Influence of Family History on the Age of Onset and Complication Spectrum in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Familial Impact on T2DM Onset and Complications
Abstract
Background:
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is a prevalent chronic health condition globally, with its onset and complications significantly influenced by genetic and environmental factors. This study aimed to assess the influence of family history on the age of onset and complication spectrum among T2DM patients.
Methods: This descriptive cross-sectional study recruited 500 participants diagnosed with T2DM. Data were collected through structured interviews and clinical assessments, focusing on demographics, medical and family history, age of onset, and diabetes-related complications.
Chi-Square and logistic regression analyses were employed to examine the association between family history and diabetes complications, adjusting for confounders.
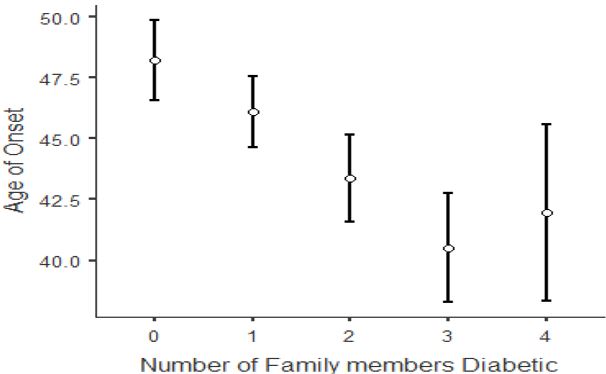
Results: Among the participants, 73.8% reported a positive family history. The mean age of onset for those with a family history was significantly lower (43.8 ± 9.86 years) compared to those without (48.24 ± 9.87 years; p < 0.001). Patients with higher HbA1c levels were younger, had an earlier onset of diabetes, and a higher prevalence of hypertension. The age of onset was earlier, if more family members had a history of diabetes. Complications were present in 80.8% of the cohort, with the most common being diabetic peripheral neuropathy (70.6%). Logistic regression analysis indicated that having siblings with diabetes was a significant predictor for general diabetic complications (OR=2.589, CI: 1.481 to 4.53, p<.001), diabetic retinopathy (OR=1.981, CI: 1.20 to 3.26, p=0.007), and diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) (OR=1.709, CI: 1.042 to 2.8, p=0.034).
Conclusion: The study highlights the significant influence of family history on the age of onset and the spectrum of complications in T2DM. These findings suggest the necessity for comprehensive family history assessments in clinical settings to identify at-risk individuals for early intervention and personalized management strategies.
Downloads
References
2. Alberti KGMM, Zimmet P, Shaw J. International Diabetes Federation: a consensus on Type 2 diabetes prevention. Diabetic Medicine. 2007;24:451–63.
3. Ikwuka AO, Omoju DI, Mahanera OK. PROFILING OF CLINICAL DYNAMICS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS IN PATIENTS: A PERSPECTIVE REVIEW. World Journal of Current Med and Pharm Research. 2023;210–8.
4. Anjana RM, Unnikrishnan R, Deepa M, Pradeepa R, Tandon N, Das AK, et al. Metabolic non-communicable disease health report of India: the ICMR-INDIAB national cross-sectional study (ICMR-INDIAB-17). The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 2023;11:474–89.
5. Galicia-Garcia U, Benito-Vicente A, Jebari S, Larrea-Sebal A, Siddiqi H, Uribe KB, et al. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. IJMS. 2020;21:6275.
6. Farmaki P, Damaskos C, Garmpis N, Garmpi A, Savvanis S, Diamantis E. Complications of the Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. CCR. 2021;16:249–51.
7. Papazafiropoulou A, Papanas N, Melidonis A, Maltezos E. Family History of Type 2 Diabetes: Does Having a Diabetic Parent Increase the Risk? CDR. 2016;13:19–25.
8. Fajtova V. IMPACT OF FAMILY HISTORY OF DIABETES ON DIABETES CONTROL AND COMPLICATIONS. Endocr Pract. 2019;25:197–8.
9. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47:S20–42.
10. A. G, S. G, R. U. Study on the impact of family history of diabetes among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in an urban area of Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017;4:4151.
11. Panat AV, Kulkarni DA, Ghooi RB. Population based family history analysis of Brahmins in a small town in India for the prevalence of type-2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Hum Genet. 2013;19:342–5.
12. Anjana RM, Deepa M, Pradeepa R, Mahanta J, Narain K, Das HK, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes in 15 states of India: results from the ICMR–INDIAB population-based cross-sectional study. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 2017;5:585–96.
13. Das M, Pal S, Ghosh A. Family history of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Asian Indians. J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2012;3:104–8.
14. Pradeepa R, Mohan V. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in India. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021;69:2932–8.
15. Chaudhuri P, Das M, Lodh I, Goswami R. Role of Metabolic Risk Factors, Family History, and Genetic Polymorphisms (PPARγ and TCF7L2) on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Risk in an Asian Indian Population. Public Health Genomics. 2021;24:131–8.
16. Cheung JTK, Lau E, Tsui CCT, Siu ELN, Tse NKW, Hui NYL, et al. Combined associations of family history and self-management with age at diagnosis and cardiometabolic risk in 86,931 patients with type 2 diabetes: Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation (JADE) Register from 11 countries. BMC Med. 2022;20:249.
17. Al Ali M, El Hajj Chehadeh S, Osman W, Almansoori K, Abdulrahman M, Tay G, et al. Investigating the association of rs7903146 of TCF7L2 gene, rs5219 of KCNJ11 gene, rs10946398 of CDKAL1 gene, and rs9939609 of FTO gene with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Emirati population. Meta Gene. 2019;21:100600.
18. Kowluru RA, Mohammad G. Epigenetic modifications in diabetes. Metabolism. 2022;126:154920.
19. Hossan T, Kundu S, Alam SS, Nagarajan S. Epigenetic Modifications Associated with the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. EMIDDT. 2019;19:775–86.
20. González-Gil EM, Giménez-Legarre N, Cardon G, Mavrogianni C, Kivelä J, Iotova V, et al. Parental insulin resistance is associated with unhealthy lifestyle behaviours independently of body mass index in children: The Feel4Diabetes study. Eur J Pediatr. 2022;181:2513–22.
21. Yuan T, Yang T, Chen H, Fu D, Hu Y, Wang J, et al. New insights into oxidative stress and inflammation during diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis. Redox Biology. 2019;20:247–60.
Copyright (c) 2024 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


