Analysis of ease of insertions, its attempts and time taken to insert for i-gel and cLMA in paediatric cases.
Abstract
Aim: Analysis of ease of insertions, its attempts and time taken to insert for i-gel and cLMA in paediatric cases.
Methods: We did a prospective, randomised single-blind study on Eighty patients of either sex belonging to American Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA) physical status class I or II, between 6 months to 8 years of age, scheduled to undergo elective surgery for less than one and half hour duration under general anaesthesia. In this study we analysed the ease of insertion, attempts and time were taken to insert the supraglottic airway device.
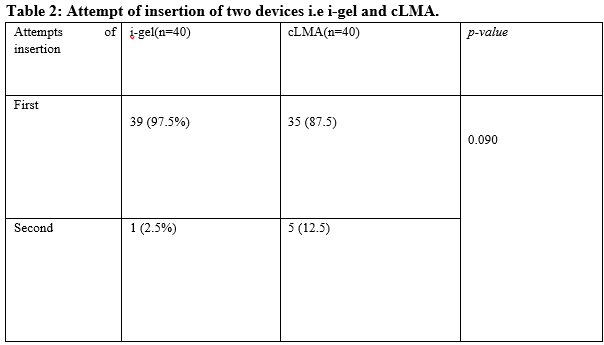
Results: The ease of insertion observed was easy in 39(97.5%) in the i-gel group and 35(87.5%) in cLMA group in our study. The i-gel was placed successfully in 39 out of 40 (97.5%) patients in the first attempt, and achieved 100% insertion on the second attempt. Correct positioning of cLMA in the first attempt was seen in 35 out of 40 (87.5%) patients. The remaining 5 patients (12.5%) required a second attempt. The average insertion time of cLMA (12.88 ± 1.771 seconds) was longer than the average time of insertion of i-gel (9.48 ± 1.037 seconds), and these differences were highly significant statistically (p= 0.000).
Conclusion: To conclude, i-gel and cLMA is effective and safe devices for use in children. Both are easy to insert and have insignificant morbidity, however, time taken and attempts of insertions for i-gel was lesser than cLMA. Also, the ease of insertion was relatively easy for i-gel than cLMA in pediatric cases.
Downloads
References
Beylacq L, Bordes M, Semjen F, Cros AM. The I-gel, a single-use supraglottic airway device with a non-inflatable cuff and an esophageal vent: an observational study in children. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009 Mar;53(3):376-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01869. x. PMID: 19243322.
Vaida S. Airway management- Supraglottic airway devices. [online]. Available
From.URL:http://www.atitimisoara.ro/_files/documents/files/2004/Airway%20management upraglottic%20airway%20devices.pdf. [Accessed on: 15th April 2011].
i-gel airway. Instruction manual. Berkshire, U.K.: Intersurgical Ltd.;2007. p. 3-19. Available at: www.i-gel.com. [Accessed on 13th March 2011].
Beringer RM, Kelly F, Cook TM, Nolan J, Hardy R, Simpson T, White MC. A cohort evaluation of the paediatric i-gel(™) airway during anaesthesia in 120 children. Anaesthesia. 2011 Dec;66(12):1121-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2011.06884.x. Epub 2011 Sep 1.
Goyal R, Shukla RN, Kumar G. Comparison of size 2 i-gel supraglottic airway with LMA-ProSeal™ and LMA-Classic™ in spontaneously breathing children undergoing elective surgery. Paediatr Anaesth. 2012 Apr;22(4):355-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2011.03757.x. Epub 2011 Dec 8.
Siddiqui AS, Ahmed J, Siddiqui SZ, Haider S, Raza SA. New single use supraglottic airway device with non-inflatable cuff and gastric tube channel. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012 Jul;22(7):419-23.
Diemunsch P. I-gel in paediatric surgery: First global study at Strasbourg’s university hospital. [online].
Available from URL http://www.i-gel.com/news/wp-content/uploads/Article-Intersurgical_Pierre- Diemunsch.pdf. [Accessed on 15th April 2011]
Hughes C, Place K, Berg S, Mason D. A clinical evaluation of the I-gel ™ supraglottic airway device in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2012 Aug;22(8):765-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2012.03893.x. Epub 2012 Jun 1.
Lee JR, Kim MS, Kim JT, Byon HJ, Park YH, Kim HS, Kim CS. A randomised trial comparing the i-gel (TM) with the LMA Classic (TM) in children. Anaesthesia. 2012 Jun;67(6):606-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2012.07072.x. Epub 2012 Feb 21.
Tokgöz O, Tüfek A , Beyaz SG, Yüksel MU, Çelik F, Aycan IO , Güzel A. Comparison of the efficacies of I-gel™ and LMA-ProSeal™ for airway management in pediatric patients. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences. [Online] 2013; 43:1-6 Available from: http://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/havuz/sag-1206-30.pdf [Accessed 19th Janurary 2013].
Jackson KM, Cook TM. Evaluation of four airway training manikins as patient simulators for the insertion of eight types of supraglottic airway devices. Anaesthesia. 2007;62:388-93.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


