Study on the Correlation Between Vitamin D and BMI in Type 2Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
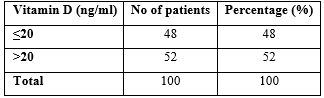
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with increased morbidity and mortality due to thedevelopment of complications, especially due to poor glycaemic control. Besides its role in calciumhomeostasis, Vitamin D has been involved in the pathophysiology as well as glycaemic control oftype 2 DM. 100 patients diagnosed with type 2 DM were included. Vitamin D levels along with BMIwere measured in all the individuals. In our study, we had the youngest patient with 18years andthe oldest patient with 78years. In the present study, we had maximum patients in the age groupbetween 41 to 50 years similar to various other studies. In our study male was 68% with femaleswere 38%. In the present study, we estimated vitamin D levels in all subjects and categorizationwas done as <20 and more than 20 ng/dl.48% of patients had vitamin D levels below 20ng/dl. Inthe present study, we compared the values of BMI with vitamin D levels where we did not noticemuch difference with the mean of individual category. In conclusion, we have identified a correlationconcerning vitamin D levels when compared with BMI statistically. Since the physiological role ofVitamin D in pancreatic beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity is well appreciated, and consideringthat almost 50% of the diabetes patients in the present study are Vitamin D deficient, it issuggested that Vitamin D levels improve the BMI in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
Downloads
References
2. Hebebrand, J.; Hinney, A. Environmental and genetic risk factors in obesity. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 18, 83–94. [PubMed]
3. Parker, J.; Hashmi, O.; Dutton, D.; Mavrodaris, A.; Stranges, S.; Kandala, S.B.; Clarke, A.; Franco, O.H. Levels of vitamin D and cardiometabolic disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas 2010, 65, 225–236. [PubMed]
4. Ahmad NS, Islahudin F, Paraidathathu T. Factors associated with good glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig 2014;5:563 9.
5. Griz LH, Bandeira F, Gabbay MA, Dib SA, Carvalho EF. Vitamin D and diabetes mellitus: An update 2013. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 2014;58:1 8.
6. Harinarayan CV. Vitamin D and diabetes mellitus. Hormones(Athens) 2014;13:163 81.
7. Scragg R, Sowers M, Bell C; Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D, diabetes, and ethnicity in the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Diabetes Care 2004;27:2813 8.
8. Pittas AG, Dawson Hughes B, Li T, Van Dam RM, Willett WC, Manson JE, et al. Vitamin D and calcium intake in relation to type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes Care 2006;29:650 6.
9. Nwosu BU, Maranda L. The effects of vitamin D supplementation on hepatic dysfunction, Vitamin D status, and glycemic control in children and adolescents with Vitamin D deficiency and either type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS One 2014;9:e99646.
10. Rolim MC, Santos BM, Conceição G, Rocha PN. Relationship between Vitamin D status, glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in Brazilians with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2016;8:77.
11. Bayani MA, Akbari R, Banasaz B, Saeedi F. Status of Vitamin D in diabetic patients. Caspian J Intern Med 2014;5:40 2.
12. Kostoglou Athanassiou I, Athanassiou P, Gkountouvas A,Kaldrymides P. Vitamin D and glycemic control in diabetes mellitus type 2. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab 2013;4:122 8.
13. Olt S. Relationship between Vitamin D and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8:19180 3.
14. Perez Diaz I, Sebastian Barajas G, Hernandez Flores ZG, Rivera Moscoso R, Osorio Landa HK, Flores Rebollar A. The impact of Vitamin D levels on glycemic control and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. J Endocrinol Invest 2015;38:1365 72
15. American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016;39 Suppl 1:S13 22
16. The relationship of glycemic exposure (HbA1c) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes 1995;44:968 83.
17. Priyanka P. Brahmkshatriya, Anita A.Mehta, Banshi D. Saboo, Ramesh K. Goyal. Characterist and prevalence of latent autoimmune diabetic in adults. International Scholarly Research Network .ISRN Pharmacology. Volume 2012, Article ID 580202, 8 pages. doi: 10. 5402/2012/580202
18. Mohan V, Sandeep V, Deepa R, Shah B, Varghese C. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes: Indian Scenario. Indian J Med Res 125, March 2007, pp 217-30. MOHAN et al: EPIDEMIOLOGY OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
19. Targher G, Bertolini L, Padovani R, Zenari L, Scala L, Cigolini M, Arcaro G. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 concentrations and carotid artery intimamedia thickness among type 2 diabetic patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf ). 2006;65(5):593–7
20. Bellan M, Guzzaloni G, Rinaldi M, Merlotti E, Ferrari C, Tagliaferri A, Pirisi M, Aimaretti G, Scacchi M, Marzullo P. Altered glucose metabolism rather than naive type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is related to vitamin D status in severe obesity. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:57
21. Kositsawat J, Freeman VL, Gerber BS, Geraci S. Association of A1C levels with vitamin D status in US adults: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(6):1236–8.
22. Yu JR, Lee SA, Lee JG, Seong GM, Ko SJ, Koh G, Kong MH, Park KY, Kim BJ, Lim DM, et al. Serum vitamin d status and its relationship to metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chonnam Med J. 2012;48(2):108–15.
23. Al-Timimi DJ, Ali AF. Serum 25(OH) D in diabetes mellitus type 2: relation to glycaemic control. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7(12):2686–8.
24. Manickam B, Neagu V, Kukreja SC, Barengolts E. Relationship between glycated hemoglobin and circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration in African American and Caucasian American men. Endocr Pract. 2013;19(1):73–80.
25. Luo C, Wong J, Brown M, Hooper M, Molyneaux L, Yue DK. Hypovitaminosis D in Chinese type 2 diabetes: lack of impact on clinical metabolic status and biomarkers of cellular inflammation. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2009;6(3):194–9.
26. Al-Asoosi AA, Ali AH, Nair VS. Does insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes alter vitamin D status? Prim Care Diabetes. 2013;7(4):283–7.
27. Holick, M.F. Vitamin D: Important for prevention of osteoporosis, cardiovascular heart disease, type 1 diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and some cancers. South Med. J. 2005, 98, 1024–1027. [PubMed]
28. Rafiq, S.; Jeppesen, P.B. Is hypovitaminosis d related to incidence of type 2 diabetes and high fasting glucose level in healthy subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 59. [PubMed]
29. Wong, K.E.; Kong, J.; Zhang,W.; Szeto, F.L.; Ye, H.; Deb, D.K.; Brady, M.J.; Li, Y.C. Targeted expression of human vitamin D receptor in adipocytes decreases energy expenditure and induces obesity in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 33804–33810. [PubMed]
30. Stein, E.M.; Strain, G.; Sinha, N.; Ortiz, D.; Pomp, A.; Dakin, G.; McMahon, D.J.; Bockman, R.; Silverberg, S.J. Vitamin D insufficiency prior to bariatric surgery: Risk factors and a pilot treatment study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 176–183. [PubMed]
31. Kayaniyil S, Vieth R, Retnakaran R, Knight JA, Qi Y, Gerstein HC, et al. Association of Vitamin D with insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction in subjects at risk for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010;33:1379 81.
32. Pittas AG, Dawson Hughes B, Sheehan P, Ware JH, Knowler WC, Aroda VR, et al. Vitamin D supplementation and prevention of type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019;381:520 30.
Copyright (c) 2022 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


