
Downloads
References
2. Salonen R, Salonen JT. Progression of carotid atherosclerosis and its determinants: a population-based ultrasonography study. Atherosclerosis. 1990 Feb;81(1):33-40. [PubMed]
3. Jie J. Cao, MD, MPH; Chau Thach, PhD; Teri A. Manolio, MD, PhD; Bruce M. Psaty, MD, PhD; Lewis H. Kuller, MD, DrPH; Paulo H.M. Chaves, MD, PhD; Joseph F. Polak, MD, MPH; Kim Sutton-Tyrrell, PhD; David M. Herrington, MD, MHS; Thomas R. Price, MD; Mary Cushman, MD, MSc Carotid Intima-Media Thickness, and Incidence of Ischemic Stroke in the Elderly 1991;22:1155-1163.
4. Lee EJ, Kim HJ, Bae JM, Kim JC, Han HJ, Park CS, Park NH, Kim MS, Ryu JA. Relevance of common carotid intima-media thickness and carotid plaque as risk factors for ischemic stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 May;28(5):916-9. [PubMed]
5. Nikić P, Savić M, Zarić N, Durić D. [Common carotid artery intima-media thickness, carotid atherosclerosis and subtypes of ischemic cerebral disease]. Med Pregl. 2003;56 Suppl 1:85-91.
6. Michiel L. Bots, MD, PhD; Arno W. Hoes, MD, PhD; Peter J. Koudstaal, MD, PhD; Albert Hofman, MD, PhD; ; Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD Common Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Risk of Stroke and Myocardial Infarction The Rotterdam Study 1997;96:1432-37.
7. G. Geroulakos, D. J. O'gorman, E. Kalodiki, D. J. Sheridan And A. N. Nicolaides The carotid intima-media thickness as a marker of the presence of severe symptomatic coronary artery disease European Heart Journal 1994 15(6):781-85.
8. A Kablak-Ziembicka, W Tracz, T Przewlocki, P Pieniazek, A Sokolowski and M Konieczynska. Association of increased carotid intima-media thickness with the extent of coronary artery disease. Heart 2004; 90:1286-90. [PubMed]
9. Poredos P. Intima-media thickness: indicator of cardiovascular risk and measure of the extent of atherosclerosis. Vasc Med. 2004 Feb;9(1):46-54. [PubMed]
10. Joke M. Dijk, Yolanda van der Graaf, Michiel L. Bots, Diederick E. Grobbee1, Ale Algra on behalf of the SMART study group Carotid intima–media thickness and the risk of new vascular events in patients with manifest atherosclerotic disease: the SMART study European Heart Journal 2006 27(16):1971-78.
11. Staub D, Meyerhans A, Bundi B, Schmid HP, Frauchiger B. Prediction of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: comparison of the internal carotid artery resistive index with the common carotid artery intima-media thickness. Stroke. 2006 Mar;37(3):800-5. Epub 2006 Jan 26.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


