A Multi-centre Study to Evaluate the Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Biosimilar Infliximab (Infimab™) in Ankylosing Spondylitis in Real-world Clinical Settings - A perspective from Eastern India
Abstract
Introduction: Owing to dearth of data on infliximab biosimilars in Indian patients, a pan-India case database-based study with infliximab biosimilar BOW015 (Infimab™) was carried out to capture its efficacy and safety in real world clinical settings in India. Here, we assessed its efficacy and safety in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) among patients in the East India cohort.
Materials and methods: Data were collected from multiple centers across the eastern region of India. Patients diagnosed with AS, within the preceding 4-6 months during the preceding one year were included in the study. Patients who were given BOW015 for other indications, prior innovator infliximab or other biologics were excluded from the study. Primary variable was Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Scale (ASDAS) response defined as change of > 2 in the ASDAS score from the baseline by 4-6 months of follow up.
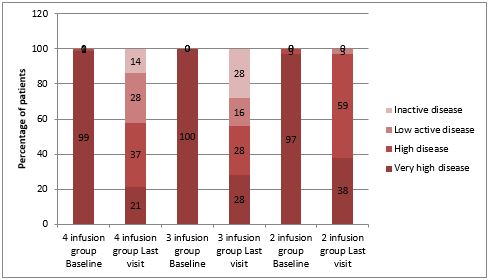
Results: The cohort consisted of 149 patients, predominantly male (69.8%), with mean (±SD) age of 36.75 (±11.11) years and mean (±SD) body weight of 58.26 (±15.4) kgs. Of the treated patients, 91 (61.1%) patients were administered four doses, 10 (6.7%) patients were administered three doses, 37 (24.8%) patients were administered two doses and 11 (7.4%) patients were administered only a single dose of BOW015. In the final analysis set, 81 patients had data at baseline and 4th visit. Among the 81 patients, 74 (91%) patients achieved major improvement, 5 (6%) patients achieved clinically important improvement and 2 (3%) were non-responders at 4th visit. Secondarily, cross categorization of the cohort into disease activity categories by number of infusions administered from baseline to 4th visit and assessment of trends in Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) scores were also carried out and these too confirmed the efficacy of BOW015.
Conclusion: Infimab™ (BOW015) showed significant improvement in ASDAS and BASDAI in patients with AS at the end of 4-6 months of follow up with its clinical benefits being apparent as early as first dose of BOW015.
Downloads
References
Chen B, Li J, He C, Li D, Tong W, Zou Y, et al. Role of HLA-B27 in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2017 Apr;15(4):1943-1951. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6248.
Reveille JD. The genetic basis of ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2006 Jul;18(4):332-41. doi: 10.1097/01.bor.0000231899.81677.04.
Garcia-Montoya L, Gul H, Emery P. Recent advances in ankylosing spondylitis: understanding the disease and management. F1000Res. 2018 Sep 21;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1512. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.14956.1.
Crommelin DJ, Storm G, Verrijk R, de Leede L, Jiskoot W, Hennink WE. Shifting paradigms: biopharmaceuticals versus low molecular weight drugs. Int J Pharm. 2003 Nov 6;266(1-2):3-16. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5173(03)00376-4.
Schett G, Elewaut D, McInnes IB, Dayer JM, Neurath MF. How cytokine networks fuel inflammation: Toward a cytokine-based disease taxonomy. Nat Med. 2013 Jul;19(7):822-4. doi: 10.1038/nm.3260.
Cortes A, Pulit SL, Leo PJ, Pointon JJ, Robinson PC, Weisman MH, et al. Major histocompatibility complex associations of ankylosing spondylitis are complex and involve further epistasis with ERAP1. Nat Commun. 2015 May 21;6:7146. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8146.
Jacobs I, Petersel D, Isakov L, Lula S, Lea Sewell K. Biosimilars for the Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Systematic Review of Published Evidence. BioDrugs. 2016 Dec;30(6):525-570. doi: 10.1007/s40259-016-0201-6.
Smolen JS, Emery P. Infliximab: 12 years of experience. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 May 25;13 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S2. doi: 10.1186/1478-6354-13-S1-S2.
Keffer J, Probert L, Cazlaris H, Georgopoulos S, Kaslaris E, Kioussis D, et al. Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: a predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4025-31. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04978.x.
US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Statistical approaches to establishing bioequivalence: Guidance for industry. Rockville, MD, USA, 2001.http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/ucm070244.pdf (accessed September 2015)
US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) and Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). Scientific considerations in demonstrating biosimilarity to a reference product: Guidance for industry. Rockville, MD, USA, 2015. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/DrugsGuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM291128.pdf(accessed September 2015)
Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. "European Medicines Agency Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) guideline on the evaluation of anticancer medicinal products in man." London, UK: European Medicines Agency (2006).
EMA. European Medicines Agency–Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). Reflection paper on the data requirements for intravenous liposomal products developed with reference to an innovator liposomal product. EMA/CHMP/806058/2009/Rev. 02, February 2013." (2013).
GaBI Online - Generics and Biosimilars Initiative. Positive phase III data for Epirus infliximab biosimilar [www.gabionline.net]. Mol, Belgium: Pro Pharma Communications International; [cited 2014 Oct 3]. Available from: www.gabionline.net/Biosimilars/Research/Positive-phase-III-data-for-Epirusinfliximab - biosimilar. Accessed on July 01, 2019.
