Comparison of i-gel with LMA ProSeal for ease of insertion in adultanaesthetised paralysed patients: a prospective randomized trial
Abstract
Background: i-gel, a recently developed non-inflatable supraglottic airway device, a suitable better alternative to cuffed inflatable suprglottic airway device like LMA ProSeal.
Aim and objectives: This study aimed to compare the ease of insertion to achieve early successful airway between LMA ProSeal and i-gel. The secondary objectives were to compare hemodynamic parameters and any airway complications.
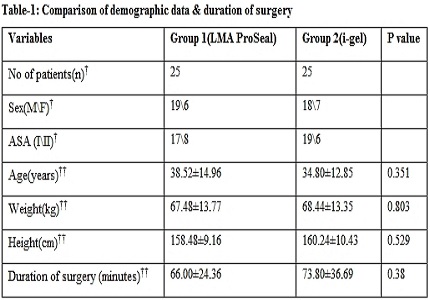
Materials and methods: This prospective randomized study done in fifty (n=25, each group) ASA I and II adult patients, aged between 20 and 65 years of either sex scheduled for elective surgeries. Patients airway was secured with appropriate size either LMA ProSeal or i-gel. The time taken for successful insertion, number of attempts and ease ofgastric tube placement were recorded. Hemodynamic parameters at basal (pre operative), 1, 3 & 5 minutes after insertion were recorded. Blood stain of device and any postoperative airway complications were noted.
Results: Time taken for successful insertion was significantly less in i-gel group [Group 1(LMA ProSeal) 20.56±2.00, Group 2 (i-gel) 12.08±1.53, p=0.001*]. Time taken for gastric tube placement was significantly less in i-gel group [Group 1(LMA ProSeal) 31.96±4.58, Group 2 (i-gel) 21.48±2.55, p=0.001*]. Among hemodynamic parameters, heart rate immediately after insertion of device was stable in i-gel group. The numbers of insertion attempts were also less with i-gel group.
Conclusion: In our study, ease ofinsertion with less number of attempts was observed with i-gel group.So i-gel found to be the better alternative to LMA ProSeal.
Downloads
References
2. Levitan RM, Kinkle WC. Initial anatomic investigations of the I-gel airway: a novel supraglottic airway without inflatable cuff. Anaesthesia. 2005 Oct;60(10):1022-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2005.04258.x. [PubMed]
3. Jadhav PA, Dalvi NP, Tendolkar BA . I-gel versus laryngeal mask airway-Proseal: Comparison of twosupraglottic airway devices in short surgical procedures. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Apr-Jun;31(2):221-5. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.155153.
4. Kannaujia A, Srivastava U, Saraswat N, Mishra A, Kumar A, Saxena S. A preliminary study of I-Gel: A new supraglottic airway device. Indian J Anaesth. 2009 Feb;53(1):52-6. [PubMed]
5. Singh I, Gupta M, Tandon M. Comparison of Clinical Performance of I-Gel TM with LMA-Proseal in Elective Surgeries. Indian J Anaesth. 2009 Jun;53(3):302-5. [PubMed]
6. Kini G, Devanna GM, Mukkapati KR, Chaudhuri S, Thomas D. Comparison of I-gel with proseal LMA in adult patients undergoing elective surgical procedures under general anesthesia without paralysis: A prospective randomized study. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 2014;30:183-7. [PubMed]
7. Chauhan G, Nayar P, Seth A, Gupta K, Panwar M, Agrawal N. Comparison of clinical performance of the I-gel with LMA proseal. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Jan;29(1):56-60. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.105798. [PubMed]
8. Brimacombe J, Keller C, Fullekrug B, et al. A multicenter study comparing the ProSeal with the Classic laryngeal mask airway in anesthetized, nonparalyzed patients. Anesthesiology 2002; 96(2): 289–95. [PubMed]
9. Shin WJ, Cheong YS, Yang HS, Nishiyama T. The supraglottic airway I-gel in comparison with ProSeal laryngeal mask airway and classic laryngeal mask airway in anaesthetized patients. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010 Jul;27(7):598-601. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e3283340a81.
10. Das B, Mitra S, Jamil SN, Varshney RK. Comparison of three supraglottic devices in anesthetised paralyzed children undergoing elective surgery. Saudi J Anaesth. 2012 Jul;6(3):224-8. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.101212.
11. Gatward JJ, Cook TM, Seller C, Handel J, Simpson T, Vanek V, et al. Evaluation of the size 4 i-gel™ airway in one hundred non-paralysed patients. Anaesthesia. 2008 Oct;63(10):1124-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2008.05561.x. Epub 2008 Jul 9.
12. Sharma B, Sehgal R, Sahai C, Sood J. PLMA vs. I-gel: A Comparative Evaluation of Respiratory Mechanics in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;26(4):451-7.
13. Lopez-Gil M, Brimacombe J, Garcia G. A randomized non crossover study comparing the proseal andclassic laryngeal mask airway in anaesthetized children. Br J Anaesth. 2005 Dec;95(6):827-30. Epub 2005 Oct 6. [PubMed]
14. Ekinci O, Abitagaoglu S, Turan G, Sivrikaya Z, Bosna G, Özgultekin A. The comparison of ProSeal and I-gel laryngeal mask airways in anesthetized adult patients under controlled ventilation. Saudi Med J. 2015 Apr;36(4):432-6. doi: 10.15537/smj.2015.4.10050. [PubMed]
15. Shimbori H, Ono K, Miwa T, Morimura N, Noguchi M, Hiroki K. Comparison ofthe LMA-ProSeal and LMA-Classic in children.Br J Anaesth. 2004 Oct;93(4):528-31. Epub 2004 Aug 6. [PubMed]
16. Hernandez MR, Klock PA Jr, Ovassapian A. Evolution of the extraglottic airway: a review of its history, applications, and practical tips for success. Anesth Analg. 2012 Feb;114(2):349-68. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31823b6748. Epub 2011 Dec 16.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


