Study of the effect of intrathecal dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant in spinal anesthesia for Gynecological Surgery
Abstract
Background: A randomized controlled study was designed to investigate the effects of addition of dexmetomedine to hyperbaric bupivacaine 0.5% for spinal anaesthesia in patients undergoing gynaecological surgeries, in terms of vital parameters, onset and duration of sensory andmotor block, intra and post operative pain and adverse effects.
Methods: Sixty adult ASA Grade I and II patients were randomly divided equally in to dexmetomedine and control group. Control group received intrathecal 3.0 ml of 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine with 0.5 ml of normal saline and dexmetomedine group received identical volume of intrathecal dexmetomedine 5 μg with hyperbaric bupivacaine.
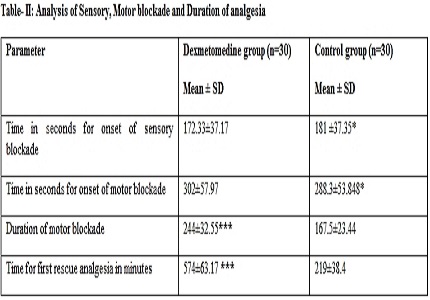
Results: Mean time for post operative analgesia was significantly longer in dexmetomedine group (9.6 hours) than in the control group (3.55 hours). (p-value<0.01). Heart rate and blood pressure compared at 30 minute and 45 minute intervalswere significantly less in dexmetomedine group. (p-value< 0.05). Bradycardia and hypotension did not require any therapeutic intervention. Dexmetomedine group patients were found to be more sedated than control group.
Conclusion: Adding dexmetomedine 5 μg to intrathecal bupivacaine prolongs the duration of spinal anaesthesia and analgesia. It is safe and is likely to be as effective as higher doses of bupivacaine without severe adverse effects
Downloads
References
2. Coskuner I, Tekin M, Kati I, Yagmur C, Elcicek K. Effects of dexmedetomidine on the duration of anaesthesia and wakefulness in bupivacaine epidural block.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2007 Jun;24(6):535-40. Epub 2007 Jan 23. [PubMed]
3. Carollo DS, Nossaman BD, Ramadhyani U. Dexmedetomidine: a review of clinical applications. CurrOpinAnaesthesiol. 2008 Aug;21(4):457-61. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e328305e3ef. [PubMed]
4. Collins SL, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. The visual analogue pain intensity scale: what is moderate pain in millimetres? Pain. 1997 Aug;72(1-2):95-7. [PubMed]
5. Pöpping DM, Zahn PK, Van Aken HK, Dasch B, Boche R, Pogatzki-Zahn EM. Effectiveness and safety of postoperative pain management: a survey of 18 925 consecutive patients between 1998 and 2006 (2nd revision): a database analysis of prospectively raised data. Br J Anaesth. 2008 Dec;101(6):832-40. doi: 10.1093/bja/aen300. Epub 2008 Oct 2.
6. Takano YO, Yaksh TL. Characterization of the pharmacology of intrathecally administered alpha-2 agonists and antagonists in rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.1992May1;261(2):764-72.
7. Yaksh TL, Jage J, Takano Y. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of medullar agents: c. The spinal action of α2-adrenergic agonists as analgesics. Baillière's clinical anaesthesiology. 1993 Jan 1;7(3):597-614.
8. Fukushima K, Nishimi Y, Mori K, Takeda J. Effect of epidurally administered dexmedetomidine on sympathetic activity and postoperative pain in man. AnesthAnalg. 1996;82:S121.
9. Singh NR, Wapang AO, Singh SS. Dexmedetomidine as an Intrathecal Adjuvant in Spinal Anaesthesia: A Study. International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (IJHSR). 2015;5(9):146-52.
10. Bajwa S, Kulshrestha A. Dexmedetomidine: an adjuvant making large inroads into clinical practice. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2013 Oct;3(4):475-83. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.122044. [PubMed]
11. Roberts SB, Wozencraft CP, Coyne PJ, Smith TJ. Dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant analgesic for intractable cancer pain.J Palliat Med. 2011 Mar;14(3):371-3. doi: 10.1089/jpm.2010.0235. Epub 2011 Jan 17. [PubMed]
12. Kim JE, Kim NY, Lee HS, Kil HK.Effects of intrathecaldexmedetomidine on low-dose bupivacaine spinal anesthesia in elderly patients undergoing transurethral prostatectomy.Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 2013;36(6):959-65.
