A Study of patients with Pulmonary tuberculosis and its relationship with diabetes and outcome of treatment in this patient
Abstract
Background: There is synergistic effect between diabetes mellitus and pulmonary tuberculosis. India has highest number of tuberculosis patient and India has also second highest number of patients with diabetes mellitus in world. The dual curse of these two diseases may have an impact on both side as outcome of treatment and poor glycaemic control. There were many studies have been done about relationship between diabetes and tuberculosis but still there is a large gap about its synergistic effect.
Methods: In this study we include164 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis with age more than 18 years 72 out of 164 patients are diabetic and 92 patients are nondiabetic. Demographic details, physical and clinical examination, Blood sugar fasting and post prandial, Hba1c, x-rays chest, sputum for AFB and CBNAAT test have been done all patients then ATT given to patients and appropriate antidiabetic treatment given to diabetic patients. follow up done on to all patients on 2nd month and 6th months.
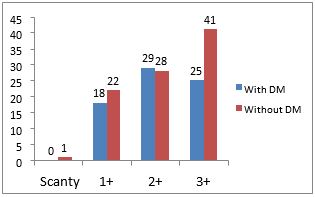
Results: In this study commonest age group for tuberculosis infection is 45-54 but in diabetic patients common age group for tuberculosis infection is 55-64. Patients of diabetic and tuberculosis commonly having elevated Hba1c and relatively poor treatment outcome reflected by sputum conversion rate 77.7%, 16.7%has failed treatment and also diabetic patients has 3+ sputum positivity.
Conclusions: In patients with tuberculosis screening of diabetes may improve treatment outcome and prevent complications by appropriate management of diabetes and tuberculosis.
Downloads
References
2. Vishwanathan AA, Gawde NC. Effect of type II diabetes mellitus on treatment outcomes of tuberculosis. Lung India. 2014;31(3):244-8.
3. Pérez-Guzman C, Torres-Cruz A, Villarreal-Velarde H, Salazar-Lezama MA, Vargas MH. Atypical radiological images of pulmonary tuberculosis in 192 diabetic patients: A comparative study. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2001;5:455-61.
4. Samir B. Al-Adhami, Basim S. Al-Mgoter. Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Iraqi J. Comm. Med. 2008;21(1):47-54.
5. Patel JC, Ugini SS. Diabetes and tuberculosis. Ind J Tub.1977;XXIV (4):155-8.
6. Alisjahbana B, van Crevel R, Sahiratmadia E, den Heijer M, Maya A, Istriana E, et al. Diabetes mellitus is strongly associated with tuberculosis in Indonesia. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006;10(6):696700.
7. Chiang CY, Lee JJ, Chien ST, Enarson DA, Chang YC, Chen YT, et al. Glycemic control and radiographic manifestations of tuberculosis in diabetic patients. PLoS One. 2014;9:e93397.
8. Avuthu S, Mahishale V, Patil B, Eti A. Glycemic control and radiographic manifestations of pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sub-Saharan Afr J Med. 2015;2:5-9
Copyright (c) 2023 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


