CORRELATION BETWEEN IMPULSE OSCILLOMETRY AND SPIROMETRY IN ASSESSMENT OF SMALL AIRWAY DYSFUNCTION IN ASYMPTOMATIC SMOKERS
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The traditional pulmonary function tests may be inadequate to detect Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) pathological damage and smoking-related lung disease. Therefore, more reliable methods for airway evaluation are required for patients with COPD. Impulse oscillation system (IOS) is a novel method for reactance and airway resistance measurements. It is a kind of forced oscillation, where sound waves oscillate at different frequencies, usually between 5 and 20 Hz, and propagate through the bronchial tree. It measures the proximal airway resistance (measured at 20 Hz [R20]), the peripheral airway resistance (measured at R5–R20), and the overall airway resistance (measured at 5 Hz [R5]). Resistance and reactance make up impedance. IOS provides more detailed information than spirometry on regional lung function and should be considered as being complementary to spirometry to comprehensively assess lung function in COPD. Also, small airway dysfunction (SAD), if detected early, can help in preventing progression of the disease with proper counselling and smoking cessation.
OBJECTIVES: The objective of our study is to assess the correlation between impulse oscillometry and spirometry parameters in small airway dysfunction in asymptomatic smokers in a tertiary care centre; to determine the association of smoking index with impulse oscillometry small airway dysfunction parameter R5-R20.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Study was conducted in Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Medical college Hospital, Thiruvananthapuram. The present cross- sectional study included asymptomatic current smokers, eligible participants underwent spirometry and oscillometry and results compared.
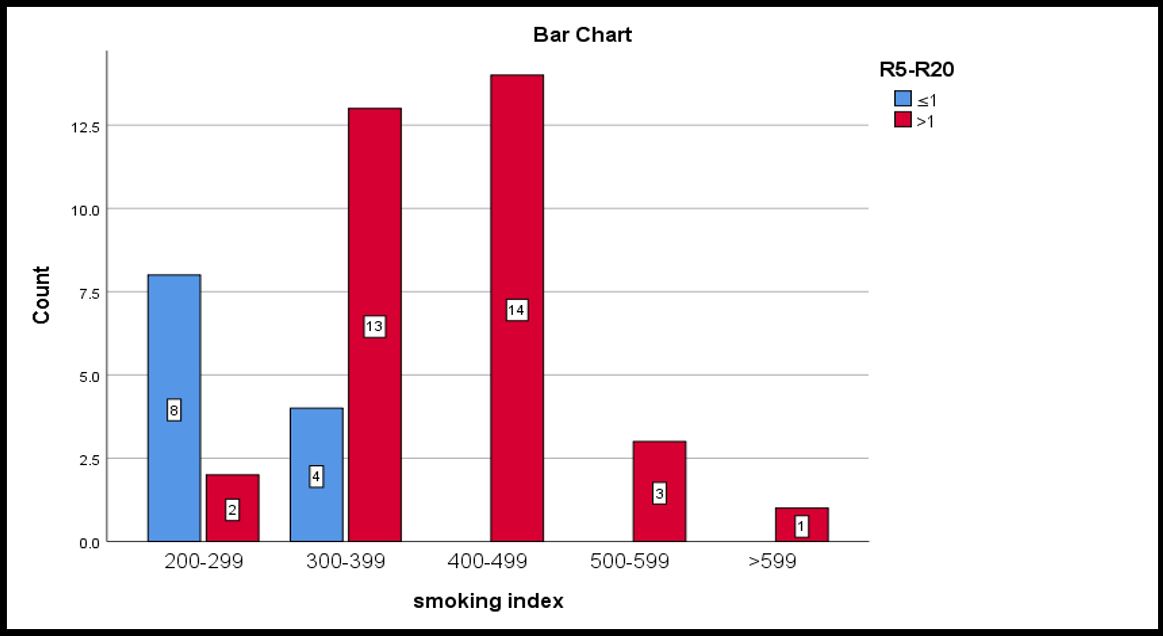
RESULTS: Out of 45 patients studied, 44.4% (n=20), fell within the 45-60 age range. The majority of participants, comprising 37.8% (n=17), had a Smoking Index ranging from 300 to 399. Correlation analysis between FEF (25-75) vs (R5-R20) done by Pearson correlation test reported very mild negative correlation between them (r=-0.053, p=0.728). Chi square test reported significant association between smoking index & R5-R20 (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION: Impulse oscillometry is capable to detect SAD in asymptomatic smokers with preserved spirometry and with FEF(25-75) values in the normal range. We verify that IOS offers parameters that can contribute to conventional pulmonary function tests.
