Etiology and endoscopic profile of dysphagia in adults - Single center study at a tertiary care center in South India.
Abstract
Background: Dysphagia is defined as difficulty in deglutition. It can be either structural or motility abnormality in the passage of food from the oral cavity to the stomach. Upper GI endoscopy is the most important tool to diagnose dysphagia and rule out premalignant and malignant lesions. The purpose of the study was to classify various causes of dysphagia.
Methods: This prospective observational study was conducted on 206 patients with complaints of dysphagia. Detailed history, physical examination was done. Upper GI endoscopy was done in all cases, and biopsies were taken if required. Oropharyngeal and neurological dysphagia were excluded from the study. The statistical analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel. The mean, percentage and proportions were calculated.
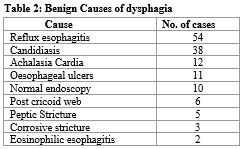
Results: Two hundred and six patients were included in the study. Out of 206 patients, 127 were females, and 79 were males. The mean age was 43.62 years. The commonest age group was 21- 40 years contributing 41.7% cases, followed by 41-60 years contributing to 30.8% cases. Benign etiology (n= 141) was more common than that of malignant (n= 65). The commonest benign etiology was reflux esophagitis (n =54) followed by esophageal candidiasis (n= 38). The commonest malignant etiology was adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (n= 38), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (n= 24).
Conclusions: The upper GI endoscopy is effective and safe modality to diagnose dysphagia. Benign etiologies were more common among females, but malignant causes were more common among males. The incidence of esophageal malignancy increases with advanced age.
Downloads
References
Tawil J, Fass R. Globus: Current Concepts and Dilemmas. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov/Dec;52(10):845-852. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001129.
Eslick GD, Talley NJ. Dysphagia: epidemiology, risk factors and impact on quality of Life--a population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008 May;27(10):971-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03664.x.
Lindgren S, Janzon L. Prevalence of swallowing complaints and clinical findings among 50-79-year-old men and women in an urban population. Dysphagia. 1991;6(4):187-92. doi: 10.1007/BF02493524.
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. "Prevalence of speech, voice and language disorders in the United States." Rockville, MD: American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (1994).
Ekberg O, Hamdy S, Woisard V, Wuttge-Hannig A, Ortega P. Social and psychological burden of dysphagia: its impact on diagnosis and treatment. Dysphagia. 2002 Spring;17(2):139-46. doi: 10.1007/s00455-001-0113-5.
Lind CD. Dysphagia: evaluation and treatment. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2003 Jun;32(2):553-75. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8553(03)00024-4.
Wilkins T, Gillies RA, Thomas AM, Wagner PJ. The prevalence of dysphagia in primary care patients: a HamesNet Research Network study. J Am Board Fam Med. 2007 Mar-Apr;20(2):144-50. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2007.02.060045.
Richter JE. Practical approach to the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal dysphagia. Compr Ther. 1998 Sep;24(9):446-53.
Carucci LR, Turner MA. Dysphagia revisited: common and unusual causes. Radiographics. 2015 Jan-Feb;35(1):105-22. doi: 10.1148/rg.351130150.
Sahu, Siddharth, et al. Endoscopic evaluation of patients presenting with dysphagia at rural Hospital AVBRH." Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University 12.3 (2017): 196.
Sura L, Madhavan A, Carnaby G, Crary MA. Dysphagia in the elderly: management and nutritional considerations. Clin Interv Aging. 2012;7:287-98. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S23404.
Kruger D. Assessing esophageal dysphagia. JAAPA. 2014 May;27(5):23-30. doi: 10.1097/01.JAA.0000446227.85554.fb.
Kahrilas PJ, Hirano I. Diseases of the esophagus. In: Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, et al., eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012.
Vaezi MF, Pandolfino JE, Vela MF. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of achalasia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Aug;108(8):1238-49; quiz 1250. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.196.
Esfandyari T, Potter JW, Vaezi MF. Dysphagia: a cost analysis of the diagnostic approach. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 Nov;97(11):2733-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.07061.x.
Fucile S, Wright PM, Chan I, Yee S, Langlais ME, Gisel EG. Functional oral-motor skills: Do they change with age? Dysphagia. 1998 Fall;13(4):195-201. doi: 10.1007/PL00009571.
Logemann JA, Stewart C, Hurd J, Aschman D, Matthews N. Diagnosis and Management of Dysphagia in Seniors. 2008. Available at: http://americandysphagianetwork.org/physician_education_course.
Malagelada, J. R., et al. World Gastroenterology Organization Practice Guidelines. Dysphagia (2007).
Puhakka HJ, Aitsalo K. Oesophageal carcinoma: endoscopic and clinical findings in 258 patients. J Laryngol Otol. 1988 Dec;102(12):1137-41. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100107534.
Malik IA, Khan WA, Khan ZK. Pattern of malignant tumors observed in a university hospital: a retrospective analysis. J Pak Med Assoc. 1998 May;48(5):120-2.
Samarasam, Inian. Esophageal cancer in India: Current status and future perspectives." International Journal of Advanced Medical and Health Research 4.1 (2017): 5.
Cherian JV, Sivaraman R, Muthusamy AK, Jayanthi V. Carcinoma of the esophagus in Tamil Nadu (South India): 16-year trends from a tertiary center. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2007 Sep;16(3):245-9.
Mitra T, Dixit VK, Shukla SK, Yadav DP, Thakur P, Thakur RK. Clinical profile of patients presenting with dysphagia - an experience from a tertiary care center in North India. JGH Open. 2019 Nov 29;4(3):472-476. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12284.
Kidambi T, Toto E, Ho N, Taft T, Hirano I. Temporal trends in the relative prevalence of dysphagia etiologies from 1999-2009. World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 28;18(32):4335-41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4335.
Copyright (c) 2022 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


