B+Myeloid MPAL: boys have it all?
Abstract
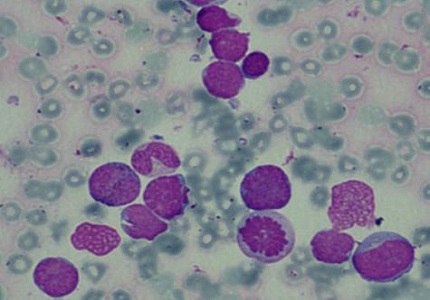
Background: MPAL are rare, accounts 4% of acute leukemias .B+MYELOID are extremely rare. There is not much information on biologic features of these strange leukemias. Present study from Kidwai state cancer institute focused on rare types of MPAL, especially B+MYELOID MPAL.
Design and Methods: We classified MPAL based on WHO 2008 classification and summarised diagnostic criteria, cytochemistry, cytogenetics clinical , immunophenotyping and molecular featuresofB+MYELOID MPAL.
Results: Out of 27 MPAL cases reported in the present study 13 cases were B/Myeloid, followed by B+T MPAL ,T+Myeloid .Very few cases of undifferentiated and unclassifiable leukemias were reported. 13 B/myeloid MPAL cases were reported majority of these, to our surprise were seen in children (8 cases) .Only 5 cases were seen in adults. Except a single Ph (+) case in a girl, rest all pediatric B/Myeloid cases, surprisingly were seen in Boys.
Conclusion: Among MPAL high incidence of B+MYELOID 13/27 cases (48%) was noted. High incidence of B/myeloid MPAL was seen in children and majority were Boys (87.5%).All paediatric cases were treated by MCP 841 Protocol &attained remission at end of induction, 5/8 cases were referred for Bone marrow transplant.3 cases are on follow up after median of 6 months and are in remission.
Downloads
References
2. Borowitz M J Bene MC, Harris NL, PorwitA,Matutes E Acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage :WHO classification of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue 4th ed.IARC,Lyon,France:2008.pp 150-155. [PubMed]
3. EstellaMatutes,RicardoMorilla,NahlaFarahat,FelixCarbonell,JohnSwansbury,MartinDyer,DanielCatovsky .Recent Advances in the cyto biology of Leukemias,Definition of Acute BiphenotypicLeukemia.Haematologica 1997; 82(1):64-66.
4. Tseih Sun .Mixed phenotypic acute leukemia: In Flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry and molecular genetics for hematologic neoplasms: 2nd edition. Wolterskluwer/Lippincott Williams & wilkins,Phildelphia.2012;chapter 16:168-173.
5. Sameer kulkarni,MichaelLill and DimitriosTzachanis .HSOA Journal of Hematology.Blood transfusion and Disorders.JHematolBloodTransfus Disord2014;vol1:issue1.
6. RenuSukumaran,RekhaANair,PriyaMaryJacob,KunjulekshmiAmmaraveendrannairAnila,ShruthyPrem,RajeshwaryBinitha et al .Flowcytometry analysis of Mixed phenotype acute leukemia: Experience from a tertiary oncology center.Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.June 2015;58,181-186.DOI 10.4103/0377-4929.155309.
7. Gerr H, Zimmermann M, Schrappe M, Dworzak M, Ludwig WD, Bradtke J, Moericke A, Schabath R, Creutzig U, Reinhardt D. Acute leukaemias of ambiguous lineage in children: characterization, prognosis and therapy recommendations. Br J Haematol. 2010 Apr;149(1):84-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.08058.x. Epub 2010 Jan 18.
8. Zhang YM, Wu DP, Sun AN, Qiu HY, Sun YM, He GS, Jin ZM, Tang XW, Miao M, Fu ZZ, Han Y, Chen SN, Zhu MQ. [Study on the clinical characteristics of 32 patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemia]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Jan;32(1):12-6. [PubMed]
9. Owaidah TM, Al Beihany A, Iqbal MA, Elkum N, Roberts GT. Cytogenetics, molecular and ultrastructural characteristics of biphenotypic acute leukemia identified by the EGIL scoring system. Leukemia. 2006 Apr;20(4):620-6. [PubMed]
10. Weir EG, Ali Ansari-Lari M, Batista DA, Griffin CA, Fuller S, Smith BD, Borowitz MJ. Acute bilineal leukemia: a rare disease with poor outcome. Leukemia. 2007 Nov;21(11):2264-70. Epub 2007 Jul 5. [PubMed]
11. JeffreyE.Rubnitz,MihaelaOnciu,Stanley Pounds ,Sheila shurt ,Xueyancao,suiana c Raimondi et al ,Acute mixed lineage leukemia in children: the experience of St Jude Children’s Research Hospital.Blood 2009;113:5083-5089. [PubMed]
12. Zhang Y, Tan L, Zhang X, Wei H, Hu Q. Clinical Study of Acute Mixed-lineage Leukemia in 14 Children. Iran J Pediatr. 2011 Dec;21(4):521-5.
13. Gujral S, Polampalli S, BadrinathY, Kumar A, SubramanianPG,Raje G, et al.Clinico-hematological profile in biphenotypic acute leukemia.Indian Journal of Cancer, April-June, 2009; Vol. 46: No. 2pp. 160-168.Doi 10.4103/0019-509x49156.
14. Kohla SA, Sabbah A A,Omri H E, Ibrahim FA,Otazu I B, Alhajri H Yassin M A.Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia with Two Immunophenotypically Distinct B and T Blasts Populations,Double Ph(+) Chromosome and complex Karyotype.Clin Med Insights Blood Disord.2015;sept21.doi:10.4137/CMBDs24631.c collection2015.
15. Wolach O, Stone RM. How I treat mixed-phenotype acute leukemia. Blood. 2015 Apr 16;125(16):2477-85. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-551465. Epub 2015 Jan 20. [PubMed]
16. Weinberg OK, Arber DA. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: historical overview and a new definition. Leukemia. 2010 Nov;24(11):1844-51. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.202. Epub 2010 Sep 16.
17. LingzhiYan,NanaPing,MinggingZhu,AiningSun,YongquanXue,ChanggengRuanetal.Clinicalimmunophenotypic, Cytogenetic, And Molecular Genetic Features In 117 Adult Patients With Mixed-Phenotype Acute Leukemia Defined By WHO-2008 Classification.Haematologica November 2012 ; 97: 1708-1712.DOI.10.3324/HAEMATOL.2012.064485.
18. Maciejewski JP, Haferlach T. Introduction: molecular pathogenesis of hematologic malignancies. Semin Oncol. 2012 Feb;39(1):9-12. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2011.12.002.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