.
Lambert J, Wyand M, Lassen C, Shneyer L, Thomson E, Knight A, et al. Bioavailability, safety and immunogenicity of biosimilar infliximab (BOW015) compared to reference infliximab. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Apr;54(4):315-22. doi: 10.5414/CP202530.
Amin SN, Kapadia A, Shamil M. Short-term and long-term outcomes of biosimilar infliximab (BOW015) treatment in rheumatoid arthritis- A single-centre retrospective study. ABS312. Int J Rheumat Dis. 2017;20(1):17-131.
Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol. 1994 Dec;21(12):2286-91.
Pham T, Landewé R, van der Linden S, Dougados M, Sieper J, Braun J, et al. An international study on starting tumour necrosis factor-blocking agents in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Dec;65(12):1620-5. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.042630.
Landewé R, van Tubergen A. Clinical Tools to Assess and Monitor Spondyloarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015 Jul;17(7):47. doi: 10.1007/s11926-015-0522-3.
Machado P, Landewé R, Lie E, Kvien TK, Braun J, Baker D, et al. Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society. Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS): defining cut-off values for disease activity states and improvement scores. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Jan;70(1):47-53. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.138594.
Machado PM, Landewé R, Heijde DV; Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS). Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS): 2018 update of the nomenclature for disease activity states. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Oct;77(10):1539-1540. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213184.
Poddubnyy D. Axial spondyloarthritis: is there a treatment of choice? Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013 Feb;5(1):45-54. doi: 10.1177/1759720X12468658.
Gulácsi L, Brodszky V, Baji P, Kim H, Kim SY, Cho YY, et al. Biosimilars for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: economic considerations. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015;11 Suppl 1:S43-52. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2015.1090313.
Rubin LA, Amos CI, Wade JA, Martin JR, Bale SJ, Little AH, et al. Investigating the genetic basis for ankylosing spondylitis. Linkage studies with the major histocompatibility complex region. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Aug;37(8):1212-20. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370816.
Díaz-Peña R, Vidal-Castiñeira JR, López-Vázquez A, López-Larrea C. HLA-B*40:01 Is Associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis in HLA-B27-positive Populations. J Rheumatol. 2016 Jun;43(6):1255-6. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.151096.
Ezard C, Kumari R, Willott R, Butt S, Gadsby K, Deighton C. What is meant by active disease in the NICE recommendation on use of combination therapy in early RA? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012 May;51(5):947-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker513.
Lee SS, Kim TH, Park W, Song YW, Suh CH, Kim SK, et al. Impact of Infliximab Biosimilar CT-P13 Dose and Infusion Interval on Real-World Drug Survival and Effectiveness in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis. J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 1;10(19):4568. doi: 10.3390/jcm10194568.
Park W, Yoo DH, Miranda P, Brzosko M, Wiland P, Gutierrez-Ureña S, et al. Efficacy and safety of switching from reference infliximab to CT-P13 compared with maintenance of CT-P13 in ankylosing spondylitis: 102-week data from the PLANETAS extension study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Feb;76(2):346-354. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208783.
Maksymowych WP, Jhangri GS, Lambert RG, Mallon C, Buenviaje H, Pedrycz E, et al. Infliximab in ankylosing spondylitis: a prospective observational inception cohort analysis of efficacy and safety. J Rheumatol. 2002 May;29(5):959-65.
Maksymowych WP, Salonen D, Inman RD, Rahman P, Lambert RG; CANDLE Study Group. Low-dose infliximab (3 mg/kg) significantly reduces spinal inflammation on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized placebo-controlled study. J Rheumatol. 2010 Aug 1;37(8):1728-34. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.091043.
Cherouvim EP, Zintzaras E, Boki KA, Moutsopoulos HM, Manoussakis MN. Infliximab Therapy for Patients With Active and Refractory Spondyloarthropathies at the Dose of 3 mg/kg: A 20-Month Open Treatment. J Clin Rheumatol. 2004 Aug;10(4):162-8. doi: 10.1097/01.rhu.0000135551.47780.
Tenga G, Goëb V, Lequerré T, Bacquet-Deschryver H, Daragon A, Pouplin S, et al. A 3 mg/kg starting dose of infliximab in active spondyloarthritis resistant to conventional treatments is efficient, safe and lowers costs. Joint Bone Spine. 2011 Jan;78(1):50-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2010.04.017.
Kim TH, Lee SS, Park W, Song YW, Suh CH, Kim S, et al. A 5-year Retrospective Analysis of Drug Survival, Safety, and Effectiveness of the Infliximab Biosimilar CT-P13 in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis. Clin Drug Investig. 2020 Jun;40(6):541-553. doi: 10.1007/s40261-020-00907-5.
Baji P, Péntek M, Szántó S, Géher P, Gulácsi L, Balogh O, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of biosimilar infliximab and other biological treatments in ankylosing spondylitis: systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Eur J Health Econ. 2014 May;15 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S45-52. doi: 10.1007/s10198-014-0593-5.
Agrawal, I., et al. AB0690 Clinical experience with infliximab biosimilar (BOW015) in ankylosing spondylitis-efficacy and safety analysis from an indian perspective." (2017): 1295-1295.
Copyright (c) 2022 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


