The Severity of diabetic retinopathy and its relationship with duration of diabetes and hypertension
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the risk factors affecting diabetic retinopathy and its severity in type 2 diabetic patients about the duration of diabetes and hypertension.
Methods: A retrospective chart analysis was done of patient data collected from the patients visiting our tertiary institute (Karnataka Institute of Endocrinology and Research) from November 1st, 2022 to October 31st, 2023. In these diabetic patients, the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and its severity concerning the duration of diabetes and hypertension was evaluated. Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema (DME) were classified based on the International Clinical Disease Severity Scale for Diabetic Retinopathy (DR).
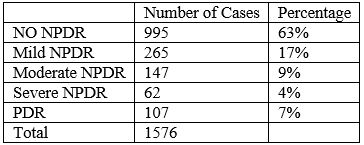
Result: 5363 was the total number of diabetic patients included in this study. The prevalence of Diabetic retinopathy(DR) was 13.95% with diabetes for less than 5 years, 37% with diabetes for 5 to 10 years and 58.74% for more than 10 years. In diabetic patients with associated hypertension, the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (DR) was 36 % as compared to 28.4% without associated hypertension. In multivariate analysis for factors associated with diabetic retinopathy, the odds ratio (OR) was 3.61% (95% CI, 3.08 – 4.23, P – Value < 0.001) in patients with diabetes between 5 – 10 years and in patients with diabetes above 10 years the odds ratio (OR) was 8.69 (95% CI, 7.36 – 10.26, P – Value < 0.001) as compared to patients with diabetes < 5 years. The odds ratio (OR) for developing DR was 1.19 (95% CI, 1.03 – 1.37, P – Value 0.015) in patients with diabetes and hypertension as compared to diabetic patients without hypertension.
Conclusion: The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy is higher in diabetic patients with longer duration of diabetes and diabetic patients with associated hypertension. It is important to evaluate all diabetic patients for diabetic retinopathy and maintain good glycemic and hypertensive control. Managing comorbidities along with diabetes reduces the prevalence and complications of diabetic retinopathy.
Downloads
References
2. Geiss LS, Rolka DB, Engelgau MM. Elevated blood pressure among U.S. adults with
diabetes, 1988–1994. Am J Prev Med 2002; 22: 42–48.
3. Parving HH. Controlling hypertension in diabetes. Acta Diabetol 2002; 39: S35–S40.
4. Walraven I, Mast MR, Hoekstra T, et al. Real-world evidence of suboptimal blood pressure control in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Hypertens. 2015; 33:2091–8.
5. Wong TY, Cheung N, Tay WT, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy: the Singapore Malay Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115(11):1869–75.
6. Zheng Y, Lamoureux EL, Lavanya R, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic retinopathy in migrant Indians in an urbanized society in Asia: the Singapore Indian eye study. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119(10):2119–24.
7. Devatha S, Preethi. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients at Tertiary Hospital, Bangalore, India. Int J Med Res Rev [Internet]. 2024Mar.28
8. Donald s. fong , lloyd aiello, thomas w. gardner et al. Retinopathy in Diabetes, diabetes care , volume 27, supplement 1, january 2004
9. Klein R, Knudtson MD, Lee KE, Gangnon R, Klein BE. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy XXIII: the twenty-five-year incidence of macular edema in persons with type 1 diabetes. Ophthalmology. 2009 Mar; 116(3):497-503. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.10.016. Epub 2009 Jan 22. PMID: 19167079; PMCID: PMC2693093.
10. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT): results of feasibility study. The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes Care. 1987 Jan-Feb; 10(1):1-19. doi: 10.2337/diacare.10.1.1. PMID: 2882967.
11. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008 Oct 9;359(15):1577-89. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0806470. Epub 2008 Sep 10. PMID: 18784090.
12. Al-Adsani AM. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in Kuwaiti type 2 diabetic patients. Saudi Med J. 2007 Apr;28(4):579-83. PMID: 17457481.
13. Shukla UV, Tripathy K. Diabetic Retinopathy. 2023 Aug 25. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. PMID: 32809640.
14. Lingam G, Wong TY. Systemic medical management of diabetic retinopathy. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2013 Oct-Dec;20(4):301-8. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.120010. PMID: 24339679; PMCID: PMC3841947.
15. Richmond Woodward, Evarista Mgaya, Christopher Mwanansao, Robert N. Peck , Alan Wu, and Grace Sun. Retinopathy in adults with hypertension and diabetes mellitus in western Tanzania: A cross-sectional study; Med Int Health; 2020 Oct;25(10):1214-1225.doi: 10.1111/tmi.13463. Epub 2020 Aug 3.
16. Margarete Voigt, Sebastian Schmidt , Thomas Lehmann, Benjamin Köhler, Christof Kloos , Ulrich A Voigt , et al. Prevalence and Progression Rate of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Correlation with the Duration of Diabetes; ExpClin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2018 Sep;126(9):570-576. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-120570. Epub 2017 Nov 28.
17. Klien R, Klien BE, et al. The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy prevalence and risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is 30 or more years. Arch Ophthalmol.1984 April;102(4):527-32
18. R Klein 1, B E Klein, S E Moss, K J Cruickshanks.The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: XVII. The 14-year incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy and associated risk factors in type 1 diabetes Ophthalmology ; 1998 Oct;105(10):1801-15.doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(98)91020-X
19. Stratton IM, Kohner EM, Aldington SJ, et al. UKPDS 50: risk factors for incidence and progression of retinopathy in type II diabetes over 6 years from diagnosis. Diabetologia2001;44:156–63.
20. Pradeepa, R,Anitha, B, MohanV, GanesanA, Rema M. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in a South Indian Type 2 diabetic population–the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES) Eye Study 4. Diabet Med. 2008, 25, 536–542.
21. Peter H Scanlon, Stephen J Aldington, and Irene M Stratton.Epidemiological Issues in Diabetic Retinopathy; Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2013 Oct-Dec; 20(4): 293–300. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.120007
22. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ. 1998;317:703–13.
23. Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Gifford N, Schrier RW. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000;23:B54–64.
24. N Wat , R Lm Wong , I Yh Wong . Associations between diabetic retinopathy and systemic risk factors ; Hong Kong Med J2016 Dec;22(6):589-99.doi:10.12809/hkmj164869. Epub 2016 Oct 24.
25. Zhang M, Wu J, Wang Y, Wu J, Hu W, Jia H, Sun X. Associations between blood pressure levels and diabetic retinopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: A population-based study. Heliyon. 2023 Jun 1;9(6):e16830. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16830. PMID: 37484372; PMCID: PMC10360950.
Copyright (c) 2024 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