Downloads
References
2. Rikitake Y, Kim HH, Huang Z, Seto M, Yano K, Asano T, et al. Inhibition of Rho kinase (ROCK) leads to increased cerebral blood flow and stroke protection. Stroke. 2005 Oct;36(10):2251–7.
3. Nishi SPE, Wang Y, Kuo YF, Goodwin JS, Sharma G. Spirometry use among older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: 1999-2008. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013 Dec;10(6):565–73.
4. Kwon DS, Choi YJ, Kim TH, Byun MK, Cho JH, Kim HJ, et al. FEF25-75% Values in Patients with Normal Lung Function Can Predict the Development of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020 Nov 12;15:2913–21.
5. Dubois AB, Brody AW, Lewis DH, Burgess BF. Oscillation mechanics of lungs and chest in man. J Appl Physiol. 1956 May;8(6):587–94.
6. Goldman MD. Clinical application of forced oscillation. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2001;14(5):341–50.
7. King GG, Bates J, Berger KI, Calverley P, Melo PL de, Dellacà RL, et al. Technical standards for respiratory oscillometry. Eur Respir J [Internet]. 2020 Feb 1 [cited 2024 Jun 29];55(2). Available from: https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/55/2/1900753
8. Ranga V, Kleinerman J. Structure and function of small airways in health and disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Dec;102(12):609–17.
9. McNulty W, Usmani OS. Techniques of assessing small airways dysfunction. Eur Clin Respir J. 2014 Oct 17;1:10.3402/ecrj.v1.25898.
10. Weibel ER. Principles and methods for the morphometric study of the lung and other organs. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol. 1963 Feb;12:131–55.
11. Tatsis G, Horsfield K, Cumming G. Distribution of dead space volume in the human lung. Clin Sci Lond Engl 1979. 1984 Nov;67(5):493–7.
12. Wiebe BM, Laursen H. Human lung volume, alveolar surface area, and capillary length. Microsc Res Tech. 1995 Oct 15;32(3):255–62.
13. Baraldo S, Turato G, Saetta M. Pathophysiology of the small airways in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Int Rev Thorac Dis. 2012;84(2):89–97.
14. Wagner EM, Liu MC, Weinmann GG, Permutt S, Bleecker ER. Peripheral lung resistance in normal and asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):584–8.
15. Resistance of central and peripheral airways measured by a retrograde catheter | Journal of Applied Physiology [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jun 29]. Available from: https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/jappl.1967.22.3.395
16. Ronish BE, Couper DJ, Barjaktarevic IZ, Cooper CB, Kanner RE, Pirozzi CS, et al. Forced Expiratory Flow at 25%-75% Links COPD Physiology to Emphysema and Disease Severity in the SPIROMICS Cohort. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis Miami Fla. 2022 Apr 29;9(2):111–21.
17. Quanjer PH, Stanojevic S, Cole TJ, Baur X, Hall GL, Culver BH, et al. Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3-95-yr age range: the global lung function 2012 equations. Eur Respir J. 2012 Dec;40(6):1324–43.
18. D X, Z C, S W, K H, J X, L Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of small airway dysfunction, and association with smoking, in China: findings from a national cross-sectional study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:1081–93.
19. Knox-Brown B, Patel J, Potts J, Ahmed R, Aquart-Stewart A, Cherkaski HH, et al. Small airways obstruction and its risk factors in the Burden of Obstructive Lung Disease (BOLD) study: a multinational cross-sectional study. Lancet Glob Health. 2023 Jan;11(1):e69–82.
20. McDonough JE, Yuan R, Suzuki M, Seyednejad N, Elliott WM, Sanchez PG, et al. Small-airway obstruction and emphysema in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2011 Oct 27;365(17):1567–75.
21. Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005 Aug 1;26(2):319–38.
22. Goldman MD, Saadeh C, Ross D. Clinical applications of forced oscillation to assess peripheral airway function. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2005 Aug 25;148(1–2):179–94.
23. Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agustí AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb 15;187(4):347–65.
24. Boggs PB, Bhat KD, Vekovius WA, Debo MS. Volume-adjusted maximal mid-expiratory flow (Iso-volume FEF25-75%): definition of “Significant” responsiveness in healthy, normal subjects. Ann Allergy. 1982 Mar;48(3):137–8.
25. Gupta N, Sachdev A, Gupta D, Gupta S. Oscillometry – The future of estimating pulmonary functions. Karnataka Paediatr J. 2021 Jan 25;35(2):79–87.
