Efficacy of standard treatment protocol in recently diagnosed Lupus Nephritis at our tertiary care teaching hospital
Abstract
Introduction: Lupus Nephritis occurred in approximately 50% of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients at some point during their illness and is associated with a poor prognosis.
Material and Method: A prospective observational study of 50 newly diagnosed LN cases was conducted to investigate the response of standard treatment protocol (Cyclophosphamide -NIH protocol and Mycophenolate Mofetil-MMF).
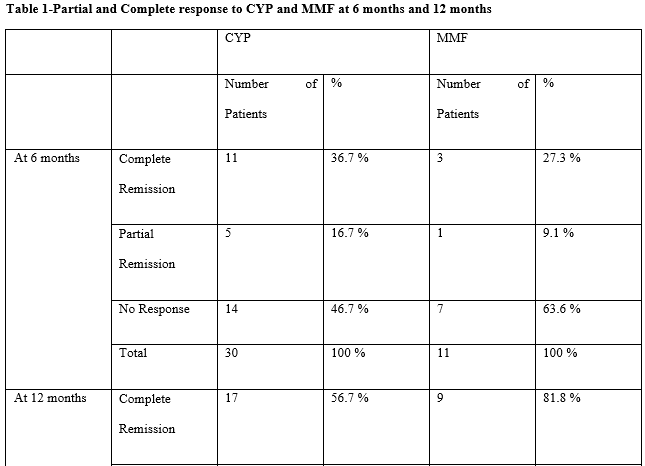
Results: Of the 50 newly diagnosed cases of LN, 94 % (n=47) were females, and 6 % (n=3) were males, with class IV LN accounting for the majority of patients 69.39 % (n=34). At six months, 36.7 % (n=11) of patients in the cyclophosphamide (CYP) group had a complete response. Only 27.3 % of patients in the MMF group had a complete response; however, this difference was not statistically significant. At the end of one year, only 56.7 % of the CYP group and 81.8 % of the MMF group had a complete response; however, this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.282). Although the initial response with CYP was better and later in the MMF group, these differences were not significant statistically. Tuberculosis or its reactivation was the most common complication during treatment, either with MMF or CYP. One patient died due to latent tuberculosis reactivation, another as a result of severe disease activity at presentation (proteinuria was 20 gm/24 hours in that patient), and the third as a result of pneumonia with septicemia.
Conclusion: Treatment with either CYP or MMF is equally effective, but underlying infection, particularly tuberculosis, should be ruled out before initiating therapy.
Downloads
References
Dhir V, Aggarwal A, Lawrence A, Agarwal V, Misra R. Long-term outcome of lupus nephritis in Asian Indians. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012 May;64(5):713-20. doi: 10.1002/acr.21597.
Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, Sebastiani GD, Gil A, Lavilla P, et al. Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 10-year period: a comparison of early and late manifestations in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003 Sep;82(5):299-308. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000091181.93122.55.
Gladman D, Ginzler E, Goldsmith C, Fortin P, Liang M, Urowitz M, Bacon P, Bombardieri S, Hanly J, Hay E, et al. Systemic lupus international collaborative clinics: development of a damage index in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;19(11):1820-1.
Gladman D, Ginzler E, Goldsmith C, Fortin P, Liang M, Urowitz M, et al. The development and initial validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Mar;39(3):363-9. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390303.
Weening JJ, D'Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Feb;15(2):241-50. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000108969.21691.5d. Erratum in: J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Mar;15(3):835-6.
Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Sep;40(9):1725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400928.
Appel GB, Contreras G, Dooley MA, Ginzler EM, Isenberg D, Jayne D, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for induction treatment of lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 May;20(5):1103-12. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008101028.
Austin HA 3rd, Klippel JH, Balow JE, le Riche NG, Steinberg AD, Plotz PH, Decker JL. Therapy of lupus nephritis. Controlled trial of prednisone and cytotoxic drugs. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 6;314(10):614-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603063141004.
Hsu CY, Chiu WC, Yang TS, Chen CJ, Chen YC, Lai HM, et al. Age- and gender-related long-term renal outcome in patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus. 2011 Oct;20(11):1135-41. doi: 10.1177/0961203311404912.
Faurschou M, Dreyer L, Kamper AL, Starklint H, Jacobsen S. Long-term mortality and renal outcome in a cohort of 100 patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010 Jun;62(6):873-80. doi: 10.1002/acr.20116.
Sharma M, Das HJ, Doley PK, Mahanta PJ. Clinical and histopathological profile of lupus nephritis and response to treatment with cyclophosphamide: A single center study. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2019 Mar-Apr;30(2):501-507. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.256857.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