13. Seop Chang Y, Kim JE, Sung TY. Low-dose Bupivacaine with Dexmedetomidine Prevents Hypotension After Spinal Anesthesia. The Open Anesthesiology Journal. 2015 Dec 28;9(1).
14. Abdallah FW, Abrishami A, Brull R. The facilitatory effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on the duration of spinal anesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2013 Jul 1;117(1):271-8.
15. Al-Mustafa MM, Abu-Halaweh SA, Aloweidi AS, Murshidi MM, Ammari BA, Awwad ZM, Al-Edwan GM, Ramsay MA. Effect of dexmedetomidine added to spinal bupivacaine for urological procedures. Saudi medical journal. 2009;30(3):365-70.
16. Wu HH, Wang HT, Jin JJ, Cui GB, Zhou KC, Chen Y, Chen GZ, Dong YL, Wang W. Does dexmedetomidine as a neuraxial adjuvant facilitate better anesthesia and analgesia? A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 26;9(3):e93114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093114. eCollection 2014.
17. Jung SH, Lee SK, Lim KJ, Park EY, Kang MH, Lee JM, Lee JJ, Hwang SM, Hong SJ. The effects of single-dose intravenous dexmedetomidine on hyperbaric bupivacaine spinal anesthesia.J Anesth. 2013 Jun;27(3):380-4. doi: 10.1007/s00540-012-1541-0. Epub 2013 Jan 10.
18. Kanazi GE, Aouad MT, Jabbour-Khoury SI, Al Jazzar MD, Alameddine MM, Al-Yaman R, Bulbul M, Baraka AS. Effect of low-dose dexmedetomidine or clonidine on the characteristics of bupivacaine spinal block.ActaAnaesthesiol Scand. 2006 Feb;50(2):222-7. [PubMed]
19. Halder S, Das A, Mandal D, Chandra M, Ray S, Biswas MR, Mandal P, Das T. Effect of different doses of dexmedetomidine as adjuvant in bupivacaine-induced subarachnoid block for traumatized lower limb orthopaedic surgery: A prospective, double-blinded and randomized controlled study. J ClinDiagn Res. 2014 Nov 1;8. [PubMed]
20. Gupta R, Verma R, Bogra J, Kohli M, Raman R, Kushwaha JK. A Comparative study of intrathecaldexmedetomidine and fentanyl as adjuvants to Bupivacaine.Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology. 2011 Jul 1;27(3):339. [PubMed]
21. Shahi V, Verma AK, Agarwal A, Singh CS. A comparative study of magnesium sulfate vsdexmedetomidine as an adjunct to epidural bupivacaine.Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology. 2014 Oct 1;30(4):538.
22. Solanki SL, Bharti NA, Batra YK, Jain A, Kumar P, Nikhar S. The analgesic effect of intrathecaldexmedetomidine or clonidine, with bupivacaine, in trauma patients undergoing lower limb surgery: a randomised, double-blind study. Anaesthesia and intensive care. 2013 Jan 1;41(1):51.
23. Reddy VS, Shaik NA, Donthu B, Sannala VK, Jangam V. Intravenous dexmedetomidine versus clonidine for prolongation of bupivacaine spinal anesthesia and analgesia: A randomized double-blind study. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology. 2013 Jul 1;29(3):342.
24. Hanoura SE, Hassanin R, Singh R. Intraoperative conditions and quality of postoperative analgesia after adding dexmedetomidine to epidural bupivacaine and fentanyl in elective cesarean section using combined spinal-epidural anesthesia. Anesthesia, essays and researches. 2012 Dec;7(2):168-72.
25. Grewal A. Dexmedetomidine: New avenues. J AnaesthesiolClinPharmacol. 2011 Jul;27(3):297-302. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.83670. [PubMed]
26. Sudheesh K, Harsoor S. Dexmedetomidine in anaesthesia practice: A wonder drug? Indian J Anaesth. 2011 Jul;55(4):323-4. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.84824.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