26. Oostveen E, MacLeod D, Lorino H, Farré R, Hantos Z, Desager K, et al. The forced oscillation technique in clinical practice: methodology, recommendations and future developments. Eur Respir J. 2003 Dec 1;22(6):1026–41.
27. Peslin R, Jardin P, Duvivier C, Begin P. In-phase rejection requirements for measuring respiratory input impedance. J Appl Physiol. 1984 Mar;56(3):804–9.
28. Salvi S, Ghorpade D, Vanjare N, Madas S, Agrawal A. Interpreting lung oscillometry results: Z-scores or fixed cut-off values? ERJ Open Res. 2023 Mar 27;9(2):00656–2022.
29. Pisi R, Aiello M, Frizzelli A, Calzetta L, Marchi L, Bertorelli G, et al. Detection of Small Airway Dysfunction in Asymptomatic Smokers with Preserved Spirometry: The Value of the Impulse Oscillometry System. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:2585–90.
30. Skloot G, Goldman M, Fischler D, Goldman C, Schechter C, Levin S, et al. Respiratory symptoms and physiologic assessment of ironworkers at the World Trade Center disaster site. Chest. 2004 Apr;125(4):1248–55.
31. Li LY, Yan TS, Yang J, Li YQ, Fu LX, Lan L, et al. Impulse oscillometry for detection of small airway dysfunction in subjects with chronic respiratory symptoms and preserved pulmonary function. Respir Res. 2021 Feb 24;22(1):68.
32. Su ZQ, Guan WJ, Li SY, Ding M, Chen Y, Jiang M, et al. Significances of spirometry and impulse oscillometry for detecting small airway disorders assessed with endobronchial optical coherence tomography in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:3031–44.
33. Malu K, Mullerpattan J, Mahashur A. Detection of small airways disease by impulse oscillometry among smokers and non-smokers with normal spirometry. Eur Respir J [Internet]. 2022 Sep 4 [cited 2024 Jul 1];60(suppl 66). Available from: https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/60/suppl_66/4064
34. Liwsrisakun C, Chaiwong W, Pothirat C. Comparative assessment of small airway dysfunction by impulse oscillometry and spirometry in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma with and without fixed airflow obstruction. Front Med [Internet]. 2023 May 17 [cited 2024 Jul 1];10. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2023.1181188/full
35. Aggarwal AN, Agarwal R, Dhooria S, Prasad K, Sehgal IS, Muthu V, et al. Joint Indian Chest Society-National College of Chest Physicians (India) guidelines for spirometry. Lung India Off Organ Indian Chest Soc. 2019 Apr;36(Suppl 1):S1–35.
36. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease - GOLD [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jul 2]. 2024 GOLD Report. Available from: https://goldcopd.org/2024-gold-report/
37. Pefura-Yone EW, Kengne AP, Tagne-Kamdem PE, Afane-Ze E. Clinical significance of low forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of vital capacity following treated pulmonary tuberculosis: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2014 Jul 1;4(7):e005361.
38. Chen Y sheng, Li X qin, Li H ru, Miao Y, Lian S qing, Lu F feng, et al. Risk Factors for Small Airway Obstruction among Chinese Island Residents: A Case-Control Study. PLOS ONE. 2013 Jul 18;8(7):e68556.
39. Thamrin C, Dellacà RL, Hall GL, Kaczka DW, Maksym GN, Oostveen E, et al. Technical standards for respiratory oscillometry: test loads for calibration and verification. Eur Respir J. 2020 Oct;56(4):2003369.
40. Al-Mutairi SS, Sharma PN, Al-Alawi A, Al-Deen JS. Impulse oscillometry: an alternative modality to the conventional pulmonary function test to categorise obstructive pulmonary disorders. Clin Exp Med. 2007 Jun;7(2):56–64.
41. Kanda S, Fujimoto K, Komatsu Y, Yasuo M, Hanaoka M, Kubo K. Evaluation of respiratory impedance in asthma and COPD by an impulse oscillation system. Intern Med Tokyo Jpn. 2010;49(1):23–30.
42. Winkler J, Hagert-Winkler A, Wirtz H, Schauer J, Kahn T, Hoheisel G. [Impulse oscillometry in the diagnosis of the severity of obstructive pulmonary disease]. Pneumol Stuttg Ger. 2009 May;63(5):266–75.
43. Verbanck S, Schuermans D, Meysman M, Paiva M, Vincken W. Noninvasive assessment of airway alterations in smokers: the small airways revisited. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004 Aug 15;170(4):414–9
Copyright (c) 2025 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


