Etiological classification of seizures in pediatric age group (6-12years) – MRI study
Abstract
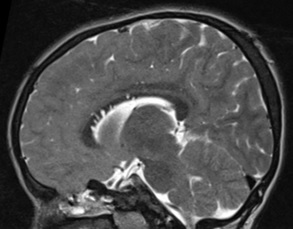
Background: A seizure is an occurrence of signs or symptoms due to abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. The present study aims to study the etiological factors and clinical profile for new-onset seizures in children aged 6-12 years and to determine the frequency of Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) abnormalities in the pediatrics age group with new-onset unprovoked seizure and those with inadequately investigated longstanding epilepsy and classify the etiology based on the MRI findings.
Methods: A prospective study involving a total of 50 patients was recruited aged between 6 to 12 years. All of them underwent neuro-imaging with MRI. Uncooperative patients were imaged following sedation and monitoring by the anesthetist. All children aged 6-12 years who presented with new-onset seizures were included. All MR images were obtained at a 3-mm section thickness except magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo images, which are obtained at a 1.8-mm section thickness.
Results: Of the 50 patients 28 presented with generalized tonic-clonic seizures, 12 with simple partial seizures, 10 with complex partial seizures. Generalized seizures were a more common presentation than partial seizures in children 6-12 years of age.
Conclusion: With the positivity of the MRI in the new-onset seizure in children between 6-12 years in our study gives an important aspect of the essential factor of imaging in pediatric new-onset seizures.
Downloads
References
Verma A, Kunju PAM, Kanhare S, Maheshwari N. IAP Textbook of Pediatric Neurology. New Delhi- Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (p) Ltd. 2014;112.
Behrman, Kleigman, Jenson. Nervous system In- Nelson text book of paediatrics. 18th ed. 2nd vol. p- 2457-2478.
Rayamajhi A, Singh R, Prasad R, Khanal B, Singhi S. Study of Japanese encephalitis and other viral encephalitis in Nepali children. Pediatr Int. 2007 Dec;49(6)978-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2007.02495.x.
Hauser WA, Beghi E. First seizure definitions and worldwide incidence and mortality. Epilepsia. 2008;49 Suppl 1;8-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01443.x.
Chen CY, Chang YJ, Wu HP. New-onset seizures in pediatric emergency. Pediatr Neonatol. 2010 Apr;51(2)103-11. doi: 10.1016/S1875-9572(10)60019-8.
Sharma S, Riviello JJ, Harper MB, Baskin MN. The role of emergent neuroimaging in children with new-onset afebrile seizures. Pediatrics. 2003 Jan;111(1)1-5. doi: 10.1542/peds.111.1.1.
Pearce MS, Salotti JA, Little MP, McHugh K, Lee C, Kim KP, et al. Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours- a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2012 Aug 4;380(9840)499-505. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60815-0.
Saha S P, Bhattachrya S, Roy B K, Basu A, Maity A, Das S K. A prospective incidence study of epilepsy in a rural community of West-Bengal, India". (2008).
Singhi, Sunit, and Pratibha Singhi. "Clinical profile and etiology of partial seizures in North Indian infants and children". Journal of Epilepsy. 10;1(1997)32-36.
Kanitkar M, Purkayastha SB, Deshpande Nd. Role of ct scan in partial seizures in children. Med J Armed Forces India. 1994 Jan;50(1)23-26. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(17)31032-8.
Baheti, Ramesh, B D Gupta. "A study of CT and EEG findings in patients with generalised ar partial seizures is western Rajasthan". Journal, Indian Academy of Clinical Medicine. 4;1(2003)25-9.
Hussain J, Srinivasan S, Serane VT, Mahadevan S, Elangovan S, Bhuvaneswari V. Cranial computed tomography in partial motor seizures. Indian J Pediatr. 2004 Jul;71(7)641-4. doi: 10.1007/BF02724126.
Shinnar S, Berg AT, Moshé SL, Petix M, Maytal J, Kang H, et al. Risk of seizure recurrence following a first unprovoked seizure in childhood- a prospective study. Pediatrics. 1990 Jun;85(6)1076-85.
Berg AT, Testa FM, Levy SR, Shinnar S. Neuroimaging in children with newly diagnosed epilepsy- A community-based study. Pediatrics. 2000 Sep;106(3)527-32. doi: 10.1542/peds.106.3.527.
Misra S, Das BK, Srivastava AK. Neuroimaging study in children with seizures. JNPS. 2007;27(1)13-6.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


